
Calculate
Suppose that back in the 1970s, Steve was asked to build speakers for two friends. The first friend, Jan, needed a speaker for her band. The second friend, Ed, needed a speaker built into the back of his hatchback automobile. Steve figured the following costs for each:
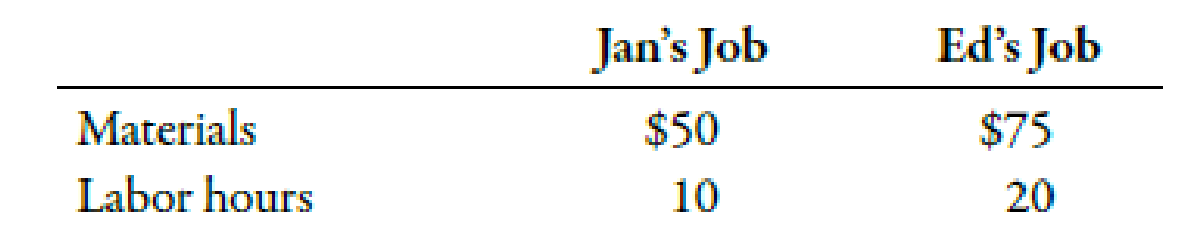
Steve knew that Jan’s job would be easier, since he had experience in building the type of speaker she needed. Her job would not require any special equipment or specialized fitting. Ed’s job, on the other hand, required specialized design and precise fitting. Steve thought he might need to build a mock-up of the speaker first, to fit it into the space. In addition, he might have to add to his tool collection to complete the job. Normally, Steve figured a wage rate of $6 per hour and charged 20% of labor and materials as an
Required:
- 1. Prepare job-order cost sheets for the two jobs, showing total cost.
- 2. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Which cost do you think is more likely to be accurate? How might Steve build in some of the uncertainty of Ed’s job into a budgeted cost?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 4 Solutions
Managerial Accounting
- You started your own construction business and need to determine the cost of materials used to build one house, and how many materials you will need to do so. Where would you begin to determine the standard price and quantity needs to build one house? What would produce a difference between the standard cost to build a house and the actual cost? What would cause a favorable outcome? What would cause an unfavorable outcome? What action might your company take if you had an unfavorable total direct materials cost variance?arrow_forwardMarginal cost?arrow_forwardLisa is a contractor, and she owns a small home renovation company that specializes in kitchen renovations. Lisa fears she has been underbidding her projects, and that translates into lost profits that could help sustain her through slow periods. She is putting together an estimate for a potential client and has determined the following activities: Activity Cost Driver Rate Estimated Use for Job Demo of Existing Space Square Footage $3.26 /square foot 520 square feet Cabinet Installation # of Hours $205 /hour 8 hours Countertop Installation Square Footage $12.00/square foot 280 square feet Previously, Lisa was billing at a flat rate of $16 per square foot of the demo space with no additional markup. Lisa would like to add a 20% markup to the cost to arrive at the final bid price. Using Activity-Based Costing (ABC), what is the final bid price for her potential customer? (Round intermediate calculations and final answer to 2 decimal places, eg. 25,000.25.) Final bid price $arrow_forward
- Moisha is developing material standards for her company. The operations manager wants grade A widgets because they are the easiest to work with and are the quality the customers want. Grade B will not work because customers do not want the lower grade, and it takes more time to assemble the product than with grade A materials. Moisha calls several suppliers to get prices for the widget. All are within $0.05 of each other. Since they will use millions of widgets, she decides that the $0.05 difference is important. The supplier who has the lowest price is known for delivering late and low-quality materials. Moisha decides to use the supplier who is $0.02 more but delivers on time and at the right quality. This supplier charges $0.42 per widget. Each unit of product requires 5 widgets. What is the standard cost per unit for widgets? Round your answer to two decimal places. Standard cost per unit $fill in the blank 1arrow_forwardMoisha is developing material standards for her company. The operations manager wants grade A widgets because they are the easiest to work with and are the quality the customers want. Grade B will not work because customers do not want the lower grade, and it takes more time to assemble the product than with grade A materials. Moisha calls several suppliers to get prices for the widget. All are within $0.05 of each other. Since they will use millions of widgets, she decides that the $0.05 difference is important. The supplier who has the lowest price is known for delivering late and low-quality materials. Moisha decides to use the supplier who is $0.02 more but delivers on time and at the right quality. This supplier charges $0.57 per widget. Each unit of product requires 4 widgets. What is the standard cost per unit for widgets? Round your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardMoisha is developing material standards for her company. The operations manager wants grade A widgets because they are the easiest to work with and are the quality the customers want. Grade B will not work because customers do not want the lower grade, and it takes more time to assemble the product than with grade A materials. Moisha calls several suppliers to get prices for the widget. All are within $0.05 of each other. Since they will use millions of widgets, she decides that the $0.05 difference is important. The supplier who has the lowest price is known for delivering late and low-quality materials. Moisha decides to use the supplier who is $0.02 more but delivers on time and at the right quality. This supplier charges $0.44 per widget. Each unit of product requires 6 widgets. What is the standard cost per unit for widgets? Round your answer to two decimal places. Standard cost per unit $arrow_forward
- Pamela is opening a pastry shop in which she will make and sell special birthday cupcakes. She is trying to decide how many mixers to purchase. Her estimated fixed and average variable costs, if she purchases one, two, or three mixers, are shown in the table. Assume that average variable costs do not vary with output. Suppose that Pamela is producing 100 cupcakes with one mixer, but she has a sudden increase in demand, so she begins to produce 200 cupcakes. Explain how her average total cost will change in the short run and in the long run. (Hint: Don't write more than 3 sentences) Table: Cupcakes at Dessert Delight Number of Fixed Costs Average mixers variable cost 1 $1,000 $10 1,500 2,500 2 3arrow_forwardSuppose that you have been given a summer job as an Intern at Issac Alrcams, a company that manufactures sophisticated spy cameras for remote-controlled millitary reconnalssance alrcraft. The company, which is privately owned, has approached a bank for a loan to help finance its growth. The bank requires financlal statements before approving the loan. Requlred: Classify each cost listed below as elther a product cost or a perlod cost for the purpose of preparing financial statements for the bank. Costs Product Cost or Period Cost 1. Depreciation on salespersons' cars. 2. Rent on equipment used in the factory. 3. Lubricants used for machine maintenance. 4. Salaries of personnel who work in the finished goods warehouse. 5. Soap and paper towels used by factory workers at the end of a shift. 6. Factory supervisors' salaries. 7. Heat, water, and power consumed in the factory. 8. Materials used for boxing products for shipment overseas. (Units are not normally boxed.) 9. Advertising costs.…arrow_forwardGreg Morrison recently graduated from mortuary school. He is considering opening his own funeral home. A funeral home is a high-fixed cost business, as it requires considerable expenditures for facilities, labor, and equipment, no matter how many families are served. Assume the annual fixed cost of operations is $800,000. Further assume that the only significant variable cost relates to burial containers like urns and caskets. An average casket costs $1,200. Greg's banker has asked a variety of questions in contemplation of providing a loan for this business. The banker has suggested that Greg can reduce his fixed costs by $150,000 if he will not buy any vehicles. Greg can instead rent vehicles as needed. The variable cost of renting is $700 per family served. Will this suggestion help Greg reach the break-even point sooner?arrow_forward
- Greg Morrison recently graduated from mortuary school. He is considering opening his own funeral home. A funeral home is a high-fixed cost business, as it requires considerable expenditures for facilities, labor, and equipment, no matter how many families are served. Assume the annual fixed cost of operations is $800,000. Further assume that the only significant variable cost relates to burial containers like urns and caskets. An average casket costs $1,200. Greg's banker has asked a variety of questions in contemplation of providing a loan for this business. If the average family is charged $6,000 for services and a burial container, how many families must be served to clear the break-even point?arrow_forwardGreg Morrison recently graduated from mortuary school. He is considering opening his own funeral home. A funeral home is a high-fixed cost business, as it requires considerable expenditures for facilities, labor, and equipment, no matter how many families are served. Assume the annual fixed cost of operations is $800,000. Further assume that the only significant variable cost relates to burial containers like urns and caskets. An average casket costs $1,200. Greg's banker has asked a variety of questions in contemplation of providing a loan for this business. If the banker believes Greg will only serve 100 families during the first year in business, how much will the business lose during its first year of operation?arrow_forwardSuppose that you have been given a summer job as an intern at Issac Aircams, a company that man- ufactures sophisticated spy cameras for remote-controlled military reconnaissance aircraft. The company, which is privately owned, has approached a bank for a loan to help it finance its growth. The bank requires financial statements before approving such a loan. You have been asked to help prepare the financial statements and were given the following list of costs: Depreciation on salespersons’ cars. Rent on equipment used in the factory. Lubricants used for machine maintenance. Salaries of personnel who work in the finished goods warehouse. Soap and paper towels used by factory workers at the end of a shift. Factory supervisors’ salaries. Heat, water, and power consumed in the factory. Materials used for boxing products for shipment overseas. (Units are not normally boxed.) Advertising costs. Workers’ compensation insurance for factory employees. Depreciation on…arrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning



