
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780321885326
Author: Jane B. Reece, Martha R. Taylor, Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, Kelly A. Hogan
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 1CC
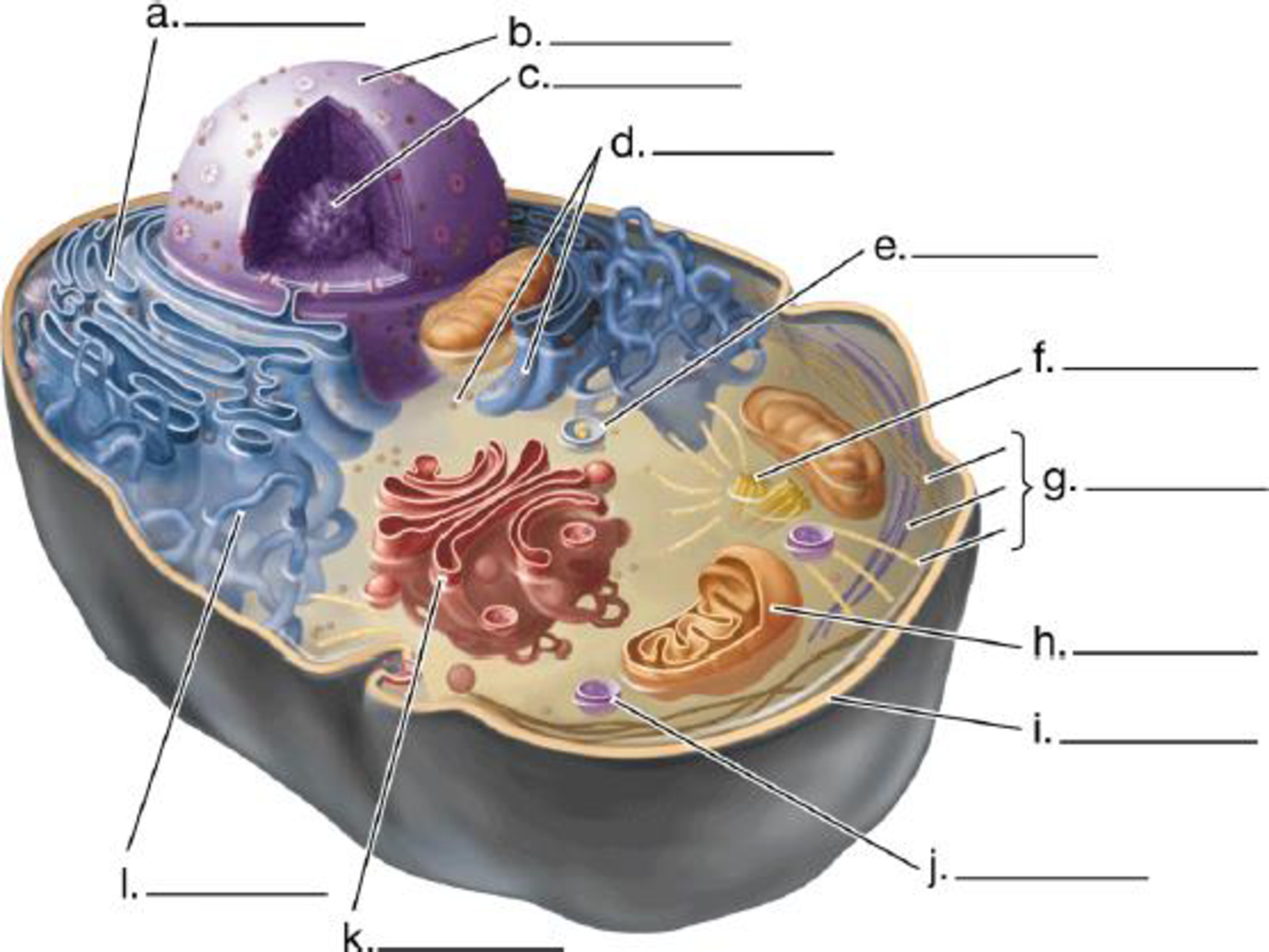
Label the structures in this diagram of an animal cell. Review the functions of each of these organelles.
Expert Solution & Answer
Summary Introduction
To review: The structures and functions of each of the organelles in the given animal cell.
Introduction:
A cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of living organisms. It is bounded by a cell membrane. Cells contain different organelles. Each organelle has its own specific features and functions. Each cellular organelle possesses different structural peculiarities.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
Fig. 1 shows various structural organelles of an animal cell.
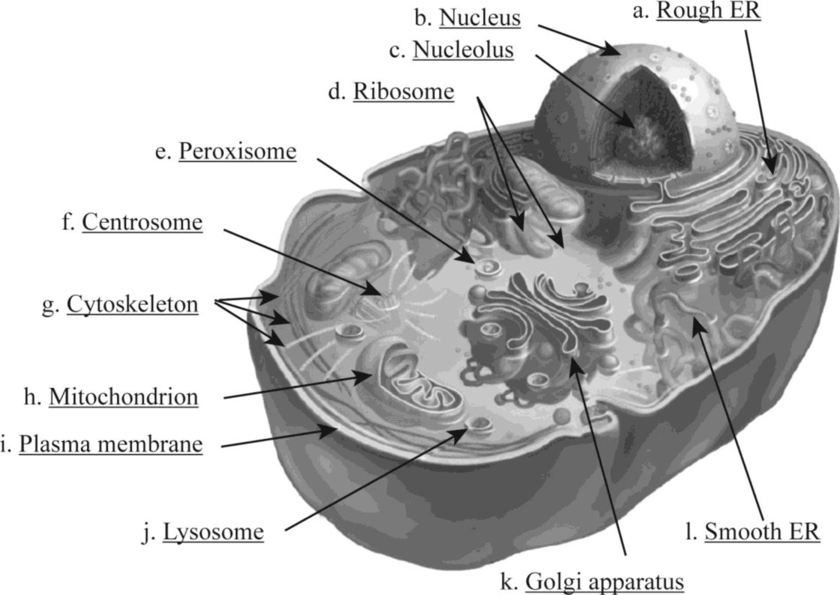
Fig. 1: Structure of an animal cell
The functions of various organelles are very specific.
- a. Rough ER: It is a network of membranous sacs and tubes; its external surface is attached with the ribosome. It helps in protein processing and secretion. Also, the addition of carbohydrate with protein occurs to produce glycoprotein, which helps in the production of a new membrane within the cell.
- b. Nucleus: It is a membrane-bound organelle covered by the nuclear envelope. The nucleus contains the nucleolus and chromatin material. The chromatin material consists of DNA and proteins.
- c. Nucleolus: It is a core region in the nucleus where components of the ribosome assemble.
- d. Ribosome: It is a non-membranous structure found in the cytoplasm of the cell. It is the core organelle for protein synthesis. It can be found free or attached with the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
- e. Peroxisome: It is a specialized single membrane–bound vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell. It produces hydrogen peroxide as a by-product and converts it to water.
- f. Centrosome: The formation of microtubules initiates at the centrosome. It contains a pair of centrioles.
- g. Cytoskeleton: It consists of a network of fibrous substances within the cytoplasm of a cell. The cytoskeleton consists of three main fibers called microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. It helps in providing rigidity and gives structural support to the cell.
- h. Mitochondrion: It is double membrane–bound organelle. It is important for cellular respiration and energy generation in the form of ATP. The two phospholipid bilayer membranes enclosed with the mitochondria play a great role in functioning of mitochondria. It is also called as the “power house” of the cell.
- i. Plasma membrane: It is the protective compartment of the cell. It is composed of a lipid bilayer.
- j. Lysosome: It is a single membrane–bound organelle. It is the storage unit of hydrolytic enzymes. Breakdown of indigested substances takes place in lysosomes, and cell organelles are recycled here.
- k. Golgi apparatus: It is a single membrane–bound organelle stack of the flattened membranous sac. It is the active unit of modification, sorting, and secretion of cell products.
- l. Smooth ER: It is a network of membranous sacs and tubes but not attached with the ribosome. It helps in detoxification and lipid synthesis. It helps in folding of protein and transferring of the synthesized protein.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Students have asked these similar questions
1. In vivo testing provides valuable insight into a drug’s kinetics. Assessing drug kinetics following multiple different routes of administration provides greater insight than just a single route of administration alone. The following data was collected in 250 g rats following bolus iv, oral (po), and intraperitoneal (ip) administration.Using this data and set of graphs, determine:
(a) k, C0, V, and AUC* for the bolus iv data (b) k, ka, B1, and AUC* for the po data (c) k, ka, B1, and AUC* for the ip data (d) relative bioavailability for po vs ip, Fpo/Fip (e) absolute po bioavailability, (f)Fpo absolute ip bioavailability, Fip
MAKE SURE ANSWERS HAVE UNITS if appropriate.
SHOW ALL WORK, including equation used, variables used and each step to your solution.
2. Drug quantification from plasma is commonly performed by using techniques such as HPLC or LC/MS. However, these methods do have limitations, and investigators may choose to use a radiolabeled analog of a drug instead. Radioligands are molecules that contain radioactive isotopes, commonly 3H or 14C. This technique allows investigators to quantify drug concentration from radiation measurements. The following measurements were made in 250 g rats following oral administration of 18.2 µCi of a 14C-labeled drug of interest: Time (min) Plasma Radiation Levels (µCi/L) 0 0.0 2 9.7 4 19.2 7 25.3 9 37.8 12 39.6 14 45.8 17 48.8 20 52.0 25 56.4 30 59.2 35 60.1 40 61.1 45 62.1 50 62.8 60 63.1 70 62.1 80 60.1 90 57.3 100 55.5 110 53.7 120 52.2 150 48.0 180 45.0 240 39.0
Note that a µCi is a measure of the amount of radioactivity and hence is a measure of the amount of drug present. Given that the oral bioavailability of this drug is known to be essentially 100%, estimate the following from this…
The current nutrition labelling regulation in Hong Kong requires food manufacturer to list E+7 information on the package of pre-packaged food products. Do you think that more nutrients, such as calcium and cholesterol, shall be included?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (8th Edition)
Ch. 4 - Label the structures in this diagram of an animal...Ch. 4 - Prob. 2TYKCh. 4 - Prob. 3TYKCh. 4 - Which of the following clues would tell you...Ch. 4 - Prob. 5TYKCh. 4 - What four cellular components are shared by...Ch. 4 - Describe two different ways in which cilia can...Ch. 4 - In which cell would you find the most lysosomes?...Ch. 4 - Prob. 9TYKCh. 4 - Prob. 10TYK
Ch. 4 - In which cell would you find the most...Ch. 4 - In what ways do the internal membranes of a...Ch. 4 - Is this statement true or false? Animal cells have...Ch. 4 - Describe the structure of the plasma membrane of...Ch. 4 - Prob. 15TYKCh. 4 - Describe the pathway of the protein hormone...Ch. 4 - How might the phrase ingested but not digested be...Ch. 4 - Cilia are found on cells in almost every organ of...Ch. 4 - SCIENTIFIC THINKING Microtubules often produce...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- View History Bookmarks Window Help Quarter cements ents ons (17) YouTube Which amino acids would you expect to find marked on the alpha helix? canvas.ucsc.edu ucsc Complaint and Grievance Process - Academic Personnel pach orations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 000000 000000000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 00000000 scope vious De 48 12.415 KATPM FEB 3 F1 F2 80 F3 a F4 F5 2 # 3 $ 85 % tv N A の Mon Feb 3 10:24 PM Lipid bilayer Submit Assignment Next > ZOOM < Å DII 8 བ བ F6 16 F7 F8 F9 F10 34 F11 F12 & * ( 6 7 8 9 0 + 11 WERTY U { 0 } P deletearrow_forwardDifferent species or organisms research for ecologyarrow_forwardWhat is the result of the following gram stain: positive ○ capsulated ○ acid-fast ○ negativearrow_forward
- What type of stain is the image below: capsule stain endospore stain gram stain negative stain ASM MicrobeLibrary.org Keplingerarrow_forwardWhat is the result of the acid-fast stain below: Stock Images by Getty Images by Getty Images by Getty Images by Getty Image Getty Images St Soy Getty Images by Getty Images by Getty Images Joy Getty encapsulated O endosporulating negative ○ positivearrow_forwardYou have a stock vial of diligence 75mg in 3ml and need to draw up a dose of 50mg for your patient.how many mls should you draw up to give this dosearrow_forward
- You are recquired to administer 150mg hydrocortisone intravenously,how many mls should you give?(stock =hydrocortisone 100mg in 2mls)arrow_forwardIf someone was working with a 50 MBq F-18 source, what would be the internal and external dose consequences?arrow_forwardWe will be starting a group project next week where you and your group will research and ultimately present on a current research article related to the biology of a pathogen that infects humans. The article could be about the pathogen itself, the disease process related to the pathogen, the immune response to the pathogen, vaccines or treatments that affect the pathogen, or other biology-related study about the pathogen. I recommend that you choose a pathogen that is currently interesting to researchers, so that you will be able to find plenty of articles about it. Avoid choosing a historical disease that no longer circulates. List 3 possible pathogens or diseases that you might want to do for your group project.arrow_forward
- not use ai pleasearrow_forwardDNK dagi nukleotidlar va undan sintezlangan oqsildagi peptid boglar farqi 901 taga teng bo'lib undagi A jami H boglardan 6,5 marta kam bo'lsa DNK dagi jami H bog‘lar sonini topingarrow_forwardOne of the ways for a cell to generate ATP is through the oxidative phosphorylation. In oxidative phosphorylation 3 ATP are produced from every one NADH molecule. In respiration, every glucose molecule produces 10 NADH molecules. If a cell is growing on 5 glucose molecules, how much ATP can be produced using oxidative phosphorylation/aerobic respiration?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning


Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning




Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Dissection Basics | Types and Tools; Author: BlueLink: University of Michigan Anatomy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-_B17pTmzto;License: Standard youtube license