
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305116399
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 37, Problem 37.62AP
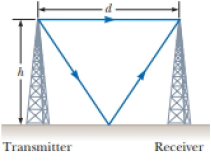
Figure P36.35 shows a radio-wave transmitter and a receiver separated by a distance d and both a distance h above the ground. The receiver can receive signals both directly from the transmitter and indirectly from signals that reflect from the ground. Assume the ground is level between the transmitter and receiver and a 180° phase shift occurs upon reflection. Determine the longest wavelengths that interfere (a) constructively and (b) destructively.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Can someone help me
Need help on the following questions on biomechanics. (Please refer to images below)A gymnast weighing 68 kg attempts a handstand using only one arm. He plants his handat an angle resulting in the reaction force shown.A) Find the resultant force (acting on the Center of Mass)B) Find the resultant moment (acting on the Center of Mass)C) Draw the resultant force and moment about the center of mass on the figure below. Will the gymnast rotate, translate, or both? And in which direction?
Please help me on the following question (Please refer to image below)An Olympic lifter (m = 103kg) is holding a lift with a mass of 350 kg. The barexerts a purely vertical force that is equally distributed between both hands. Each arm has amass of 9 kg, are 0.8m long and form a 40° angle with the horizontal. The CoM for each armis 0.5 m from hand. Assuming the lifter is facing us in the diagram below, his right deltoidinserts 14cm from the shoulder at an angle of 13° counter-clockwise from the humerus.A) You are interested in calculating the force in the right deltoid. Draw a free body diagramof the right arm including the external forces, joint reaction forces, a coordinate system andstate your assumptions.B) Find the force exerted by the right deltoidC) Find the shoulder joint contact force. Report your answer using the magnitude and directionof the shoulder force vector.
Chapter 37 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
Ch. 37 - Which of the following causes the fringes in a...Ch. 37 - Using Figure 36.6 as a model, sketch the...Ch. 37 - One microscope slide is placed on top of another...Ch. 37 - While using a Michelson interferometer (shown in...Ch. 37 - Four trials of Young's double-slit experiment are...Ch. 37 - Suppose Youngs double-slit experiment is performed...Ch. 37 - Green light has a wavelength of 500 nm in air. (i)...Ch. 37 - A thin layer of oil (n = 1.25) is floating on...Ch. 37 - A monochromatic beam of light of wavelength .500...Ch. 37 - According to Table 35.1, the index of refraction...
Ch. 37 - Suppose you perform Youngs double-slit experiment...Ch. 37 - A plane monochromatic light wave is incident on a...Ch. 37 - A film of' oil on a puddle in a parking lot shows...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.1CQCh. 37 - Prob. 37.2CQCh. 37 - Explain why two flashlights held close together do...Ch. 37 - A lens with outer radius of curvature R and index...Ch. 37 - Consider a dark fringe in a double-slit...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.6CQCh. 37 - What is the necessary condition on the path length...Ch. 37 - In a laboratory accident, you spill two liquids...Ch. 37 - A theatrical smoke machine fills the space bet...Ch. 37 - Two slits are separated by 0.320 mm. A beam of...Ch. 37 - Light of wavelength 530 nm illuminates a pair of...Ch. 37 - A laser beam is incident on two slits with a...Ch. 37 - A Youngs interference experiment is performed with...Ch. 37 - Youngs double-slit experiment is performed with...Ch. 37 - Why is the following situation impossible? Two...Ch. 37 - Light of wavelength 620 nm falls on a double slit,...Ch. 37 - In a Youngs double-slit experiment, two parallel...Ch. 37 - pair of narrow, parallel slits separated by 0.250...Ch. 37 - Light with wavelength 442 nm passes through a...Ch. 37 - The two speakers of a boom box are 35.0 cm apart....Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.12PCh. 37 - Two radio antennas separated by d = 300 in as...Ch. 37 - A riverside warehouse has several small doors...Ch. 37 - A student holds a laser that emits light of...Ch. 37 - A student holds a laser that emits light of...Ch. 37 - Radio waves of wavelength 125 m from a galaxy...Ch. 37 - In Figure P36.10 (not to scale), let L = 1.20 m...Ch. 37 - Coherent light rays of wavelength strike a pair...Ch. 37 - Monochromatic light of wavelength is incident on...Ch. 37 - In the double-slit arrangement of Figure P36.13, d...Ch. 37 - Youngs double-slit experiment underlies the...Ch. 37 - Two slits are separated by 0.180 mm. An...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.24PCh. 37 - In Figure P37.18, let L = 120 cm and d = 0.250 cm....Ch. 37 - Monochromatic coherent light of amplitude E0 and...Ch. 37 - The intensity on the screen at a certain point in...Ch. 37 - Green light ( = 546 nm) illuminates a pair of...Ch. 37 - Two narrow, parallel slits separated by 0.850 mm...Ch. 37 - A soap bubble (n = 1.33) floating in air has the...Ch. 37 - A thin film of oil (n = 1.25) is located on...Ch. 37 - A material having an index of refraction of 1.30...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.33PCh. 37 - A film of MgF2 (n = 1.38) having thickness 1.00 ...Ch. 37 - A beam of 580-nm light passes through two closely...Ch. 37 - An oil film (n = 1.45) floating on water is...Ch. 37 - An air wedge is formed between two glass plates...Ch. 37 - Astronomers observe the chromosphere of the Sun...Ch. 37 - When a liquid is introduced into the air space...Ch. 37 - A lens made of glass (ng = 1.52) is coated with a...Ch. 37 - Two glass plates 10.0 cm long are in contact at...Ch. 37 - Mirror M1 in Figure 36.13 is moved through a...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.43PCh. 37 - One leg of a Michelson interferometer contains an...Ch. 37 - Radio transmitter A operating at 60.0 MHz is 10.0...Ch. 37 - A room is 6.0 m long and 3.0 m wide. At the front...Ch. 37 - In an experiment similar to that of Example 36.1,...Ch. 37 - In the What If? section of Example 36.2, it was...Ch. 37 - An investigator finds a fiber at a crime scene...Ch. 37 - Raise your hand and hold it flat. Think of the...Ch. 37 - Two coherent waves, coming from sources at...Ch. 37 - In a Youngs interference experiment, the two slits...Ch. 37 - In a Youngs double-slit experiment using light of...Ch. 37 - Review. A flat piece of glass is held stationary...Ch. 37 - A certain grade of crude oil has an index of...Ch. 37 - The waves from a radio station can reach a home...Ch. 37 - Interference effects are produced at point P on a...Ch. 37 - Measurements are made of the intensity...Ch. 37 - Many cells are transparent anti colorless....Ch. 37 - Consider the double-slit arrangement shown in...Ch. 37 - Figure P36.35 shows a radio-wave transmitter and a...Ch. 37 - Figure P36.35 shows a radio-wave transmitter and a...Ch. 37 - In a Newtons-rings experiment, a plano-convex...Ch. 37 - Why is the following situation impossible? A piece...Ch. 37 - A plano-concave lens having index of refraction...Ch. 37 - A plano-convex lens has index of refraction n. The...Ch. 37 - Interference fringes are produced using Lloyds...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.68APCh. 37 - Astronomers observe a 60.0-MHz radio source both...Ch. 37 - Figure CQ37.2 shows an unbroken soap film in a...Ch. 37 - Our discussion of the techniques for determining...Ch. 37 - The condition for constructive interference by...Ch. 37 - Both sides of a uniform film that has index of...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.74CPCh. 37 - Monochromatic light of wavelength 620 nm passes...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.76CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need help with part B. I cant seem to get the correct answer. Please walk me through what youre doing to get to the answer and what that could bearrow_forwardQuestion 6: Chlorine is widely used to purify municipal water supplies and to treat swimming pool waters. Suppose that the volume of a particular sample of Cl₂ gas is 8.70 L at 895 torr and 24°C. (a) How many grams of Cl₂ are in the sample? ⚫ Atomic mass of CI = 35.453 g/mol • Molar mass of Cl₂ = 2 x 35.453 = 70.906 g/mol Solution: Use the Ideal Gas Law: Step 1: Convert Given Values • Pressure: P = 895 torr → atm PV= = nRT 1 P = 895 × = 1.1789 atm 760 • Temperature: Convert to Kelvin: T24273.15 = 297.15 K • Gas constant: R = 0.0821 L atm/mol. K Volume: V = 8.70 L Step 2: Solve for n . PV n = RT n = (1.1789)(8.70) (0.0821)(297.15) 10.25 n = = 0.420 mol 24.405 Step 3: Calculate Mass of Cl₂ Final Answer: 29.78 g of Cl₂. mass nx M mass= (0.420)(70.906) mass= 29.78 garrow_forwardE1 R₁ w 0.50 20 Ω 12 R₁₂ ww ΒΩ R₂ 60 E3 C RA w 15 Ω E2 0.25 E4 0.75 Ω 0.5 Ωarrow_forward
- What is the force (in N) on the 2.0 μC charge placed at the center of the square shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) 5.0 με 4.0 με 2.0 με + 1.0 m 1.0 m -40 με 2.0 μCarrow_forwardWhat is the force (in N) on the 5.4 µC charge shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) −3.1 µC5.4 µC9.2 µC6.4 µCarrow_forwardAn ideal gas in a sealed container starts out at a pressure of 8900 N/m2 and a volume of 5.7 m3. If the gas expands to a volume of 6.3 m3 while the pressure is held constant (still at 8900 N/m2), how much work is done by the gas? Give your answer as the number of Joules.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Spectra Interference: Crash Course Physics #40; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-ob7foUzXaY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY