
(a)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance, when
(a)
Answer to Problem 4.118SP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
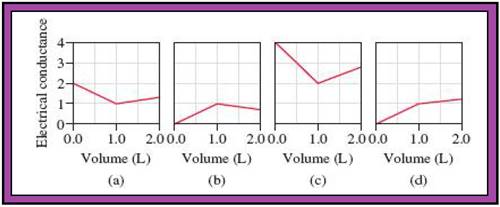
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
If Conductance unit of
(b)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance when,
(b)
Answer to Problem 4.118SP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
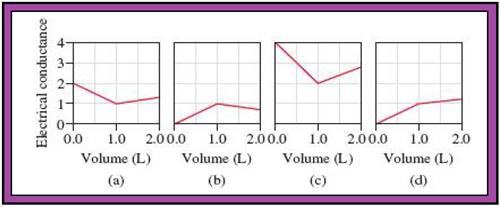
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
(c)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance when,
(c)
Answer to Problem 4.118SP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
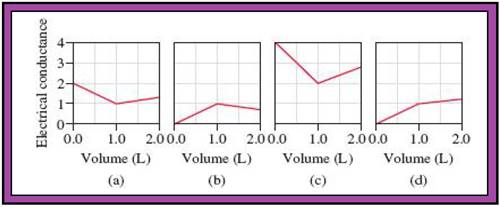
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
(d)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance, when
(d)
Answer to Problem 4.118SP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
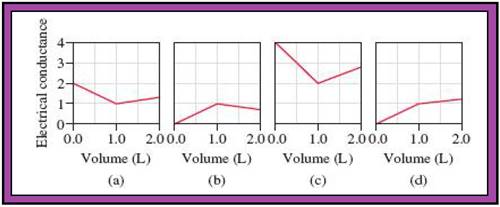
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
(e)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance, when
(e)
Answer to Problem 4.118SP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
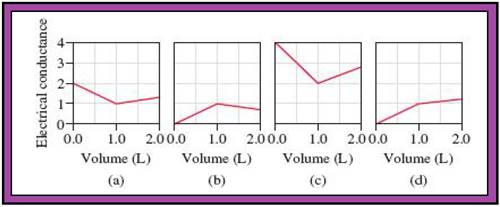
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
Match the calculated conductance unit of each reaction in given diagrams in Fig.1.
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK GENERAL CHEMISTRY: THE ESSENTIAL CO
- Predict the major products of this reaction: excess H+ NaOH ? A Note that the first reactant is used in excess, that is, there is much more of the first reactant than the second. If there won't be any products, just check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privarrow_forward1. For each of the reaction "railroads" below, you are either asked to give the structure(s) of the starting material(s) or product(s), or provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the transformation, as indicated by the boxes. a. NaOMe H+ .CO,H HO₂C MeOH (excess) MeOH H3C Br يع CH3 1. LiAlH4 2. H3O+ 3. PBг3 H3C 1. Et-Li 2. H3O+ -CO₂Me -CO₂Me OH CH3 CH3 ল CH3arrow_forwardPredict the intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this organic reaction: NaOMe ག1, ད།་, - + H You can draw 1 and 2 in any arrangement you like. 2 work up Note: if either 1 or 2 consists of a pair of enantiomers, just draw one structure using line bonds instead of 3D (dash and wedge) bonds at the chiral center. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Parrow_forward
- What is the total energy cost associated with the compound below adopting the shown conformation? CH3 HH DH CH3arrow_forwardΗΝ, Draw Final Product C cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Edit Enamine H3O+ CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H Edit Iminium Ionarrow_forwardHow many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?arrow_forward
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





