
(a)
Interpretation: An explanation for the differences observed in the
Concept introduction: The glass transition temperature and the melt transition temperature are often used to characterize the behavior of a polymer on heating. They are denoted by
Answer to Problem 31.38P
The given
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of polymers is,
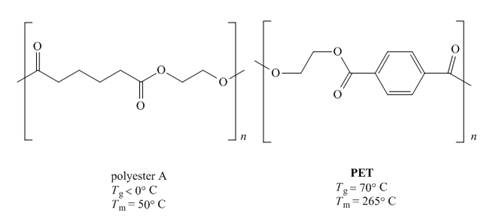
Figure 1
The above polymer chains have both crystalline regions and amorphous regions. The ordered crystalline regions are called crystallites. Crystallites are the sections where polymer chain is bind together by intermolecular interactions. On the contrary amorphous regions are sections where polymer chains are randomly arranged. These sections are held together by weak intermolecular interactions.
A polymer containing high crystallites area possesses high
The given
The given
(b)
Interpretation: An explanation for the differences observed in the
Concept introduction: The glass transition temperature and the melt transition temperature are often used to characterize the behavior of a polymer on heating. They are denoted by
Answer to Problem 31.38P
The given
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of polymers is,
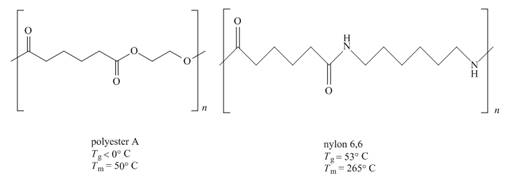
Figure 2
The above polymer chains have both crystalline regions and amorphous regions. The ordered crystalline regions are called crystallites. Crystallites are the sections where polymer chain is bind together by intermolecular interactions. On the contrary amorphous regions are sections where polymer chains are randomly arranged. These sections are held together by weak intermolecular interactions.
A polymer containing high crystallites area possesses high
The given
The given
(c)
Interpretation: The comparison between the
Concept introduction: The glass transition temperature and the melt transition temperature are often used to characterize the behavior of a polymer on heating. They are denoted by
Answer to Problem 31.38P
The
Explanation of Solution
Kevlar is a polyamide, synthesized by
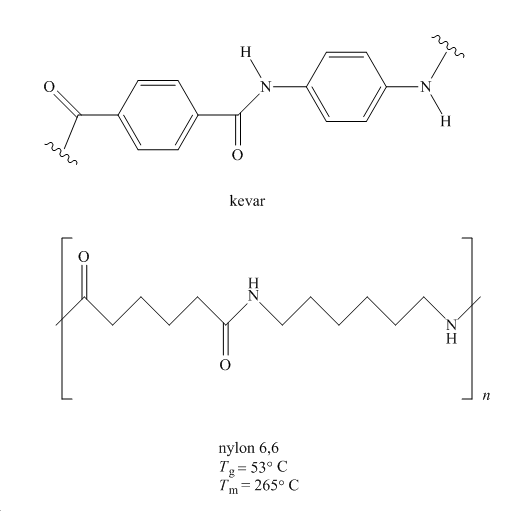
Figure 3
Since more ordered polymers have more
The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 31 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole


