
Concept explainers
Use the bond energies in Table 5.1 to calculate the energy changes associated with each of these reactions. Then, label each reaction as endothermic or exothermic.
- a. 2 H2(g) + CO(g) → CH3OH(g)
- b. H2(g) + O2(g) → H2O2(g)
- c. 2 BrCl(g) → Br2(g) + Cl2(g)
(a)
Interpretation:
The energy changes have to be calculated, the reaction is exothermic or endothermic has to be labelled.
Concept introduction:
Endothermic reaction: When the heat energy was absorbed by the system from the surrounding is called endothermic reaction.
Exothermic reaction: When heat energy or light energy was unconfined to the surrounding from the system is called exothermic reaction.
Net energy change is calculated from the difference between the total energy absorbed in breaking bonds and total energy released in forming bonds.
Explanation of Solution
The given is shown below,
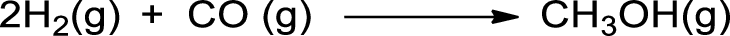
Bonds broken in the reactants are given below:
Bonds formed in the products are given below:
The overall energy change is negative, therefore, the reaction is an exothermic reaction.
(b)
Interpretation:
The energy changes have to be calculated, the reaction is exothermic or endothermic has to be labelled.
Concept introduction:
Endothermic reaction: When the heat energy was absorbed by the system from the surrounding is called endothermic reaction.
Exothermic reaction: When heat energy or light energy was unconfined to the surrounding from the system is called exothermic reaction.
Net energy change is calculated from the difference between the total energy absorbed in breaking bonds and total energy released in forming bonds.
Explanation of Solution
The given is shown below,
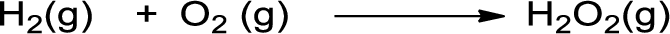
Bonds broken in the reactants are given below:
Therefore,
Bonds formed in the products are given below:
Therefore,
The overall energy change is negative, therefore, the reaction is an exothermic reaction.
(c)
Interpretation:
The energy changes have to be calculated, the reaction is exothermic or endothermic has to be labelled.
Concept introduction:
Endothermic reaction: When the heat energy was absorbed by the system from the surrounding is called endothermic reaction.
Exothermic reaction: When heat energy or light energy was unconfined to the surrounding from the system is called exothermic reaction.
Net energy change is calculated from the difference between the total energy absorbed in breaking bonds and total energy released in forming bonds.
Explanation of Solution
The given is shown below,
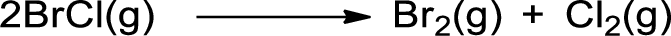
Bonds broken in the reactants are given below:
Therefore,
Bonds formed in the products are given below:
Therefore,
The overall energy change is negative, therefore, the reaction is an exothermic reaction.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Chemistry in Context
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- Consider the following gas chromatographs of Compound A, Compound B, and a mixture of Compounds A and B. Inject A B mixture Area= 9 Area = 5 Area = 3 Area Inject . མི། Inject J2 What is the percentage of Compound B in the the mixture?arrow_forwardRank these according to stability. CH3 H3C CH3 1 CH3 H3C 1 most stable, 3 least stable O 1 most stable, 2 least stable 2 most stable, 1 least stable O2 most stable, 3 least stable O3 most stable, 2 least stable O3 most stable, 1 least stable CH3 2 CH3 CH3 H₂C CH3 3 CH3 CHarrow_forwardConsider this IR and NMR: INFRARED SPECTRUM TRANSMITTANCE 0.8- 0.6 0.4 0.2 3000 10 9 8 00 HSP-00-541 7 CO 6 2000 Wavenumber (cm-1) сл 5 ppm 4 M Which compound gave rise to these spectra? N 1000 1 0arrow_forward
- Consider this reaction (molecular weights are under each compound): HC=CH + 2 HCI --> C2H4Cl 2 MW = 26 36.5 99 If 4.4 g of HC=CH are reacted with 110 mL of a 2.3 M HCI solution, and 6.0 g of product are actually produced, what is the percent yield?arrow_forwardWhat is the name of the major product of this reaction? OH CH3 H₂SO4, heat 1-methylcyclohexene O2-methyl-1-cyclohexene O 3-mthylcyclohexene 1-methyl-2-cyclohexenearrow_forwardWe added a brown solution of Br2 to one of our products, and the brown color disappeared. This indicated that our product wasarrow_forward
- Rank the following according to reactivity toward nitration: a) benzene b) bromobenzene c) nitrobenzene d) phenol Od) greatest, c) least Od) greatest, b) least Od) greatest, a) least a) greatest, b) least a) greatest, c) least Oa) greatest, d) least Ob) greatest, a) least O b) greatest, c) least Ob) greatest, d) least O c) greatest, a) least O c) greatest, b) least O c) greatest, d) leastarrow_forwardO-Nitrophenol was distilled over with the steam in our experiment while the other isomer did not. This is due to: O intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the ortho isomer O intermolecular hydrogen bonding in the the ortho isomer O the ortho isomer has a lower density O the ortho isomer has a lower molecular weightarrow_forwardK 44% Problem 68 of 15 Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. :6: :: :CI: CI CI: :0:0 Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows H H Cl CI: CI CI: Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows H :CI: Alarrow_forward
- I I H :0: Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. 0:0 :0: CI ΑΙ :CI: :CI: :0: CI Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows cl. :0: Cl © ハ CI:: CI H CO Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows 10: AI ::arrow_forwardOrder the following compounds from slowest to fastest in a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction. ii 요 OB D A E C OCE Darrow_forwardI need the most help figuring out how to find [I^-] mol/ L, [S2O8^2-] mol/L. 1st and 2nd Blank columns.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781285199030Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781285199030Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning





