
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of extra electrons and charge of the ion in the following structure is to be determined.
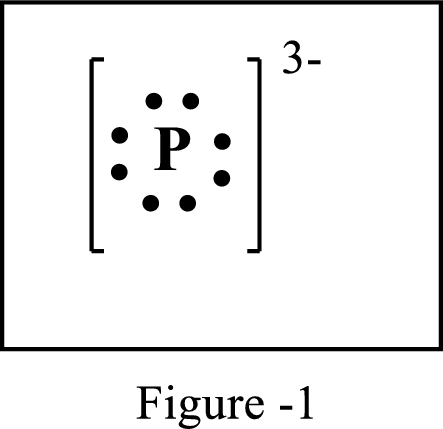
Concept Introduction:
Lewis symbol:
A Lewis symbol is a pictorial representation of an element symbol surrounded by dots indicating number of electrons in the outer energy level. The group number of the element indicates number of valence electrons.
By using an electron configuration of an atom, we can draw its Lewis symbol by drawing the chemical symbol of the element surrounded by the appropriate number of valence electrons.
Lewis structure represents the transfer of sharing of electrons between atoms in a
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of extra electrons and charge of the ion in the following structure is to be determined.
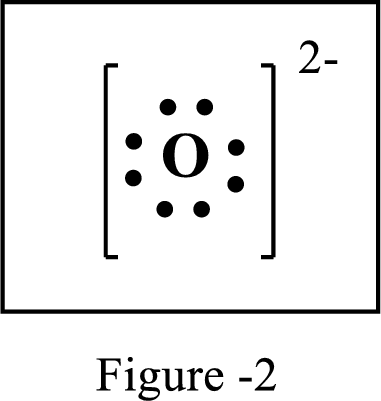
Concept Introduction:
Lewis symbol:
A Lewis symbol is a pictorial representation of an element symbol surrounded by dots indicating number of electrons in the outer energy level. The group number of the element indicates number of valence electrons.
By using an electron configuration of an atom, we can draw its Lewis symbol by drawing the chemical symbol of the element surrounded by the appropriate number of valence electrons.
Lewis structure represents the transfer of sharing of electrons between atoms in a chemical bond. For ionic compounds, there is always transfer of electrons from one element to the other.
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of extra electrons and charge of the ion in the following structure is to be determined.
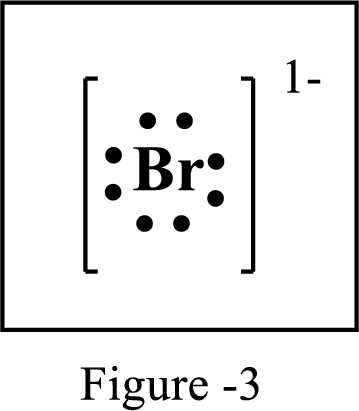
Concept Introduction:
Lewis symbol:
A Lewis symbol is a pictorial representation of an element symbol surrounded by dots indicating number of electrons in the outer energy level. The group number of the element indicates number of valence electrons.
By using an electron configuration of an atom, we can draw its Lewis symbol by drawing the chemical symbol of the element surrounded by the appropriate number of valence electrons.
Lewis structure represents the transfer of sharing of electrons between atoms in a chemical bond. For ionic compounds, there is always transfer of electrons from one element to the other.
(d)
Interpretation:
The number of extra electrons and charge of the ion in the following structure is to be determined.
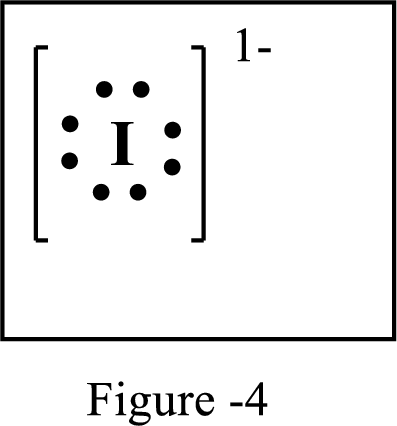
Concept Introduction:
Lewis symbol:
A Lewis symbol is a pictorial representation of an element symbol surrounded by dots indicating number of electrons in the outer energy level. The group number of the element indicates number of valence electrons.
By using an electron configuration of an atom, we can draw its Lewis symbol by drawing the chemical symbol of the element surrounded by the appropriate number of valence electrons.
Lewis structure represents the transfer of sharing of electrons between atoms in a chemical bond. For ionic compounds, there is always transfer of electrons from one element to the other.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Study Guide with Selected Solutions for Stoker's General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th
- Draw the Zaitsev product of the dehydration of this alcohol. + I X 5 OH ざ~ TSOH Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardPlease help with identifying these.arrow_forwardFor the reaction: CO2(g) + H2(g) --> CO (g) + H2O (g) Kc= 0.64 at 900 degrees celcius. if initially you start with 1.00 atmoshpere of carbon dioxide and 1 atmoshpere of hydrogen gas, what are the equilibrium partial pressuses of all species.arrow_forward
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





