
Concept explainers
Magnesium ribbon reacts with acid to produce hydro- gen gas and magnesium ions. Different masses of magnesium ribbon are added to 10 mL of the acid. The volume of the hydrogen gas obtained is a measure of the number of moles of hydrogen produced by the reaction. Various measurements are given in the table below.
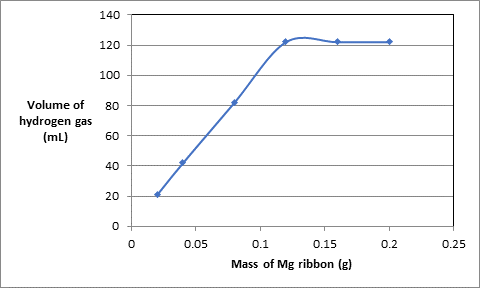
(a) Draw a graph of the results by plotting the mass of Mg versus the volume of the hydrogen gas.
(b) What is the limiting reactant in experiment 1?
(c) What is the limiting reactant in experiment 3?
(d) What is the limiting reactant in experiment 6?
(e) Which experiment uses stoichiometric amounts of each reactant?
(f) What volume of gas would be obtained if 0.300 g of Mg ribbon were used? If 0.010 g were used?
(a)
Interpretation:.
The graph between mass of Mg versus the volume of hydrogen gas should be plotted..
Concept introduction:.
The number of moles of a substance is related to mass and molar mass as follows:.
Here,mis mass andMis molar mass of the substance..
The density of solution can be calculated as follow:.
Here, m is mass and V is volume.
Answer to Problem 74QAP

Explanation of Solution
The data of mass of Mg ribbon in grams and volume of hydrogen gas produced in experiments is as follows:.
| Experiment | Mass of Mg ribbon (g) | Volume of acid used (mL) | Volume of hydrogen gas (mL) |
| 1 | 0.020 | 10.0 | 21 |
| 2 | 0.040 | 10.0 | 42 |
| 3 | 0.080 | 10.0 | 82 |
| 4 | 0.120 | 10.0 | 122 |
| 5 | 0.160 | 10.0 | 122 |
| 6 | 0.200 | 10.0 | 122 |
To plot put the data of mass of Mg ribbon on x-axis and volume of hydrogen gas at y-axis:.
(b)
Interpretation:
The limiting reactant in experiment 1 should be determined..
Concept introduction:.
The number of moles of a substance is related to mass and molar mass as follows:.
Here,mis mass andMis molar mass of the substance..
The density of solution can be calculated as follow:.
Here, m is mass and V is volume.
Answer to Problem 74QAP
Mg is limiting reactant.
Explanation of Solution
The balanced chemical reaction will be as follows:.
According to experiment 1, mass of Mg ribbon is 0.020 g, volume of acid used is 10.0 mL and volume of
The density of
Putting the values,
Molar mass of
From the balanced chemical reaction, 1 mol of hydrogen gas is produced from 1 mol of Mg thus, number of moles of Mg required to produce
The mass of Mg is 0.020 g and molar mass of Mg is 24.305 g/mol thus, number of moles of Mg will be:.
Since, number of moles of Mg required is
(c)
Interpretation:
The limiting reactant in experiment 3 should be determined..
Concept introduction:.
The number of moles of a substance is related to mass and molar mass as follows:.
Here,mis mass andMis molar mass of the substance..
The density of solution can be calculated as follow:.
Here, m is mass and V is volume.
Answer to Problem 74QAP
Mg is limiting reactant.
Explanation of Solution
The balanced chemical reaction will be as follows:.
According to experiment 3, mass of Mg ribbon is 0.080 g, volume of acid used is 10.0 mL and volume of
The density of
Putting the values,
Molar mass of
From the balanced chemical reaction, 1 mol of hydrogen gas is produced from 1 mol of Mg thus, number of moles of Mg required to produce
The mass of Mg is 0.080 g and molar mass of Mg is 24.305 g/mol thus, number of moles of Mg will be:.
Since, number of moles of Mg required is
(d)
Interpretation:
The limiting reactant in experiment 6 should be determined..
Concept introduction:.
The number of moles of a substance is related to mass and molar mass as follows:.
Here,mis mass andMis molar mass of the substance..
The density of solution can be calculated as follow:.
Here, m is mass and V is volume.
Answer to Problem 74QAP
Acid is limiting reactant.
Explanation of Solution
The balanced chemical reaction will be as follows:.
According to experiment 6, mass of Mg ribbon is 0.200 g, volume of acid used is 10.0 mL and volume of
The density of
Putting the values,
Molar mass of
From the balanced chemical reaction, 1 mol of hydrogen gas is produced from 1 mol of Mg thus, number of moles of Mg required to produce
The mass of Mg is 0.200 g and molar mass of Mg is 24.305 g/mol thus, number of moles of Mg will be:.
Since, number of moles of Mg required is
(e)
Interpretation:
The experiment that uses stoichiometric amounts of each reactant should be determined..
Concept introduction:.
The number of moles of a substance is related to mass and molar mass as follows:.
Here,mis mass andMis molar mass of the substance..
The density of solution can be calculated as follow:.
Here, m is mass and V is volume.
Answer to Problem 74QAP
Experiment 4.
Explanation of Solution
According to balance chemical reaction, 1 mol of Mg gives 1 mol of hydrogen gas thus, the experiment in which same number of moles of Mg reacts with acid to form hydrogen gas that experiment uses stoichiometric amounts of each reactant..
This cannot be experiment 1, 3 and 6 because ratio of number of moles of Mg and hydrogen gas is not 1:1 in these experiments..
Check experiment 2: mass of Mg is 0.040 g and molar mass of Mg is 24.305 g/mol thus, number of mol of Mg will be:
The volume of
The density of
Putting the values,
Molar mass of
The number of moles of Mg and hydrogen gas is not same thus, it is not experiment 2..
Check experiment 4: mass of Mg is 0.120 g and molar mass of Mg is 24.305 g/mol thus, number of mol of Mg will be:
The volume of
The density of
Putting the values,
Molar mass of
The number of moles of Mg and hydrogen gas is approximately same thus, it is experiment 4..
Check experiment 5: mass of Mg is 0.160 g and molar mass of Mg is 24.305 g/mol thus, number of mol of Mg will be:
The volume of
The density of
Putting the values,
Molar mass of
The number of moles of Mg and hydrogen gas is not same thus, it is not experiment 4..
Therefore, experiment 4 uses stoichiometric amounts of each reactant.
(f)
Interpretation:
The volume of the gas for 0.300 g and 0.010 g of Mg ribbon should be calculated.
Concept introduction:.
The number of moles of a substance is related to mass and molar mass as follows:.
Here,mis mass andMis molar mass of the substance..
The density of solution can be calculated as follow:.
Here, m is mass and V is volume.
Answer to Problem 74QAP
The volume of hydrogen gas produced from 0.120 g of Mg and 0.010 g of Mg is 122 mL and 11.32 mL respectively.
Explanation of Solution
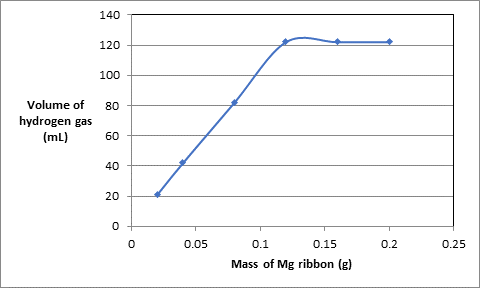
The graph between mass of Mg ribbon and volume of hydrogen gas is as follows:.

According to the graph, above the mass of Mg 0.120 g, the volume of hydrogen gas becomes constant at 122 mL thus, the volume of hydrogen gas produced if 0.120 g of Mg is burned will be 122 mL.
Considering only the straight line in the graph,.
| Experiment | Mass of Mg ribbon (g) | Volume of acid used (mL) | Volume of hydrogen gas (mL) |
| 1 | 0.020 | 10.0 | 21 |
| 2 | 0.040 | 10.0 | 42 |
| 3 | 0.080 | 10.0 | 82 |
| 4 | 0.120 | 10.0 | 122 |
The plot will be as follows:.

Comparing this with equation of straight line
For the mass of ribbon 0.010 g, the volume of hydrogen gas can be calculated as follows:.
Therefore, the volume of hydrogen gas is 11.32 mL.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
- Please predict the products for each of the following reactions. Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry (syn- vs anti- or both). If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please draw all the enantiomers. cold KMnO4, NaOH 2. DMS 1. 03 CH3OH Br2 1. 03 2. (CH3)2S H₂ Pd or Pt (catalyst) HBr 18 19 20 1 HBr ROOR (peroxide) H₂O H₂SO4 HCI HI 17 16 6 15 MCPBA 1. BH3 THF 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. OsO4 2. H₂O₂ 110 CH3CO₂H (peroxyacid) 1. MCPBA 2. H₂O* Br2 H₂O BH3 THF B12 EtOH Pd or Ni (catalyst) D₂ (deuterium) Bra A B C D H OH H OH OH H OH α α α OH H OH OH фон d H "Harrow_forwardBriefly indicate the models that describe the structure of the interface: Helmholtz-Perrin, Gouy-Chapman, Stern and Grahame models.arrow_forwardElectrochemistry. Briefly describe the Gibbs model and the Gibbs absorption equation.arrow_forward
- Briefly state the electrocapillary equation for ideally polarized electrodes.arrow_forwardWhat is surface excess according to the Gibbs model?arrow_forwardUsing Benzene as starting materid show how each of the Following molecules Contel Ve syntheswed CHI 9. b -50311 с CHY 503H Ночто d. อ •NOV e 11-0-650 NO2arrow_forward
- The molecule PYRIDINE, 6th electrons and is therefore aromatre and is Assigned the Following structure contering Since aromatk moleculoy undergo electrophilic anomatic substitution, Pyridine shodd undergo The Following reaction + HNO3 12504 a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products that could Result From this reaction 18. Bared upon the reaction mechanison determime which of these producty would be the major Product of the hegetionarrow_forwarda. Explain Why electron withdrawing groups tend to be meta-Directors. Your answer Should lyclude all apropriate. Resonance contributing Structures fo. Explain why -ll is an outho -tura drccton even though chlorine has a very High Electronegativityarrow_forward9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Vanctions +H₂504 4.50+ T C. +212 Fellz 237 b. Praw the potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Rauctions and account For any differences that appear in the two potential Puergy Diagrams which of here two reactions 19 Found to be Reversable, Rationalice your answer based upon the venation mechanisms and the potential energy diagrams.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





