
Concept explainers
(a)
To calculate: The interval at which P is moving to the left, right and is standing still.
(a)
Answer to Problem 10E
The particle is moving right in the interval
The particle is standing still in the interval
The particle is moving left in the interval
Explanation of Solution
Given Information: The movement of the particle on the number line.
Calculation:
The derivative of the movement of the particle is positive in the interval
Therefore, the particle is moving right in the interval
Horizontal line represents that the derivative of the movement of the particle is 0. That is, velocity is 0.
So, the particle is standing still in the interval
The derivative of the movement of the particle is negative in the interval
Therefore, the particle is moving left in the interval
Conclusion:
The particle is moving right in the interval
The particle is standing still in the interval
The particle is moving left in the interval
(b)
To draw: The graph for particle’s velocity and speed.
(b)
Answer to Problem 10E
The graph of the velocity and the speed of the graph is shown
Explanation of Solution
Given Information: The movement of the particle on the number line.
Calculation:
The slope of the graph shows the velocity of the particle and the slope of the particle is such that it is moving right in the interval
The graph can be sketched as follows:
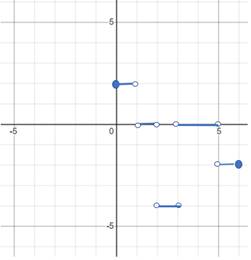
The velocity can be negative, but speed is the absolute value of the velocity and hence can never be negative.
The graph of the speed is,
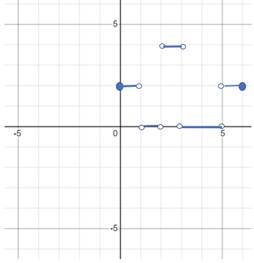
Conclusion:
The graph of the velocity and the speed of the graph is shown above.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Calculus: Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Introductory Statistics
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





