
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305501607
Author: Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 4.40P
The
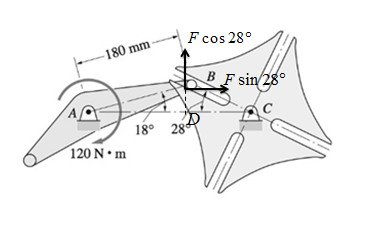
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Solve the problem show in the image. Explain each step please
The car shown in the figure below has a mass of 1673 kg. The coefficient of static friction between the rubber tires and the pavement is 0.6.
Determine the maximum incline e [degrees] that the car can drive up if it has rear-wheel drive.
0.85 m
1.2 m
1.7 m
Answer: 18.87
Calculate the normal reaction force at the rear wheels for the condition of rear-wheel drive in N.
Answer:
Equilibrium of Concurrent Force System. The piston of a reciprocating engine exerts a force of 175 kN on the
crosshead when the crank is 45° (angle B) past TDC. If the stroke of the piston is 800 mm and the length of the
connecting rod is 1.80 m, find the guide force and the force in the connecting rod. Hint: 1=½ stroke; Angle o may be
solved using Sine Law in AACO.
K= Compressive Force
in the connecting Rod
E= Piston Effort
70
120
F, = Guide Force
Fig. P-1
Fig. P-2
a
Tools:
EF cos0=0; F sin .=0.
R = Ev)* + (E#): ;
R
771 =-
: tane =
sin A sin B sin C
Chapter 4 Solutions
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
Ch. 4 - Each of the bodies shown is homogeneous and has a...Ch. 4 - Each of the bodies shown is homogeneous and has a...Ch. 4 - Each of the bodies shown is homogeneous and has a...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous bar weighs 12 lb. It is resting on...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous beam AB weighs 400 lb. For each...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous triangular plate has a mass of 12...Ch. 4 - The bracket of negligible weight is supported by a...Ch. 4 - The figure models the handle of the water cock...Ch. 4 - The high-pressure water cock is rigidly attached...Ch. 4 - Draw the FBD of the entire frame, assuming that...
Ch. 4 - The figure is a model for member CDE of the frame...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous cylinder of weight Wrests in a...Ch. 4 - Calculate the force P that is required to hold the...Ch. 4 - The 60-lb homogeneous disk is suspended from a...Ch. 4 - The 180-kg uniform boom ABC, supported by a...Ch. 4 - The table lamp consists of two uniform arms, each...Ch. 4 - At what angle will the lamp in Prob. 4.16 be in...Ch. 4 - The bent beam ABC is supported by a pin at B and a...Ch. 4 - Compute all reactions at the base A of the traffic...Ch. 4 - The man is holding up the 35-kg ladder ABC by...Ch. 4 - The 1200-lb homogeneous block is placed on rollers...Ch. 4 - The uniform plank ABC weighs 400 N. It is...Ch. 4 - The center of gravity of the 850-N man is at G. If...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous 340-lb sign is suspended from...Ch. 4 - When the truck is empty, it weighs 6000 lb and its...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous bar AB weighs 25 lb. Determine the...Ch. 4 - Determine the smallest horizontal force P that...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous beam AB weighing 800 lb carries...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous 40-kg bar ABC is held in position...Ch. 4 - The horizontal force P is applied to the handle of...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous plate of weight W is suspended...Ch. 4 - Neglecting the mass of the beam, compute the...Ch. 4 - The 1200-kg car is being lowered slowly onto the...Ch. 4 - The crate weighing 400 lb is supported by three...Ch. 4 - Find the smallest value of P for which the crate...Ch. 4 - Determine the rope tension T for which the pulley...Ch. 4 - The 40-kg homogeneous disk is resting on an...Ch. 4 - The 40-kghomogeneous disk is placed on a...Ch. 4 - The mass of the uniform bar AB is 80 kg. Calculate...Ch. 4 - The mechanism shown is a modified Geneva drive-a...Ch. 4 - The center of gravity of the 3000-lb car is at G....Ch. 4 - The 30-lb block is held in place on the smooth...Ch. 4 - The vertical post is supported by two cables (the...Ch. 4 - The uniform ladder of weight W is raised slowly by...Ch. 4 - The uniform, 30-lb ladder is raised slowly by...Ch. 4 - The 90-kg man, whose center of gravity is at G, is...Ch. 4 - The bar ABC is constrained by the pin support A...Ch. 4 - The tensioning mechanism of a magnetic tape drive...Ch. 4 - The homogeneous 300-kg cylinder is pulled over the...Ch. 4 - Compute the magnitudes of the reactions at pin A...Ch. 4 - Each of the sandbags piled on the 380-lb uniform...Ch. 4 - The 18-ft pole is supported by a pin at A and a...Ch. 4 - The supporting structure of the billboard is...Ch. 4 - The self-regulating floodgate ABC, pinned at B, is...Ch. 4 - The cantilever beam is built into a wall at O....Ch. 4 - Determine the force F required to keep the 200-kg...Ch. 4 - The uniform rod AB of weight W is supported by the...Ch. 4 - A machine operator produces the tension Tin the...Ch. 4 - The dump truck consists of a chassis and a tray,...Ch. 4 - The centers of gravity of the 50-kg lift truck and...Ch. 4 - (a) draw the free-body diagrams for the entire...Ch. 4 - (a) draw the free-body diagrams for the entire...Ch. 4 - For Probs. 4.61–4.68, (a) draw the free-body...Ch. 4 - (a) draw the free-body diagrams for the entire...Ch. 4 - (a) draw the free-body diagrams for the entire...Ch. 4 - (a) draw the free-body diagrams for the entire...Ch. 4 - (a) draw the free-body diagrams for the entire...Ch. 4 - (a) draw the free-body diagrams for the entire...Ch. 4 - The two uniform cylinders, each of weight W, are...Ch. 4 - Draw the FBDs for the following: (a) bar ABC with...Ch. 4 - Draw the FBDs for the beam ABC and the segments AB...Ch. 4 - Draw the FBDs for the entire structure and the...Ch. 4 - The beam consists of the bars AB and BC connected...Ch. 4 - For the frame shown, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitudes of the pin reactions at A...Ch. 4 - The bars AB and AC are joined by a pin at A and a...Ch. 4 - Neglecting the weights of the members, determine...Ch. 4 - Calculate the magnitudes of the pin reactions at A...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitude of the pin reaction at A...Ch. 4 - Neglecting friction and the weights of the...Ch. 4 - When activated by the force P, the gripper on a...Ch. 4 - Determine the axle loads (normal forces at A, B,...Ch. 4 - Determine the force P that would produce a tensile...Ch. 4 - The pulley-cable system supports the 150-lb...Ch. 4 - Determine the contact force between the smooth...Ch. 4 - Compute the tension in the cable and the contact...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitude of the pin reaction at B....Ch. 4 - Determine the tension in the cable at B, given...Ch. 4 - Compute the magnitude of the pin reaction at B....Ch. 4 - Neglecting the weight of the frame, find the...Ch. 4 - Determine the clamping force at A due to the 15-lb...Ch. 4 - Compute the tension in the cable BD when the...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reactions at the built-in support at...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitudes of the roller reactions...Ch. 4 - The linkage of the braking system consists of the...Ch. 4 - The window washers A and B support themselves and...Ch. 4 - The figure shows a wire cutter. Determine the...Ch. 4 - Find the tension T in the cable when the 180-N...Ch. 4 - The 400-kg drum is held by tongs of negligible...Ch. 4 - Compute the magnitudes of all forces acting on...Ch. 4 - Calculate all forces acting on member CDB.Ch. 4 - The automatic drilling robot must sustain a thrust...Ch. 4 - Determine the clamping (vertical) force applied by...Ch. 4 - Determine the axial force in member BC of the...Ch. 4 - Neglecting friction, determine the relationship...Ch. 4 - Find the magnitudes of the pin reactions at A and...Ch. 4 - The load in the bucket of a skid steer loader is...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitude of the roller reaction at...Ch. 4 - The tool shown is used to crimp terminals onto...Ch. 4 - The 12-lb force is applied to the handle of the...Ch. 4 - The blade of the bulldozer is rigidly attached to...Ch. 4 - Find the magnitudes of the pin reactions at A, C,...Ch. 4 - The pins at the end of the retaining-ring spreader...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitudes of the support reactions...Ch. 4 - Find the magnitude of the pin reaction at C....Ch. 4 - For the pliers shown, determine the relationship...Ch. 4 - The device shown is an overload prevention...Ch. 4 - The figure is a schematic of a wire cutter....Ch. 4 - The hinge shown is the type used on the doors of...Ch. 4 - Determine the force in the hydraulic cylinder EF...Ch. 4 - Determine the horizontal force P that would keep...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitudes of the forces acting on...Ch. 4 - Determine the angle at which the bar AB is in...Ch. 4 - The automobile, with center of gravity at G, is...Ch. 4 - The figure shows a three-pin arch. Determine the...Ch. 4 - The center of gravity of the nonhomogeneous bar AB...Ch. 4 - When suspended from two cables, the rocket assumes...Ch. 4 - The pump oiler is operated by pressing on the...Ch. 4 - The uniform 240-lb bar AB is held in the position...Ch. 4 - Find the force P required to (a) push; and (b)...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Using the method of joints, calculate the force in...Ch. 4 - Identify all the zero-force members in the four...Ch. 4 - The walkway ABC of the footbridge is stiffened by...Ch. 4 - Find the force in member EF.Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members AE, BE, and ED.Ch. 4 - Determine the reaction at E and the force in each...Ch. 4 - Determine the force in member AD of the truss.Ch. 4 - Determine the force in member BE of the truss.Ch. 4 - Show that all diagonal members of the truss carry...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members FG and AB in terms...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members BC, BG, and FG.Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members EF, BF, and BC.Ch. 4 - Compute the forces in members EF, NE and NO.Ch. 4 - Repeat Prob. 4.152 assuming that the 400-kN force...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members BG, CI, and CD.Ch. 4 - Assuming that P=48000lb and that it may be applied...Ch. 4 - Calculate the forces in members BC, CF, and FG.Ch. 4 - Find the forces in members CD, DH, and HI.Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members CD and DF.Ch. 4 - Compute the forces in members CD and JK, given...Ch. 4 - If PCD=6000lb and PGD=1000lb (both compression),...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members EF, BF, and BC.Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members AC, AD, and DE.Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members GI, PH, and GH....Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members CD, IJ, and NJ of...Ch. 4 - Calculate the forces in members AB and DE.Ch. 4 - (a) Find the forces in members CE, CF, and DF. (b)...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members BC and BE and the...Ch. 4 - A couple acting on the winch at G slowly raises...Ch. 4 - The uniform, 20-kg bar is placed between two...Ch. 4 - The 320-lb homogeneous spool is placed on the...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitude of the pin reaction at A,...Ch. 4 - Determine the couple C that will hold the bar AB...Ch. 4 - The 800-lb force is applied to the pin at E....Ch. 4 - The weight W=6kN hangs from the cable which passes...Ch. 4 - The 2000-lb and 6000-lb forces are applied to the...Ch. 4 - The two couples act at the midpoints of bars AB...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members AC and AD of the...Ch. 4 - Determine the angle for which the uniform bar of...Ch. 4 - Determine the magnitude of the force exerted by...Ch. 4 - Calculate the forces in members (a) DE; (b) BE;...Ch. 4 - Determine the ratio P/Q for which the parallel...Ch. 4 - The 30-lb block C rests on the uniform 14-lb bar...Ch. 4 - The 30-lb homogeneous bar AB supports the 60-lb...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members (a) EF; and (b)...Ch. 4 - Find the magnitude of the pin reaction at B caused...Ch. 4 - The breaking strength of the cable FG that...Ch. 4 - Determine the forces in members GH, BH, and BC of...Ch. 4 - The 80-N force is applied to the handle of the...Ch. 4 - The tongs shown are designed for lifting blocks of...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A photograph shows two U.S. Coast Guard icebreakers in an ice field and a simple model for an ice breaking operation. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction for contact between the ship's bow and ice are 0.08 and 0.054, respectively, and the ship produces a thrust of 106 forces between the ship's hull and water except for the thrust. Ib. Assume the ship makes contact with the ice only on its bow, and neglect all 1170 T17° Determine the normal and friction forces acting on each side of the ship's bow as it moves through the ice field with constant velocity. The normal force is x 106 lb. The friction force is x 104 Ib.arrow_forward3 - The sliding glass door rolls on the two small lower wheels ( A ) and (B ). Under normal conditions the 40 upper wheels don't touch their horizontal guide . a - compute the force ( P) required to slide the door at a steady speed if the wheel ( A ) becomes P " frozen " and does not turn in its bearing. b - Rework the problem if wheel ( B ) becomes " frozen " instead of wheel (A). if the coefficient 40 of friction between a frozen A 28" wheel and supporting surface is ( 0.3 ), and the center of mass of the ( 140 N ) door is at its geometric center. Neglect the small diameters of the wheel 44 برعاية المحتوی II >arrow_forwardProblem 3/32 3/33 A person is performing slow arm curls with a 20-lb weight as indicated in the figure. The brachialis muscle group (consisting of the biceps and brachialis muscles) is the major factor in this exercise. Deter- mine the magnitude F of the brachialis-muscle- group force and the magnitude E of the elbow joint reaction at point E for the forearm position shown in the figure. Take the dimensions shown to locate the effective points of application of the two muscle groups; these points are 8 in. directly above E and 2 in. directly to the right of E. Include the 3.2-lb forearm weight which acts at point G. State any assumptions. Ans. F = 154.2 lb, E = 131.8 lb %3D Humerus Biceps Brachialis 8" Ulna 20 lb Radius E 4" 2" 14"arrow_forward
- Considering the masses of the 2 and 3 links in the arm slide mechanism given on the side, make the dynamic force analysis of the mechanism for the given 012-56.3 degree position. Find the moment T12, the ground forces, and the internal forces that occur in each kinematic pair that keep the mechanism in balance. rad 012 = 56.3°, w12 = 7.5- rad a12 = 0 s2 S a, = 60.507 cm az = 36.056 cm A S34 a4 = 24.253 cm В |A,G2| = 25 cm %3D G3 az /G2 JAG3| = 65 cm m3 4.5 kg %3D M2 = 1.5 kg a4 J2 = 0.001 kg.m² 812 %3D 0.003 kg.m² Во An aiarrow_forwardA person is performing slow arm curls with 10-kgWeight as idicated in the left image of the figure below. The biceps group (consisting of the biceps and brachialis muscles) is the major factor in this exercise. Determine the magnitude F7 of the biceps group force and the magnitude 4 of the elbow joint reaction at point E for the forearm position. The free body diagram is shown in the right image of the figure. Take the dimensions shown to locate the effectivepoints of application of the biceps group; these points are 200 mm directly above E and 50 mm directly to the right of E. Include the eftect of the the 1.5-kg forearm mass with mass center at point G. Assuming that humerus is perfectly vertical and fixed; therefore, the elbow joint E is acting like pin connection. The forearm (E-B-G-C) is perfectly horizontal; therefore, the angle A-E-B is 90 deg.arrow_forwardA rod ABC rotating at 20rpm about a vertical axisthrough point A supports a 400N ball at its lower end. Itis fixed in position by the rod BD as shown in the figure.Neglecting the weights of rods AC and BD, compute theforce P in rod BD. Identify if this force is in tension orcompression. At what rpm will this force be zero? DrawFBD of the rod AC during the motion of the system.arrow_forward
- Write down equations for static equilibrium. Calculate the moment about C, and leave the answer in terms of the unknow force of magnitude |FB| After that Caclulate |FB|arrow_forward200 N A block placed under the head , of the claw hammer as shown greatly facilitates the extraction of the nail . If the 200-N pull on the handle is required to pull the nail 200 mm calculate the tension T in the nail and the magnitude A of the force exerted by the hammer head on the block . The contacting surfaces at A are sufficiently rough to 45 mm prevent slipping ii camarrow_forwardThe uniform crate shown in the figure weighs 200 lb. It is pulled up the incline by acounterweight W of 400 lb. Find the maximum and minimum values of d so that the crate doesnot tip over as it slides up the incline. Assume that the pulleys are weightless and frictionless.a. Identify the type of motion defined in the problem.b. Set up the equations of motion that is required to solve the problem.c. Solve for the unknown variables by substituting the given in the equations of motionthat has been set up previously.arrow_forward
- (b) Compute the work Ui-2 exerted on the that disk shown undergoes displacement of s = 0.3 m without The spring is initially slipping. unstretched. k = 200 N/m and M = 120 s = 0.3m N-m. k G wwwm- (0.2 marrow_forward4/4 Calculate the forces in members BE and BD of the loaded trusu. B 8 8 E D 1000 Ib Problem 4/4arrow_forwardThe force P applied to the brake handle enables the band brake to reduce the angular speed of a rotating drum. If the tensile strength of the band is 3800 lb, find the maximum safe value of P and the corresponding braking torque acting on the drum. Assume that the drum is rotating clockwise.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Power Transmission; Author: Terry Brown Mechanical Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YVm4LNVp1vA;License: Standard Youtube License