
At t = 0, the open switch in Figure P31.46 is thrown closed. We wish to find a symbolic expression for the current in the inductor for time t > 0. Let this current be called i and choose it to be downward in the inductor in Figure P31.46. Identify i1 as the current to the right through R1 and i2 as the current downward through R2. (a) Use Kirchhoff’s junction rule to find a relation among the three currents. (b) Use Kirchhoff’s loop rule around the left loop to find another relationship. (c) Use Kirchhoff’s loop rule around the outer loop to find a third relationship. (d) Eliminate i1 and i2 among the three equations to find an equation involving only the current i. (e) Compare the equation in part (d) with Equation 31.6 in the text. Use this comparison to rewrite Equation 31.7 in the text for the situation in this problem and show that
where R′ = R1R2/(R1 + R2).
Figure P31.46
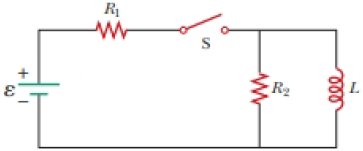
(a)
Answer to Problem 46AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The figure that shows the given circuit is shown below.
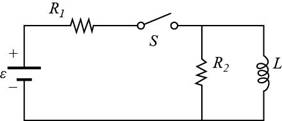
Figure (I)
According to Kirchhoff’s junction rule, the total incoming currents are equal to the total outgoing currents at a junction.
From the circuit diagram equating the incoming currents to the outgoing current,
Here,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the relation among three currents by Kirchhoff’s junction rule are
(b)
Answer to Problem 46AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The figure that shows the given circuit is shown in figure (I).
According to Kirchhoff’s loop rule, the sum of all the voltage across all the elements in a loop must be zero.
From the circuit diagram equating the voltage across the elements in the left loop is equal to zero.
Here,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the relationship between the given variables around the left loop by Kirchhoff’s loop rule is
(c)
Answer to Problem 46AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The figure that shows the given circuit is shown in figure (I).
According to Kirchhoff’s loop rule, the sum of all the voltage across all the elements in a loop must be zero.
From the circuit diagram equating the voltage across the elements in the outer loop is equal to zero.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the relationship between the given variables around the outer loop by Kirchhoff’s loop rule is
(d)
Answer to Problem 46AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The figure that shows the given circuit is shown in figure (I).
From equation (1), the expression for the
Substitute
From equation (2), the expression for the
Substitute
Equate equation (3) and equation (4) for
Further solve the above equation,
Assume
Substitute
Thus, the require equation in term of current
Conclusion:
Therefore, the equation that involve only current
(e)
Answer to Problem 46AP
Explanation of Solution
From the textbook the equation
From the part (d), the equation is given as,
Since both the equation shown above are same therefore their solution are also same.
The solution of the equation
Similarly rewrite the equation
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the equation
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 31 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
- Which of the following laws is true regarding tensile strength? • tensile strength T ①Fbreak = Wtfest Piece thickness rate (mm) ②T = test piece width rabe (mm) Fbreak break watarrow_forwardThe position of a squirrel running in a park is given by = [(0.280 m/s)t + (0.0360 m/s²)t²] + (0.0190 m/s³)ť³ĵj. What is v₂(t), the x-component of the velocity of the squirrel, as a function of time?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- You hold a spherical salad bowl 85 cm in front of your face with the bottom of the bowl facing you. The salad bowl is made of polished metal with a 40 cm radius of curvature. Where is the image of your 2.0 cm tall nose located? What is image's size, orientation, and nature. I keep getting the answer -26.2, but it keeps saying it is wrong. I just want to know what i'm doing wrong.arrow_forwardA converging lens with a focal length of 6.70 cm forms an image of a 4.60 mm tall real object that is to the left of the lens. The image is 1.50 cm tall and erect. Where are the object and image located? Is the image real or virtual? Please show all stepsarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- need help part earrow_forwardCritical damping is the case where the mass never actually crosses over equilibrium position, but reaches equilibrium as fast as possible. Experiment with changing c to find the critical damping constant. Use the same initial conditions as in the last problem. Zoom in a bit to make sure you don't allow any oscillations to take place - even small ones.arrow_forwardNASA's KC-135 Reduced Gravity Research aircraft, affectionately known as the "Vomit Comet," is used in training astronauts and testing equipment for microgravity environments. During a typical mission, the aircraft makes approximately 30 to 40 parabolic arcs. During each arc, the aircraft and objects inside it are in free-fall, and passengers float freely in apparent "weightlessness." The figure below shows the altitude of the aircraft during a typical mission. It climbs from 24,000 ft to 30,850 ft, where it begins a parabolic arc with a velocity of 155 m/s at 45.0° nose-high and exits with velocity 155 m/s at 45.0° nose-low. 31 000 45° nose high 45° nose low 24 000 Zero g 65 Maneuver time (s) (a) What is the aircraft's speed (in m/s) at the top of the parabolic arc? 110.0 m/s (b) What is the aircraft's altitude (in ft) at the top of the parabolic arc? 2.04e+04 What is the initial height at the start of the parabolic arc? What is the initial velocity at this point? What is the final…arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





