
Concept explainers
Although styrene undergoes both cationic and anionic
a. 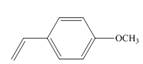 c.
c. 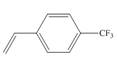
b. 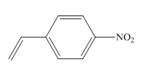 d.
d. 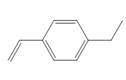
(a)
Interpretation: The method, anionic or cationic polymerization preferred with the given substituted styrene is to be identified, and an explanation corresponding to it is to be stated.
Concept introduction: An alkene
Answer to Problem 31.44P
The given substituted styrene prefers to undergo cationic polymerization, due to presence of electron releasing group on benzene ring.
Explanation of Solution
The given substituted styrene resembles to
An alkene
An electron releasing group releases electron density towards benzene ring and stabilizes carbocation formed during the cationic polymerization, whereas an electron withdrawing group withdraws electron density towards itself and stabilizes carbanion formed during the anionic polymerization.
Since the given substituted styrene involves bonding of an electron releasing group to benzene ring, it prefers to undergo cationic polymerization.
(b)
Interpretation:The method, anionic or cationic polymerization preferred with the given substituted styrene is to be identified, and an explanation corresponding to it is to be stated.
Concept introduction: An alkene
Answer to Problem 31.44P
The given substituted styrene prefers to undergo anionic polymerization, due to presence of electron withdrawing group on benzene ring.
Explanation of Solution
The given substituted styrene resembles to
An alkene
An electron releasing group releases electron density towards benzene ring and stabilizes carbocation formed during the cationic polymerization, whereas an electron withdrawing group withdraws electron density towards itself and stabilizes carbanion formed during the anionic polymerization.
Since the given substituted styrene involves bonding of an electron withdrawing group to benzene ring, it prefers to undergo anionic polymerization.
(c)
Interpretation:The method, anionic or cationic polymerization preferred with the given substituted styrene is to be identified, and an explanation corresponding to it is to be stated.
Concept introduction: An alkene
Answer to Problem 31.44P
The given substituted styrene prefers to undergo anionic polymerization, due to presence of electron withdrawing group on benzene ring.
Explanation of Solution
The given substituted styrene resembles to
An alkene
An electron releasing group releases electron density towards benzene ring and stabilizes carbocation formed during the cationic polymerization, whereas an electron withdrawing group withdraws electron density towards itself and stabilizes carbanion formed during the anionic polymerization.
Since the given substituted styrene involves bonding of an electron withdrawing group to benzene ring, it prefers to undergo anionic polymerization.
(d)
Interpretation:The method, anionic or cationic polymerization preferred with the given substituted styrene is to be identified, and an explanation corresponding to it is to be stated.
Concept introduction: An alkene
Answer to Problem 31.44P
The given substituted styrene prefers to undergo cationic polymerization, due to presence of electron releasing group on benzene ring.
Explanation of Solution
The given substituted styrene resembles to
An alkene
An electron releasing group releases electron density towards benzene ring and stabilizes carbocation formed during the cationic polymerization, whereas an electron withdrawing group withdraws electron density towards itself and stabilizes carbanion formed during the anionic polymerization.
Since the given substituted styrene involves bonding of an electron releasing group to benzene ring, it prefers to undergo cationic polymerization.
(a) The given substituted styrene prefers to undergo cationic polymerization, due to presence of an electron releasing group on benzene ring.
(b) The given substituted styrene prefers to undergo anionic polymerization, due to presence of an electron withdrawing group on benzene ring.
(c) The given substituted styrene prefers to undergo anionic polymerization, due to presence of an electron withdrawing group on benzene ring.
(d) The given substituted styrene prefers to undergo cationic polymerization, due to presence of an electron releasing group on benzene ring.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 31 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- helparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forward
- pressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward
- 6.arrow_forward0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning  Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning




