
Concept explainers
SCIENTIFIC THINKING Microtubules often produce movement through their interaction with motor proteins. But in some cases, microtubules move cell components when the length of the microtubule changes. Through a series of experiments, researchers determined that microtubules grow and shorten as tubulin proteins are added or removed from their ends. Other experiments showed that microtubules make up the spindle apparatus that “pulls” chromosomes toward opposite ends (poles) of a dividing cell. The figures below describe a clever experiment done in 1987 to determine whether a spindle microtubule shortens (depolymerizes) at the end holding a chromosome or at the pole end of a dividing cell.
Experimenters labeled the microtubules of a dividing cell from a pig kidney with a yellow fluorescent dye. As shown on the left half of the diagram below, they then marked a region halfway along the microtubules by using a laser to eliminate the fluorescence from that region. They did not mark the other side of the spindle (right side of the figure).
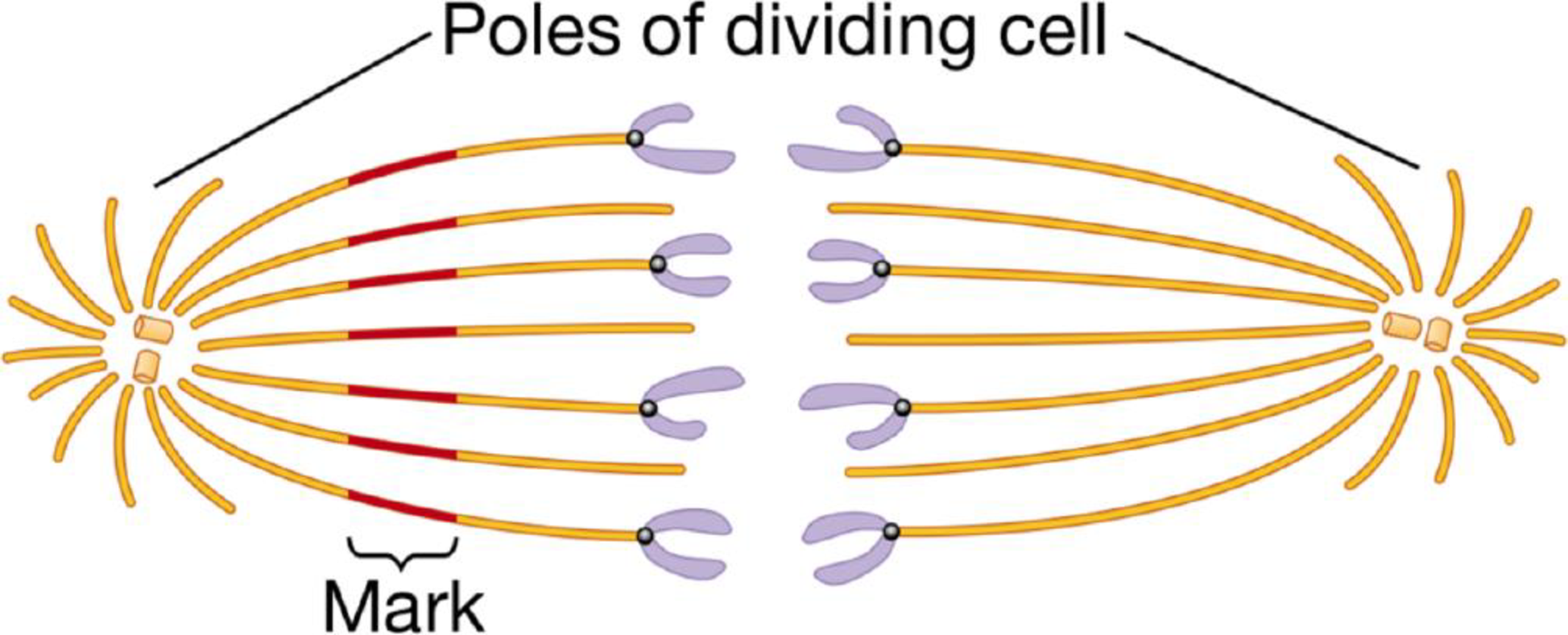
The figure below illustrates the results they observed as the chromosomes moved toward the opposite poles of the cell.
The figure below illustrates the results they observed as the chromosomes moved toward the opposite poles of the cell.
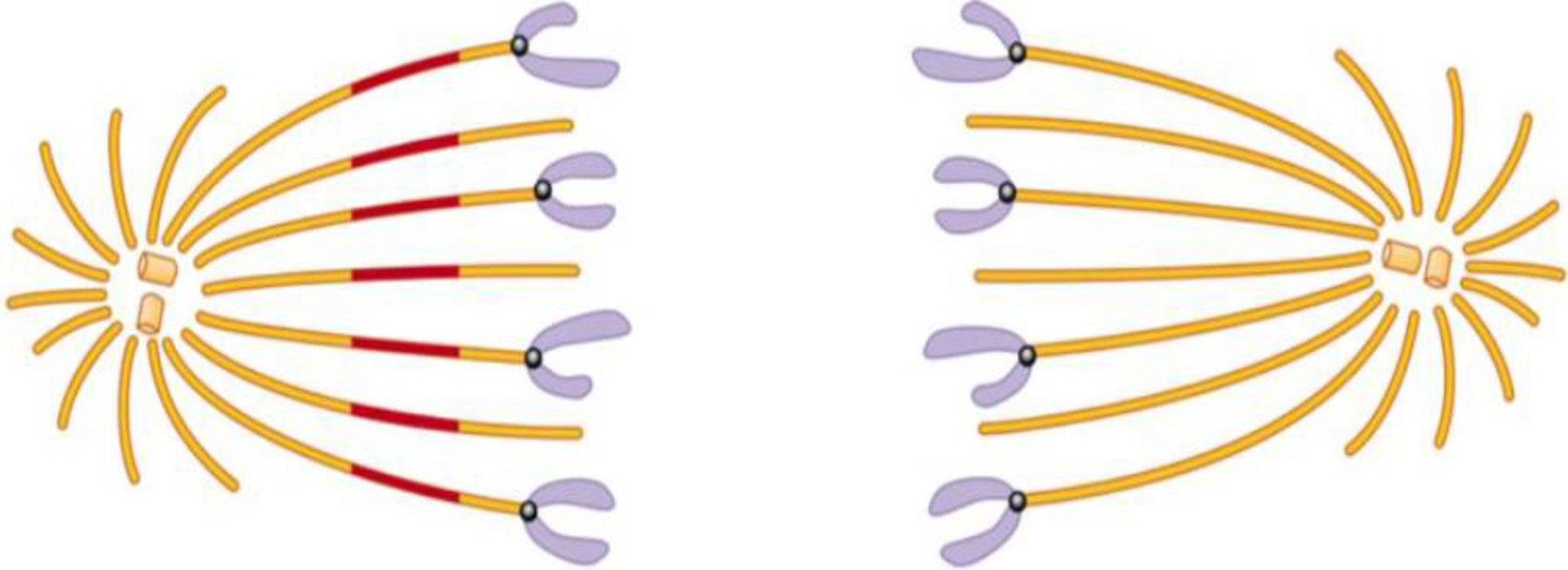
Describe these results. What would you conclude about where the microtubules depolymerize from comparing the length of the microtubules on either side of the mark? How could the experimenters determine whether this is the mechanism of chromosome movement in all cells?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (8th Edition)
- 18. Watch this short youtube video about SARS CoV-2 replication. SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle (Summer 2020) - YouTube.19. What is the name of the receptor that SARS CoV-2 uses to enter cells? Which human cells express this receptor? 20. Name a few of the proteins that the SARS CoV-2 mRNA codes for. 21. What is the role of the golgi apparatus related to SARS CoV-2arrow_forwardState the five functions of Globular Proteins, and give an example of a protein for each function.arrow_forwardDiagram of check cell under low power and high powerarrow_forward
- a couple in which the father has the a blood type and the mother has the o blood type produce an offspring with the o blood type, how does this happen? how could two functionally O parents produce an offspring that has the a blood type?arrow_forwardWhat is the opening indicated by the pointer? (leaf x.s.) stomate guard cell lenticel intercellular space none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the indicated tissue? (stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma ○ xylem ○ phloem none of thesearrow_forward
- Where did this structure originate from? (Salix branch root) epidermis cortex endodermis pericycle vascular cylinderarrow_forwardIdentify the indicated tissue. (Tilia stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma xylem phloem none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the indicated structure. (Cucurbita stem l.s.) pit lenticel stomate tendril none of thesearrow_forward
- Identify the specific cell? (Zebrina leaf peel) vessel element sieve element companion cell tracheid guard cell subsidiary cell none of thesearrow_forwardWhat type of cells flank the opening on either side? (leaf x.s.) vessel elements sieve elements companion cells tracheids guard cells none of thesearrow_forwardWhat specific cell is indicated. (Cucurbita stem I.s.) vessel element sieve element O companion cell tracheid guard cell none of thesearrow_forward

 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College





