
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781259989452
Author: Hayt
Publisher: Mcgraw Hill Publishers
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.2, Problem 1P
3.1 (a) Count the number of branches and nodes in the circuit in Fig. 3.4. (b) If ix = 3 A and the 18 V source delivers 8 A of current, what is the value of RA? (Hint: You need Ohm’s law as well as KCL.)
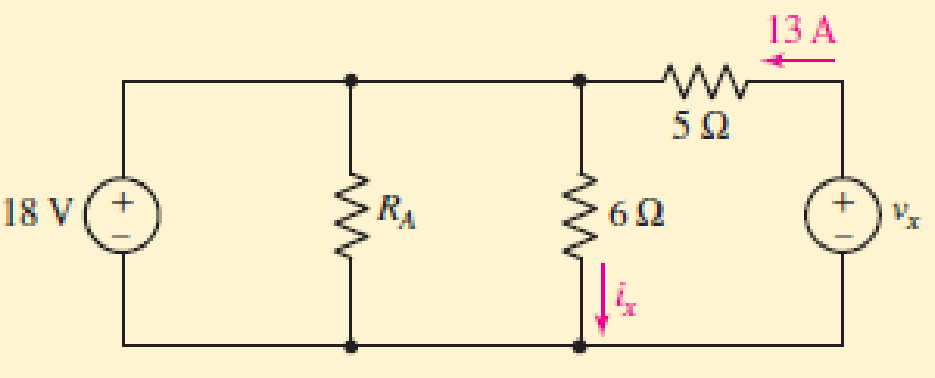
FIGURE 3.4
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please answer all questions
1. Calculate the magnitude (in RMS) of the current through R1 2. Calculate the magnitude (in RMS) of the current through R2. Simulation 1. Construct the circuit in Figure 2 in the Circuit JS simulator. Note that transformers in Circuit JS may be unstable. It is suggested to draw them by clicking from the bottom left corner to the top right corner and refresh your simulation before taking a measurement. 2. Perform a simulation, displaying the voltage across the voltage source, the current through R1, and the current through R2 in a “stacked” scope. Display the RMS average for each trace. Include a screenshot.
Analysis 1. Compare the simulation results for the currents through R1 and R2. What is the percentage difference between the calculated and simulated value for each? Comment on why there may be a discrepancy.
Please answer all
You and your crew have made it through the night and the day has brought more warmth. After searching the industrial site, you find an abundant amount of fuel to run the generators to keep you warm. You also find a memory card labelled “cure”, but your cell phone battery is dead. First things first, you will need to stay safe as the zombies continue to hunt you in your current location. The industrial site is surrounded by a metal chain-link fence. You decide you will electrify the fence to keep the zombies from scaling it. But the output voltage from the generators is not high enough to really deter them. You would like to apply around 10 kV to the fence (AC or DC, at that voltage it doesn’t really matter). You find a transformer that you can use but it only has a turn ratio of 10. You find some diodes and capacitors and construct the circuit shown in Figure 3 with the intention of hooking Vout to the fence.
1. Perform a circuit JS simulation, displaying…
2. A three-phase transformer connection Yy, 2000 kVA, 20000/6000 V has the relative short-circuit voltages Ecc = 7% and ERcc = 1.7%.It is known that when empty this transformer consumes a power Po = 12.24 kW.
Calculate:a. Parameters Zcc, Rcc, Xcc, referring to the primary and EXcc.b. If the transformer is connected at rated voltage and feeds a load of 1800 kVA, fp = 0.8, calculate the line voltage at the secondary.c. The maximum apparent power, and the maximum efficiency fp = 0.8 inductive.
Perform the exercise by the collaborators and without using artificial intelligence please
Chapter 3 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
Ch. 3.2 - 3.1 (a) Count the number of branches and nodes in...Ch. 3.3 - Determine ix and vx in the circuit of Fig. 3.7....Ch. 3.3 - For the circuit of Fig. 3.9, if vR1=1V, determine...Ch. 3.3 - Determine vx in the circuit of Fig. 3.11.Ch. 3.4 - In the circuit of Fig. 3.12b, vs1 = 120 V, vs2 =...Ch. 3.4 - 3.6 In the circuit of Fig. 3.14, find the power...Ch. 3.5 - Determine v in the circuit of Fig. 3.16.Ch. 3.5 - For the single-node-pair circuit of Fig. 3.18,...Ch. 3.6 - Determine the current i in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 3.6 - Determine the voltage v in the circuit of Fig....
Ch. 3.6 - Determine whether the circuit of Fig. 3.25...Ch. 3.7 - 3.12 Determine a single-value equivalent...Ch. 3.7 - 3.13 Determine i in the circuit of Fig. 3.29....Ch. 3.7 - Determine v in the circuit of Fig. 3.31 by first...Ch. 3.7 - 3.15 For the circuit of Fig. 3.33, calculate the...Ch. 3.8 - 3.16 Use voltage division to determine vx in the...Ch. 3.8 - In the circuit of Fig. 3.40, use resistance...Ch. 3 - Referring to the circuit depicted in Fig. 3.45,...Ch. 3 - Referring to the circuit depicted in Fig. 3.46,...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of Fig. 3.47: (a) Count the number...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of Fig. 3.47: (a) Count the number...Ch. 3 - Refer to the circuit of Fig. 3.48, and answer the...Ch. 3 - A local restaurant has a neon sign constructed...Ch. 3 - Referring to the single-node diagram of Fig. 3.50,...Ch. 3 - Determine the current labeled I in each of the...Ch. 3 - In the circuit shown in Fig. 3.52, the resistor...Ch. 3 - The circuit of Fig. 3.53 represents a system...Ch. 3 - In the circuit depicted in Fig. 3.54, ix is...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of Fig. 3.55 (which employs a...Ch. 3 - Determine the current labeled I3 in the circuit of...Ch. 3 - Study the circuit depicted in Fig. 3.57, and...Ch. 3 - Prob. 15ECh. 3 - For the circuit of Fig. 3.58: (a) Determine the...Ch. 3 - For each of the circuits in Fig. 3.59, determine...Ch. 3 - Use KVL to obtain a numerical value for the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 19ECh. 3 - In the circuit of Fig. 3.55, calculate the voltage...Ch. 3 - Determine the value of vx as labeled in the...Ch. 3 - Consider the simple circuit shown in Fig. 3.63....Ch. 3 - (a) Determine a numerical value for each current...Ch. 3 - The circuit shown in Fig. 3.65 includes a device...Ch. 3 - The circuit of Fig. 3.12b is constructed with the...Ch. 3 - Obtain a numerical value for the power absorbed by...Ch. 3 - Compute the power absorbed by each element of the...Ch. 3 - Compute the power absorbed by each element in the...Ch. 3 - Kirchhoffs laws apply whether or not Ohms law...Ch. 3 - Referring to the circuit of Fig. 3.70, (a)...Ch. 3 - Determine a value for the voltage v as labeled in...Ch. 3 - Referring to the circuit depicted in Fig. 3.72,...Ch. 3 - Determine the voltage v as labeled in Fig. 3.73,...Ch. 3 - Although drawn so that it may not appear obvious...Ch. 3 - Determine the numerical value for veq in Fig....Ch. 3 - Determine the numerical value for ieq in Fig....Ch. 3 - For the circuit presented in Fig. 3.76. determine...Ch. 3 - Determine the value of v1 required to obtain a...Ch. 3 - (a) For the circuit of Fig. 3.78, determine the...Ch. 3 - What value of IS in the circuit of Fig. 3.79 will...Ch. 3 - (a) Determine the values for IX and VY in the...Ch. 3 - Determine the equivalent resistance of each of the...Ch. 3 - For each network depicted in Fig. 3.82, determine...Ch. 3 - (a) Simplify the circuit of Fig. 3.83 as much as...Ch. 3 - (a) Simplify the circuit of Fig. 3.84, using...Ch. 3 - Making appropriate use of resistor combination...Ch. 3 - Calculate the voltage labeled vx in the circuit of...Ch. 3 - Determine the power absorbed by the 15 resistor...Ch. 3 - Calculate the equivalent resistance Req of the...Ch. 3 - Show how to combine four 100 resistors to obtain...Ch. 3 - Prob. 51ECh. 3 - Prob. 52ECh. 3 - Prob. 53ECh. 3 - Prob. 54ECh. 3 - Prob. 55ECh. 3 - Prob. 56ECh. 3 - Prob. 57ECh. 3 - Prob. 58ECh. 3 - Prob. 59ECh. 3 - Prob. 60ECh. 3 - With regard to the circuit shown in Fig. 3.98,...Ch. 3 - Delete the leftmost 10 resistor in the circuit of...Ch. 3 - Consider the seven-element circuit depicted in...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
1.2 Explain the difference between geodetic and plane
surveys,
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Comprehension Check 7-14
The power absorbed by a resistor can be given by P = I2R, where P is power in units of...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
CONCEPT QUESTIONS
15.CQ3 The ball rolls without slipping on the fixed surface as shown. What is the direction ...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. A three-phase transformer with Yd connection, 300 kVA, 12000/220 V, has been short-circuit tested on the high voltage side giving the following results: 750 V, 14.434 A, 10838 W.When the transformer is connected to nominal voltage without load it consumes 5400W. Calculate:to. Relative voltages of short circuit high voltage side: εcc, εRcc and εXcc.b. The voltage in the secondary when the transformer is connected to nominal voltage and feeds a load of 200 kW fp = 0.8 in delay.c. Apparent power of maximum efficiency and maximum efficiency with fp = 0.95 inductive. Please solve for one of the collaborators and without using artificial intelligencearrow_forwardFind value of load resistance RL that can be connected to terminals a-b for maximum power transfer. Also calculate the maximum power that can be delivered to load RL.arrow_forwardA modulating signal f(t) is bandlimited to 5 kHz is sampled at a rate of 15000 samples/sec. The samples are quantized into 128 levels. Calculate the transmission bandwidth if the following modulation types are used for signal transmission: 4- ASK 5- 8-PSK 6- FSK with Af = 25 kHzarrow_forward
- Draw the Split-Phase Manchester code for the follow ng binary data: (1001010110)arrow_forward11.54 For the network in Fig. 11.73, find the complex power absorbed by each element. 120/-20° V Figure 11.73 For Prob. 11.54. | + -1302 j5Q 4 Ωarrow_forwardFind a value of RL that can be connected to terminals a-b for maximum power transfer. Then, calculate maximum power that can be delivered to load RL.arrow_forward
- A modulating signal f(t) is bandlimited to 5 kHz is sampled at a rate of 15000 samples/sec. The samples are quantized into 128 levels. Calculate the transmission bandwidth if the following modulation types are used for signal transmission: 4- ASK 5- 8-PSK 6- FSK with Af = 25 kHzarrow_forwardA modulating signal f(t) is bandlimited to 5 kHz is sampled at a rate of 15000 samples/sec. The samples are quantized into 128 levels. Calculate the transmission bandwidth if the following modulation types are used for signal transmission: 4- ASK 5- 8-PSK 6- FSK with Af = 25 kHzarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- jan G(f) f Sketch the spectrum of g(t), which has a maximum frequency of 5 kHz, if it is sampled at the following sampling frequencies: 7 kHz, 10 kHz and 15 kHz. Indicate if and how the signal can be recovered at each sampling frequency.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer i will report your answerarrow_forwardA single tone is modulated using FM transmitter. The SNR, at the input of the demodulator 20 dB. If the maximum frequency of the modulating signal is 4 kHz, and the maximum equency deviation is 12 kHz, find the SNR, and the bandwidth (using Carson rule) at the ollowing conditions: . For the given values of fm and Af. !. If the amplitude of the modulating signal is increased by 80%. 3. If the amplitude of the modulating signal is decreased by 50%, and frequency of modulating signal is increased by 50%.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Thevenin's Theorem; Author: Neso Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=veAFVTIpKyM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY