
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
6th Edition
ISBN: 8220102801448
Author: Alexander
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 20P
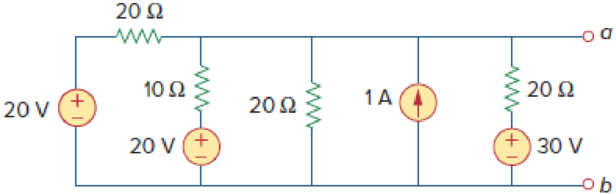
Use source transformation to reduce the circuit between terminals a and b shown in Fig. 4.88 to a single voltage source in series with a single resistor.
Figure 4.88
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please show all steps
A plane wave propagating in the +z direction in medium 1 is normally incident to medium 2 located at
the z=0 plane as below. Both mediums are general, characterized by ( ε i, Mi, Ơi ).
tot
=
[ ει μη σ]
[ε, μη σε ]
Ex
Ex
tot
E₁₂ (z) = Ee
Ex
z=0
From conservation of energy: P₁AV'(z=0) + Piav'(z=0) = P2av²(z=0).
Using the above show for lossless media that: ( 1 - ||²) = (1/M2 )|T|² .
A plane wave propagating in the +z direction in medium 1 is normally incident to medium 2 located at
the z=0 plane as below. Both mediums are general, characterized by ( ε i, Hi, σ¡ ).
[ ει μη σ]
Ex
[ ει μη ση ]
Ex
tot
E₁₂ (z) = E'₁e¹²
-122
E(z) = Ee+ E₁₁₁²
E₁x
z=0
1. Specify the electric field reflection coefficient г and transmission coefficient T:
E
ΓΔ
E
E
TA
EL
2. Show that T=1+г. Can the transmitted electric field amplitude in region 2 be LARGER than the
incident electric field amplitude?
3. Determine expressions for P₁AV'(z), PIAV'(z) and P2AV'(z) (note the sign for the reflected power
direction should be (-z).
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
Ch. 4.2 - Figure 4.3 For Practice Prob. 4.1. For the circuit...Ch. 4.2 - Figure 4.5 For Practice Prob. 4.2. Assume that Vo...Ch. 4.3 - Figure 4.8 Using the superposition theorem, find...Ch. 4.3 - Figure 4.11 Use superposition to find vx in the...Ch. 4.3 - Find I in the circuit of Fig. 4.14 using the...Ch. 4.4 - Find io in the circuit of Fig. 4.19 using source...Ch. 4.4 - Use source transformation to find ix in the...Ch. 4.5 - Using Thevenins theorem, find the equivalent...Ch. 4.5 - Find the Thevenin equivalent circuit of the...Ch. 4.5 - Obtain the Thevenin equivalent of the circuit in...
Ch. 4.6 - Find the Norton equivalent circuit for the circuit...Ch. 4.6 - Find the Norton equivalent circuit of the circuit...Ch. 4.8 - Determine the value of RL that will draw the...Ch. 4.9 - Rework Practice Prob. 4.9 using PSpice. Find the...Ch. 4.9 - Fin d the maximum power transferred to RL if the...Ch. 4.10 - The measured open-circuit voltage across a certain...Ch. 4.10 - Prob. 17PPCh. 4.10 - Obtain the current through the galvanometer,...Ch. 4 - The current through a branch in a linear network...Ch. 4 - For superposition, it is not required that only...Ch. 4 - The superposition principle applies to power...Ch. 4 - Refer to Fig. 4.67. The Thevenin resistance at...Ch. 4 - The Thevenin voltage across terminals a and b of...Ch. 4 - The Norton current at terminals a and b of the...Ch. 4 - The Norton resistance RN is exactly equal to the...Ch. 4 - Which pair of circuits in Fig. 4.68 are...Ch. 4 - A load is connected to a network. At the terminals...Ch. 4 - The source is supplying the maximum power to the...Ch. 4 - Calculate the current io in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 4 - Using Fig. 4.70, design a problem to help other...Ch. 4 - (a) In the circuit of Fig. 4.71, calculate vo and...Ch. 4 - Use linearity to determine io in the circuit of...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.73, assume vo = 1 V, and...Ch. 4 - For the linear circuit shown in Fig. 4.74, use...Ch. 4 - Use linearity and the assumption that Vo = 1 V to...Ch. 4 - Using superposition, find Vo in the circuit of...Ch. 4 - Given that I = 6 amps when Vs = 160 volts and Is =...Ch. 4 - Using Fig. 4.78, design a problem to help other...Ch. 4 - Use the superposition principle to find io and vo...Ch. 4 - Determine vo in the circuit of Fig. 4.80 using the...Ch. 4 - Use superposition to find vo in the circuit of...Ch. 4 - Apply the superposition principle to find vo in...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.83, use superposition to...Ch. 4 - Given the circuit in Fig. 4.84, use superposition...Ch. 4 - Use superposition to obtain vx in the circuit of...Ch. 4 - Use superposition to find Vo in the circuit of...Ch. 4 - Use superposition to solve for vx in the circuit...Ch. 4 - Use source transformation to reduce the circuit...Ch. 4 - Using Fig. 4.89, design a problem to help other...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig, 4.90, use source...Ch. 4 - Referring to Fig. 4.91, use source transformation...Ch. 4 - Use source transformation to find the voltage Vx...Ch. 4 - Obtain vo in the circuit of Fig. 4.93 using source...Ch. 4 - Use source transformation to find io in the...Ch. 4 - Apply source transformation to find vx in the...Ch. 4 - Use source transformation to find Io in Fig. 4.96....Ch. 4 - Use source transformation to find vo in the...Ch. 4 - Use source transformation on the circuit shown in...Ch. 4 - Determine vx in the circuit of Fig. 4.99 using...Ch. 4 - Use source transformation to find ix in the...Ch. 4 - Determine the Thevenin equivalent circuit, shown...Ch. 4 - Using Fig. 4.102, design a problem that will help...Ch. 4 - Use Thevenins theorem to find vo in Prob. 4.12....Ch. 4 - Solve for the current i in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 4 - Find the Norton equivalent with respect to...Ch. 4 - Apply Thevenins theorem to find Vo in the circuit...Ch. 4 - Obtain the Thevenin equivalent at terminals a-b of...Ch. 4 - Find the Thevenin equivalent at terminals a-b of...Ch. 4 - Find the Thevenin and Norton equivalents at...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.109, find the Thevenin...Ch. 4 - Find the Thevenin equivalent looking into...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.111, obtain the Thevenin...Ch. 4 - Find the Thevenin equivalent of the circuit in...Ch. 4 - Using Fig. 4.113, design a problem to help other...Ch. 4 - Obtain the Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 4 - Determine the Norton equivalent at terminals a-b...Ch. 4 - Find the Norton equivalent looking into terminals...Ch. 4 - Obtain the Norton equivalent of the circuit in...Ch. 4 - Given the circuit in Fig. 4.117, obtain the Norton...Ch. 4 - For the transistor model in Fig. 4.118, obtain the...Ch. 4 - Find the Norton equivalent at terminals a-b of the...Ch. 4 - Find the Thevenin equivalent between terminals a-b...Ch. 4 - Obtain the Norton equivalent at terminals a-b of...Ch. 4 - Use Nortons theorem to find Vo in the circuit of...Ch. 4 - Obtain the Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 4 - The network in Fig. 4.124 models a bipolar...Ch. 4 - Determine the Thevenin and Norton equivalents at...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.126, find the Thevenin...Ch. 4 - Obtain the Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 4 - Find the Thevenin equivalent of the circuit in...Ch. 4 - Find the Norton equivalent for the circuit in Fig....Ch. 4 - Obtain the Thevenin equivalent seen at terminals...Ch. 4 - For the circuit shown in Fig. 4.131, determine the...Ch. 4 - Find the maximum power that can be delivered to...Ch. 4 - The variable resistor R in Fig. 4.133 is adjusted...Ch. 4 - Consider the 30- resistor in Fig. 4.134. First...Ch. 4 - Find the maximum power transferred to resistor R...Ch. 4 - Determine the maximum power delivered to the...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.137, what resistor...Ch. 4 - (a) For the circuit in Fig. 4.138, obtain the...Ch. 4 - Determine the maximum power that can be delivered...Ch. 4 - For the bridge circuit shown in Fig. 4.140, find...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.141, determine the value...Ch. 4 - Solve Prob. 4.34 using PSpice or MultiSim. Let V =...Ch. 4 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to solve Prob. 4.44. For...Ch. 4 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to solve Prob. 4.52.Ch. 4 - Obtain the Thevenin equivalent of the circuit in...Ch. 4 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to find the Thevenin...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.126, use PSpice or...Ch. 4 - An automobile battery has an open circuit voltage...Ch. 4 - The following results were obtained from...Ch. 4 - When connected to a 4- resistor, a battery has a...Ch. 4 - The Thevenin equivalent at terminals a-b of the...Ch. 4 - A black box with a circuit in it is connected to a...Ch. 4 - A transducer is modeled with a current source Is...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit in Fig. 4.144. An ammeter...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit in Fig. 4.145. (a) Replace...Ch. 4 - The Wheatstone bridge circuit shown in Fig. 4.146...Ch. 4 - (a) In the Wheatstone bridge circuit of Fig. 4.147...Ch. 4 - Consider the bridge circuit of Fig. 4.148. Is the...Ch. 4 - The circuit in Fig. 4.149 models a common-emitter...Ch. 4 - An attenuator is an interface circuit that reduces...Ch. 4 - A dc voltmeter with a sensitivity of 10 k/V is...Ch. 4 - A resistance array is connected to a load resistor...Ch. 4 - A common-emitter amplifier circuit is shown in...Ch. 4 - For Practice Prob. 4.18, determine the current...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2) In the ideal transformer circuit shown below find Vo and the complex power supplied by the source. 292 www b 1:4 16 Ω ww + + 240/0° V rms -12492arrow_forward3) In the ideal autotransformer circuit shown below find 11, 12 and lo. Find the average power delivered to the load. (hint: write KVL for both sides) 20/30° V(+ 2-1602 200 turns V₂ 10 + j40 Ω 80 turns V₁arrow_forward1) Find Vo in the following circuit. Assume the mesh currents are clockwise. ΠΩ Ω ΖΩ ww 1Ω ww 24/0° (± 6 Ω j4 Ω 1Ω +arrow_forward
- Please show all stepsarrow_forward11-3) similar to Lathi & Ding, Prob. P.6.8-1 Consider the carrier modulator shown in the figure below, which transmits a binary carrier signal. The baseband generator uses polar NRZ signaling with rectangular pulses. The data rate is 8 Mbit/s. (a) If the modulator generates a binary PSK signal, what is the bandwidth of the modulated output? (b) If the modulator generates FSK with the difference fel - fco = 6 MHz (cf. Fig 6.32c), determine the modulated signal bandwidth. Binary data source Baseband signal generator Modulated output Modulator N-E---arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- Q3: Why is the DRAM cell design simpler but slower than SRAM?arrow_forward5052 ми a JXL 000 +2 16s (wt) bi jxc M 100♫ ZL. Find the Value of XL & X c if the Circuit trans for Max. Power to (ZL).arrow_forwardChoose the best answer for each: 1. What does SRAM use to store data? 。 a) Capacitors ob) Latches 。 c) Flip-flops od) Transistors 2. Which RAM type requires refreshing? o a) SRAM ob) DRAM 。 c) ROM od) Flash 3. What type of memory retains data only while power is on? a) ROM 。 b) EEPROM o c) DRAM od) Flash 4. How many addresses can a 15-bit address bus handle? o a) 32k • b) 64k o c) 16k od) lk 5. What operation occurs when data is copied out of memory without erasing? oa) Write ob) Read o c) Refresh o d) Load 6. DRAM cells store bits using: a) Flip-flops 。 b) Capacitors c) Diodes od) Resistors 7. The cache located inside the CPU is: 。 a) L2 cache o b) LI cache °c) ROM od) HDD 8. SDRAM is synchronized with: o a) Cache ob) Data Bus c) System Clock od) Hard Disk 9. The bus that carries commands is called: o a) Data Bus b) Control Bus o c) Address Bus o d) Logic Bus 10. What is the main use of SRAM? o Disk storage o Cache o Main memory o Registers 11. The smallest addressable unit in…arrow_forward
- Q4: A cache memory is 128k × 16. How many bytes can it store?arrow_forwardSketch the output of the analogue computer shown below and find its closest describing function [suppose any variable to find the DF] +1 ew2 HI e2 1.0 +21 LO SJ eo SJ ew LO 1.0 +|e1| HI -1 ew1 ek(1 + e。) |e1| k = 1+|e1| Figure V-5 Feedback Limiter Behavior ROUNDED, DUE TO DIODE NONLINEARITY LIMIT VOLTAGE 409 DIODE CONDUCTS First, write the output transaction, then draw the output wave, and then find the Describing function. I need to solve the question step by step, with an explanation of each step.arrow_forwardSketch the output of the analogue computer shown below and find its closest describing function [suppose any variable to find the DF] SJ ew2 ew₁ HI |e2| 2 LO 1.0 +21 LO -1 HI Jel 1.0+|e1| ROUNDED, DUE TO DODE NONLINEARITY LIMIT VOLTAGE DIODE CONDUCTS ew1e, -k(1+ e。) k = |e1| 1+|e1| Figure 1-5 Feedback Limiter Behavior First, write the output transaction, then draw the output wave, and then find the Describing function. I need to solve the question step by step, with an explanation of each step.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Norton's Theorem and Thevenin's Theorem - Electrical Circuit Analysis; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-kkvqr1wSwA;License: Standard Youtube License