
Concept explainers
Use the following information for Brief Exercises 4-27 and 4-28:
Quillen Company manufactures a product in a factory that has two producing departments, Cutting and Sewing, and two support departments, S1 and S2. The activity driver for S1 is number of employees, and the activity driver for S2 is number of maintenance hours. The following data pertain to Quillen:
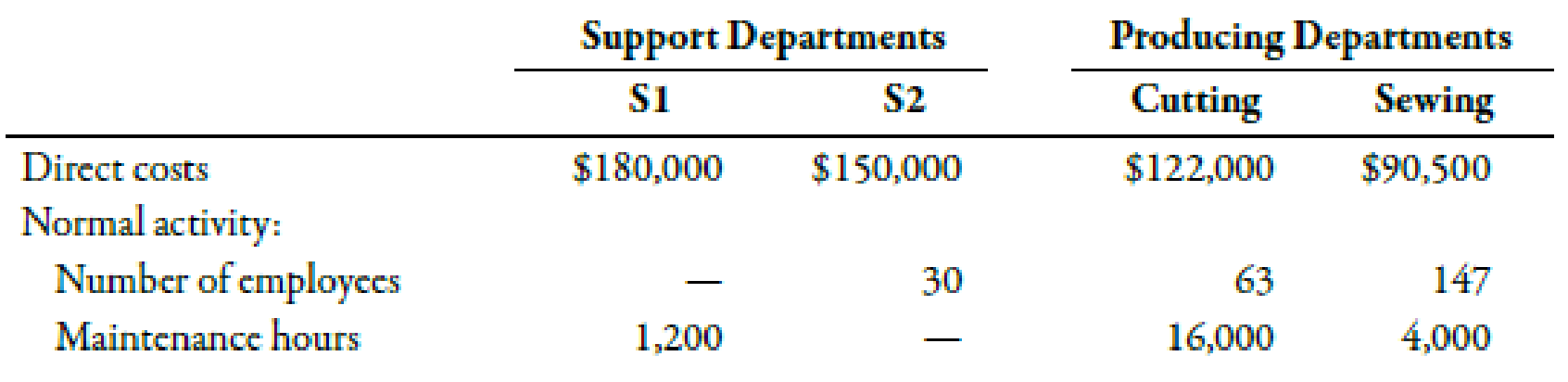
Brief Exercises 4-27 (Appendix 4B) Assigning Support Department Costs by Using the Direct Method
Refer to the information for Quillen Company above.
Required:
1. Calculate the cost assignment ratios to be used under the direct method for Departments S1 and S2. (Note: Each support department will have two ratios—one for Cutting and the other for Sewing.)
2. Allocate the support department costs to the producing departments by using the direct method.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Managerial Accounting
- A manufacturing company has two service and two production departments. Building Maintenance and Factory Office are the service departments. The production departments are Assembly and Machining. The following data have been estimated for next years operations: The direct charges identified with each of the departments are as follows: The building maintenance department services all departments of the company, and its costs are allocated using floor space occupied, while factory office costs are allocable to Assembly and Machining on the basis of direct labor hours. 1. Distribute the service department costs, using the direct method. 2. Distribute the service department costs, using the sequential distribution method, with the department servicing the greatest number of other departments distributed first.arrow_forwardUse the following information for Brief Exercises 4-34 and 4-35: Sanjay Company manufactures a product in a factory that has two producing departments, Assembly and Painting, and two support departments, S1 and S2. The activity driver for S1 is square footage, and the activity driver for S2 is number of machine hours. The following data pertain to Sanjay: Brief Exercises 4-34 (Appendix 4B) Assigning Support Department Costs by Using the Direct Method Refer to the information for Sanjay Company above. Required: 1. Calculate the cost assignment ratios to be used under the direct method for Departments S1 and S2. (Note: Each support department will have two ratiosone for Assembly and the other for Painting.) 2. Allocate the support department costs to the producing departments by using the direct method.arrow_forwardA manufacturing company has two service and two production departments. Human Resources and Machine Repair are the service departments. The production departments are Grinding and Polishing. The following data have been estimated for next years operations: The direct charges identified with each of the departments are as follows: The human resources department services all departments of the company, and its costs are allocated using the numbers of employees within each department, while machine repair costs are allocable to Grinding and Polishing on the basis of machine hours. 1. Distribute the service department costs, using the direct method. 2. Distribute the service department costs, using the sequential distribution method, with the department servicing the greatest number of other departments distributed first.arrow_forward
- The management of Gwinnett County Chrome Company, described in Problem 1A, now plans to use the multiple production department factory overhead rate method. The total factory overhead associated with each department is as follows: Instructions 1. Determine the multiple production department factory overhead rates, using direct labor hours for the Stamping Department and machine hours for the Plating Department. 2. Determine the product factory overhead costs, using the multiple production department rates in (1).arrow_forwardCrystal Scarves Co. produces winter scarves. The scarves are produced in the Cutting and Sewing departments. The Maintenance and Security departments support these production departments, and allocate costs based on machine hours and square feet, respectively. Information about each department is provided in the following table: Using the sequential method and allocating the support department with the highest costs first, allocate all support department costs to the production departments. Then compute the total cost of each production department.arrow_forwardRoberts Company produces two weed eaters: basic and advanced. The company has four activities: machining, engineering, receiving, and inspection. Information on these activities and their drivers is given below. Overhead costs: Required: 1. Calculate the four activity rates. 2. Calculate the unit costs using activity rates. Also, calculate the overhead cost per unit. 3. What if consumption ratios instead of activity rates were used to assign costs instead of activity rates? Show the cost assignment for the inspection activity.arrow_forward
- Support department cost allocation Hooligan Adventure Supply produces and sells various outdoor equipment. The Molding and Assembly production departments are supported by the Personnel and Maintenance departments. Personnel costs are allocated to the production departments based on the number of employees, and Maintenance costs are allocated based on number of service calls. Information about these departments is detailed in the following table: Instructions 1. Assuming that Hooligan Adventure Supply uses the sequential method to allocate its support department costs, which support department does it most likely allocate first? 2. Based on your response in part (1), determine the total costs allocated from each support department to each production department using the sequential method. 3. If Hooligan Adventure Supply wanted to use a more accurate support department cost allocation method, which method should it choose? What might discourage the company from using this method?arrow_forwardLansing. Inc., provided the following data for its two producing departments: Machine hours are used to assign the overhead of the Molding Department, and direct labor hours are used to assign the overhead of the Polishing Department. There are 30,000 units of Form A produced and sold and 50,000 of Form B. Required: 1. Calculate the overhead rates for each department. 2. Using departmental rates, assign overhead to live two products and calculate the overhead cost per unit. How does this compare with the plantwide rate unit cost, using direct labor hours? 3. What if the machine hours in Molding were 1,200 for Form A and 3,800 for Form B and the direct labor hours used in Polishing were 5,000 and 15,000, respectively? Calculate the overhead cost per unit for each product using departmental rates, and compare with the plantwide rate unit costs calculated in Requirement 2. What can you conclude from this outcome?arrow_forwardGeneva, Inc., makes two products, X and Y, that require allocation of indirect manufacturing costs. The following data were compiled by the accountants before making any allocations: The total cost of purchasing and receiving parts used in manufacturing is 60,000. The company uses a job-costing system with a single indirect cost rate. Under this system, allocated costs were 48,000 and 12,000 for X and Y, respectively. If an activity-based system is used, what would be the allocated costs for each product?arrow_forward
- Activity-based and department rate product costing and product cost distortions Black and Blue Sports Inc. manufactures two products: snowboards and skis. The factory overhead incurred is as follows: The activity base associated with the two production departments is direct labor hours. The indirect labor can be assigned to two different activities as follows: Instructions Determine the factory overhead rates under the multiple production department rate method. Assume that indirect labor is associated with the production departments, so that the total factory overhead is 315,000 and 540,000 for the Cutting and Finishing departments, respectively. Determine the total and per-unit factory overhead costs allocated to each product, using the multiple production department overhead rates in (1). Determine the activity rates, assuming that the indirect labor is associated with activities rather than with the production departments. Determine the total and per-unit cost assigned to each product under activity-based costing. Explain the difference in the per-unit overhead allocated to each product under the multiple production department factory overhead rate and activity-based costing methods.arrow_forwardAllocating selling and administrative expenses using activity-based costing Arctic Air Inc. manufactures cooling units for commercial buildings. The price and cost of goods sold for each unit are as follows: In addition, the company incurs selling and administrative expenses of 226,250. The company wishes to assign these costs to its three major customers, Gough Industries, Breen Inc., and The Martin Group. These expenses are related to three major nonmanufacturing activities: customer service, project bidding, and engineering support. The engineering support is in the form of engineering changes that are placed by the customer to change the design of a product. The budgeted activity costs and activity bases associated with these activities are: Activity-base usage and unit volume information for the three customers is as follows: Instructions 1. Determine the activity rates for each of the three nonmanufacturing activity pools. 2. Determine the activity costs allocated to the three customers, using the activity rates in (1). 3. Construct customer profitability reports for the three customers, dated for the year ended December 31, using the activity costs in (2). The reports should disclose the gross profit and operating income associated with each customer. 4. Provide recommendations to management, based on the profitability reports in (3).arrow_forwardFriedman Company uses JIT manufacturing. There are several manufacturing cells set up within one of its factories. One of the cells makes stands for flat-screen televisions. The cost of production for the month of April is given below. During May, 30,000 stands were produced and sold. Required: 1. Explain why process costing can be used for computing the cost of production for the stands. 2. Calculate the cost per unit for a stand. 3. Explain how activity-based costing can be used to determine the overhead assigned to the cell.arrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





