
4-44 Answer true or false.
(a) The mole is a counting unit, just as a dozen is acounting unit.
(b)
(c) Avogadro’s number, to three significant figures, is 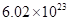 formula units per mole.
formula units per mole.
(d) 1 mol of H2O contains 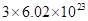 formula units.
formula units.
(e) 1 mol of H2O has the same number of molecules as 1 mol of H2O2.
(f) The molar mass of a compound is its formula weight expressed in amu.
(g) The molar mass of H2O is 18 g/mol.
(h) 1 mol of H2O has the same molar mass as 1 mol of H2O2.
(i) 1 mol of ibuprofen, C13H18O2, contains 33 mol of atoms.
(j) To convert moles to grams, multiply by Avogadro’s number.
(k) To convert grams to moles, divide by molar mass.
(l) 1 mol of H2O contains 1 mol of hydrogen atoms and one mol of oxygen atoms.
(m) 1 mol of H2O contains 2 g of hydrogen atoms and 1 g of oxygen atoms.
(n) 1 mole of H2O contains 18.06 X 10 atoms.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 4 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Q10: (a) Propose a synthesis of C from A. (b) Propose a synthesis of C from B. Br Br ...\SCH 3 A B Carrow_forward9: Complete the missing entities for following reactions (e.g., major product(s), reactants, and/or solvents) for the SN2 reactions to occur efficiently. Include curved-arrow mechanism for reactions a) to d).arrow_forwardComplete the missing entities for following reactions (e.g., major product(s), reactants, and/or solvents) for the SN2 reactions to occur efficiently. Include curved-arrow mechanism for reactions a) to d).arrow_forward
- QUESTION 3: Provide the synthetic steps that convert the starting material into the product (no mechanism required). HO OH NH CH3 multiple steps 요요 H3Carrow_forwardQ6: Predict the effect of the changes given on the rate of the reaction below. CH3OH CH3Cl + NaOCH3 → CH3OCH3 + NaCl a) Change the substrate from CH3CI to CH31: b) Change the nucleophile from NaOCH 3 to NaSCH3: c) Change the substrate from CH3CI to (CH3)2CHCI: d) Change the solvent from CH3OH to DMSO.arrow_forwardQ3: Arrange each group of compounds from fastest SN2 reaction rate to slowest SN2 reaction rate. a) CI Cl فيكم H3C-Cl A B C D Br Br b) A B C Br H3C-Br Darrow_forward
- Q2: Group these solvents into either protic solvents or aprotic solvents. Acetonitrile (CH3CN), H₂O, Acetic acid (CH3COOH), Acetone (CH3COCH3), CH3CH2OH, DMSO (CH3SOCH3), DMF (HCON(CH3)2), CH3OHarrow_forwardSuppose the rate of evaporation in a hot, dry region is 1.76 meters per year, and the seawater there has a salinity of 35 ‰. Assuming a 93% yield, how much salt (NaCl) can be harvested each year from 1 km2 of solar evaporation ponds that use this seawater as a source?arrow_forwardhelparrow_forward
- Explain why only the lone pairs on the central atom are taken into consideration when predicting molecular shapearrow_forward(ME EX1) Prblm #9/10 Can you explain in detail (step by step) I'm so confused with these problems. For turmber 13 can u turn them into lewis dot structures so I can better understand because, and then as well explain the resonance structure part. Thanks for the help.arrow_forwardProblems 19 and 20: (ME EX1) Can you please explain the following in detail? I'm having trouble understanding them. Both problems are difficult for me to explain in detail, so please include the drawings and answers.arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning





