
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305501607
Author: Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 4.166P
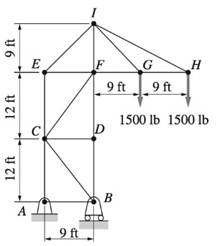
(a) Find the forces in members CE, CF, and DF. (b) Identify all the zero -force members.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
36
2) Use the method of MEMBERS to determine the true magnitude and
direction of the forces in members1 and 2 of the frame shown below
in Fig 3.2.
300lbs/ft
member-1
member-2
30°
Fig 3.2.
https://brightspace.cuny.edu/d21/le/content/433117/viewContent/29873977/View
Can you solve this for me?
5670 mm
The apartment in the ground floor of three floors building in Fig. in Baghdad city. The details of
walls, roof, windows and door are shown. The window is a double glazing and air space thickness
is 1.3cm Poorly Fitted-with Storm Sash with wood strip and storm window of 0.6 cm glass
thickness. The thickness of door is 2.5 cm. The door is Poor Installation. There are two peoples
in each room. The height of room is 280 cm. assume the indoor design conditions are 25°C DBT
and 50 RH, and moisture content of 8 gw/kga. The moisture content of outdoor is 10.5 gw/kga.
Calculate heat gain for living room :
الشقة في الطابق الأرضي من مبنى ثلاثة طوابق في مدينة بغداد يظهر في مخطط الشقة تفاصيل الجدران والسقف
والنوافذ والباب. النافذة عبارة عن زجاج مزدوج وسمك الفراغ الهوائي 1.3 سم ضعيف الاحكام مع ساتر حماية مع إطار
خشبي والنافذة بسماكة زجاج 0.6 سم سماكة الباب 2.5 سم. الباب هو تركيب ضعيف هناك شخصان في كل غرفة.
ارتفاع الغرفة 280 سم. افترض أن ظروف التصميم الداخلي هي DBT25 و R50 ، ومحتوى الرطوبة 8…
Chapter 4 Solutions
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
Ch. 4 - Each of the bodies shown is homogeneous and has a...Ch. 4 - Each of the bodies shown is homogeneous and has a...Ch. 4 - Each of the bodies shown is homogeneous and has a...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous bar weighs 12 lb. It is resting on...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous beam AB weighs 400 lb. For each...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous triangular plate has a mass of 12...Ch. 4 - The bracket of negligible weight is supported by a...Ch. 4 - The figure models the handle of the water cock...Ch. 4 - The high-pressure water cock is rigidly attached...Ch. 4 - Draw the FBD of the entire frame, assuming that...
Ch. 4 - The figure is a model for member CDE of the frame...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous cylinder of weight Wrests in a...Ch. 4 - Calculate the force P that is required to hold the...Ch. 4 - The 60-lb homogeneous disk is suspended from a...Ch. 4 - The 180-kg uniform boom ABC, supported by a...Ch. 4 - The table lamp consists of two uniform arms, each...Ch. 4 - At what angle will the lamp in Prob. 4.16 be in...Ch. 4 - The bent beam ABC is supported by a pin at B and a...Ch. 4 - Compute all reactions at the base A of the traffic...Ch. 4 - The man is holding up the 35-kg ladder ABC by...Ch. 4 - The 1200-lb homogeneous block is placed on rollers...Ch. 4 - The uniform plank ABC weighs 400 N. It is...Ch. 4 - The center of gravity of the 850-N man is at G. If...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous 340-lb sign is suspended from...Ch. 4 - When the truck is empty, it weighs 6000 lb and its...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous bar AB weighs 25 lb. Determine the...Ch. 4 - Determine the smallest horizontal force P that...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous beam AB weighing 800 lb carries...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous 40-kg bar ABC is held in position...Ch. 4 - The horizontal force P is applied to the handle of...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous plate of weight W is suspended...Ch. 4 - Neglecting the mass of the beam, compute the...Ch. 4 - The 1200-kg car is being lowered slowly onto the...Ch. 4 - The crate weighing 400 lb is supported by three...Ch. 4 - Find the smallest value of P for which the crate...Ch. 4 - Determine the rope tension T for which the pulley...Ch. 4 - The 40-kg homogeneous disk is resting on an...Ch. 4 - The 40-kghomogeneous disk is placed on a...Ch. 4 - The mass of the uniform bar AB is 80 kg. Calculate...Ch. 4 - The mechanism shown is a modified Geneva drive-a...Ch. 4 - The center of gravity of the 3000-lb car is at G....Ch. 4 - The 30-lb block is held in place on the smooth...Ch. 4 - The vertical post is supported by two cables (the...Ch. 4 - The uniform ladder of weight W is raised slowly by...Ch. 4 - The uniform, 30-lb ladder is raised slowly by...Ch. 4 - The 90-kg man, whose center of gravity is at G, is...Ch. 4 - The bar ABC is constrained by the pin support A...Ch. 4 - The tensioning mechanism of a magnetic tape drive...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous 300-kg cylinder is pulled over the...Ch. 4 - Compute the magnitudes of the reactions at pin A...Ch. 4 - Each of the sandbags piled on the 380-lb uniform...Ch. 4 - The 18-ft pole is supported by a pin at A and a...Ch. 4 - The supporting structure of the billboard is...Ch. 4 - The self-regulating floodgate ABC, pinned at B, is...Ch. 4 - The cantilever beam is built into a wall at O....Ch. 4 - Determine the force F required to keep the 200-kg...Ch. 4 - The uniform rod AB of weight W is supported by the...Ch. 4 - A machine operator produces the tension Tin the...Ch. 4 - The dump truck consists of a chassis and a tray,...Ch. 4 - The centers of gravity of the 50-kg lift truck and...Ch. 4 - (a) draw the free-body diagrams for the entire...Ch. 4 - (a) draw the free-body diagrams for the entire...Ch. 4 - For Probs. 4.61–4.68, (a) draw the free-body...Ch. 4 - (a) draw the free-body diagrams for the entire...Ch. 4 - (a) draw the free-body diagrams for the entire...Ch. 4 - (a) draw the free-body diagrams for the entire...Ch. 4 - (a) draw the free-body diagrams for the entire...Ch. 4 - (a) draw the free-body diagrams for the entire...Ch. 4 - The two uniform cylinders, each of weight W, are...Ch. 4 - Draw the FBDs for the following: (a) bar ABC with...Ch. 4 - Draw the FBDs for the beam ABC and the segments AB...Ch. 4 - Draw the FBDs for the entire structure and the...Ch. 4 - The beam consists of the bars AB and BC connected...Ch. 4 - For the frame shown, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitudes of the pin reactions at A...Ch. 4 - The bars AB and AC are joined by a pin at A and a...Ch. 4 - Neglecting the weights of the members, determine...Ch. 4 - Calculate the magnitudes of the pin reactions at A...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitude of the pin reaction at A...Ch. 4 - Neglecting friction and the weights of the...Ch. 4 - When activated by the force P, the gripper on a...Ch. 4 - Determine the axle loads (normal forces at A, B,...Ch. 4 - Determine the force P that would produce a tensile...Ch. 4 - The pulley-cable system supports the 150-lb...Ch. 4 - Determine the contact force between the smooth...Ch. 4 - Compute the tension in the cable and the contact...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitude of the pin reaction at B....Ch. 4 - Determine the tension in the cable at B, given...Ch. 4 - Compute the magnitude of the pin reaction at B....Ch. 4 - Neglecting the weight of the frame, find the...Ch. 4 - Determine the clamping force at A due to the 15-lb...Ch. 4 - Compute the tension in the cable BD when the...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reactions at the built-in support at...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitudes of the roller reactions...Ch. 4 - The linkage of the braking system consists of the...Ch. 4 - The window washers A and B support themselves and...Ch. 4 - The figure shows a wire cutter. Determine the...Ch. 4 - Find the tension T in the cable when the 180-N...Ch. 4 - The 400-kg drum is held by tongs of negligible...Ch. 4 - Compute the magnitudes of all forces acting on...Ch. 4 - Calculate all forces acting on member CDB.Ch. 4 - The automatic drilling robot must sustain a thrust...Ch. 4 - Determine the clamping (vertical) force applied by...Ch. 4 - Determine the axial force in member BC of the...Ch. 4 - Neglecting friction, determine the relationship...Ch. 4 - Find the magnitudes of the pin reactions at A and...Ch. 4 - The load in the bucket of a skid steer loader is...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitude of the roller reaction at...Ch. 4 - The tool shown is used to crimp terminals onto...Ch. 4 - The 12-lb force is applied to the handle of the...Ch. 4 - The blade of the bulldozer is rigidly attached to...Ch. 4 - Find the magnitudes of the pin reactions at A, C,...Ch. 4 - The pins at the end of the retaining-ring spreader...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitudes of the support reactions...Ch. 4 - Find the magnitude of the pin reaction at C....Ch. 4 - For the pliers shown, determine the relationship...Ch. 4 - The device shown is an overload prevention...Ch. 4 - The figure is a schematic of a wire cutter....Ch. 4 - The hinge shown is the type used on the doors of...Ch. 4 - Determine the force in the hydraulic cylinder EF...Ch. 4 - Determine the horizontal force P that would keep...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitudes of the forces acting on...Ch. 4 - Determine the angle at which the bar AB is in...Ch. 4 - The automobile, with center of gravity at G, is...Ch. 4 - The figure shows a three-pin arch. Determine the...Ch. 4 - The center of gravity of the nonhomogeneous bar AB...Ch. 4 - When suspended from two cables, the rocket assumes...Ch. 4 - The pump oiler is operated by pressing on the...Ch. 4 - The uniform 240-lb bar AB is held in the position...Ch. 4 - Find the force P required to (a) push; and (b)...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Identify all the zero-force members in the four...Ch. 4 - The walkway ABC of the footbridge is stiffened by...Ch. 4 - Find the force in member EF.Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members AE, BE, and ED.Ch. 4 - Determine the reaction at E and the force in each...Ch. 4 - Determine the force in member AD of the truss.Ch. 4 - Determine the force in member BE of the truss.Ch. 4 - Show that all diagonal members of the truss carry...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members FG and AB in terms...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members BC, BG, and FG.Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members EF, BF, and BC.Ch. 4 - Compute the forces in members EF, NE and NO.Ch. 4 - Repeat Prob. 4.152 assuming that the 400-kN force...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members BG, CI, and CD.Ch. 4 - Assuming that P=48000lb and that it may be applied...Ch. 4 - Calculate the forces in members BC, CF, and FG.Ch. 4 - Find the forces in members CD, DH, and HI.Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members CD and DF.Ch. 4 - Compute the forces in members CD and JK, given...Ch. 4 - If PCD=6000lb and PGD=1000lb (both compression),...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members EF, BF, and BC.Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members AC, AD, and DE.Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members GI, PH, and GH....Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members CD, IJ, and NJ of...Ch. 4 - Calculate the forces in members AB and DE.Ch. 4 - (a) Find the forces in members CE, CF, and DF. (b)...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members BC and BE and the...Ch. 4 - A couple acting on the winch at G slowly raises...Ch. 4 - The uniform, 20-kg bar is placed between two...Ch. 4 - The 320-lb homogeneous spool is placed on the...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitude of the pin reaction at A,...Ch. 4 - Determine the couple C that will hold the bar AB...Ch. 4 - The 800-lb force is applied to the pin at E....Ch. 4 - The weight W=6kN hangs from the cable which passes...Ch. 4 - The 2000-lb and 6000-lb forces are applied to the...Ch. 4 - The two couples act at the midpoints of bars AB...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members AC and AD of the...Ch. 4 - Determine the angle for which the uniform bar of...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitude of the force exerted by...Ch. 4 - Calculate the forces in members (a) DE; (b) BE;...Ch. 4 - Determine the ratio P/Q for which the parallel...Ch. 4 - The 30-lb block C rests on the uniform 14-lb bar...Ch. 4 - The 30-lb homogeneous bar AB supports the 60-lb...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members (a) EF; and (b)...Ch. 4 - Find the magnitude of the pin reaction at B caused...Ch. 4 - The breaking strength of the cable FG that...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members GH, BH, and BC of...Ch. 4 - The 80-N force is applied to the handle of the...Ch. 4 - The tongs shown are designed for lifting blocks of...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How do i solve this problem?arrow_forwardQ4/ A compressor is driven motor by mean of a flat belt of thickness 10 mm and a width of 250 mm. The motor pulley is 300 mm diameter and run at 900 rpm and the compressor pulley is 1500 mm diameter. The shaft center distance is 1.5 m. The angle of contact of the smaller pulley is 220° and on the larger pulley is 270°. The coefficient of friction between the belt and the small pulley is 0.3, and between the belt and the large pulley is 0.25. The maximum allowable belt stress is 2 MPa and the belt density is 970 kg/m³. (a) What is the power capacity of the drive and (b) If the small pulley replaced by V-grooved pulley of diameter 300 mm, grooved angle of 34° and the coefficient of friction between belt and grooved pulley is 0.35. What will be the power capacity in this case, assuming that the diameter of the large pulley remain the same of 1500 mm.arrow_forwardYou are tasked with designing a power drive system to transmit power between a motor and a conveyor belt in a manufacturing facility as illustrated in figure. The design must ensure efficient power transmission, reliability, and safety. Given the following specifications and constraints, design drive system for this application: Specifications: Motor Power: The electric motor provides 10 kW of power at 1,500 RPM. Output Speed: The output shaft should rotate at 150 rpm. Design Decisions: Transmission ratio: Determine the necessary drive ratio for the system. Shaft Diameter: Design the shafts for both the motor and the conveyor end. Material Selection: Choose appropriate materials for the gears, shafts. Bearings: Select suitable rolling element bearings. Constraints: Space Limitation: The available space for the gear drive system is limited to a 1-meter-long section. Attribute 4 of CEP Depth of knowledge required Fundamentals-based, first principles analytical approach…arrow_forward
- - | العنوان In non-continuous dieless drawing process for copper tube as shown in Fig. (1), take the following data: Do-20mm, to=3mm, D=12mm, ti/to=0.6 and v.-15mm/s. Calculate: (1) area reduction RA, (2) drawing velocity v. Knowing that: ti: final thickness V. Fig. (1) ofthrearrow_forwardA direct extrusion operation produces the cross section shown in Fig. (2) from an aluminum billet whose diameter 160 mm and length - 700 mm. Determine the length of the extruded section at the end of the operation if the die angle -14° 60 X Fig. (2) Note: all dimensions in mm.arrow_forwardFor hot rolling processes, show that the average strain rate can be given as: = (1+5)√RdIn(+1)arrow_forward
- : +0 usão العنوان on to A vertical true centrifugal casting process is used to produce bushings that are 250 mm long and 200 mm in outside diameter. If the rotational speed during solidification is 500 rev/min, determine the inside radii at the top and bottom of the bushing if R-2R. Take: -9.81 mis ۲/۱ ostrararrow_forward: +0 العنوان use only In conventional drawing of a stainless steel wire, the original diameter D.-3mm, the area reduction at each die stand r-40%, and the proposed final diameter D.-0.5mm, how many die stands are required to complete this process. онarrow_forwardIn non-continuous dieless drawing process for copper tube as shown in Fig. (1), take the following data: Do-20mm, to=3mm, D=12mm, ti/to=0.6 and vo-15mm/s. Calculate: (1) area reduction RA, (2) drawing velocity v. Knowing that: t₁: final thickness D₁ V. Fig. (1) Darrow_forward
- A vertical true centrifugal casting process is used to produce bushings that are 250 mm long and 200 mm in outside diameter. If the rotational speed during solidification is 500 rev/min, determine the inside radii at the top and bottom of the bushing if R-2Rb. Take: 8-9.81 m/sarrow_forwardIn conventional drawing of a stainless steel wire, the original diameter D.-3mm, the area reduction at each die stand r-40%, and the proposed final diameter D₁-0.5mm, how many die stands are required to complete this process.arrow_forwardA vertical true centrifugal casting process is used to produce bushings that are 250 mm long and 200 mm in outside diameter. If the rotational speed during solidification is 500 rev/min, determine the inside radii at the top and bottom of the bushing if R-2Rb. Take: 8-9.81 m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Engineering Basics - Statics & Forces in Equilibrium; Author: Solid Solutions - Professional Design Solutions;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQBvQ2hJZFg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY