
A water trough of semicircular cross section of radius 0.6 m consists of two symmetric parts hinged to each other at the bottom, as shown in Fig. P3-72. The two pans are held together by a cable and turnbuckle placed every 3 m along the length of the trough. Calculate the tension in each cable when the trough is filled to the rim.
The tension in the cable.
Answer to Problem 72P
The tension in the cable is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A water trough of semicircular cross section of two symmetric parts hinged at each other at the bottom and held together by a cable.
The figure below shows the free body diagram of the right-hand side part of water trough.
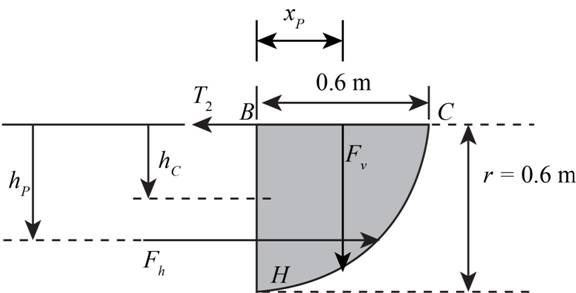
Figure-(1)
Write the Equation for the horizontal hydrostatic force on the part.
Here, density of fluid is
Write the Equation for vertical projected area.
Here, radius of the quarter circle is
Substitute
Write the Equation of the vertical force for curved surface.
Here volume of fluid above curved surface is
Write the Expression for volume of fluid above curved surface.
Substitute
Write the Expression for centre of pressure.
Write the Expression for moment of Inertia.
Substitute
Write the moment Equation about the hinge point.
Here, distance between the line of action of vertical force and hinged point is
Write the Expression for distance between the line of action of vertical force and hinged point.
Substitute
The figure below shows the free body diagram of water trough.
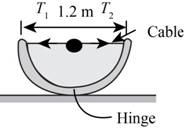
Figure-(2)
Write the expression for horizontal force equilibrium.
Figure-(2)
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute,
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Here the tension value is same
Conclusion:
The tension in the cable is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
FLUID MECHANICS FUNDAMENTALS+APPS
- The airplane weighs 144100 lbs and flies at constant speed and trajectory given by 0 on the figure. The plane experiences a drag force of 73620 lbs. 0 a.) If 11.3°, determine the thrust and lift forces = required to maintain this speed and trajectory. b.) Next consider the case where is unknown, but it is known that the lift force is equal to 7.8 times the quantity (Fthrust Fdrag). Compute the resulting trajectory angle and the lift force in this case. Use the same values for the weight and drag forces as you used for part a. 20. YAAY' Farag Ө Fthrust CC + BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom Flift Fweight The lift force acts in the y' direction. The weight acts in the negative y direction. The thrust and drag forces act in the positive and negative x' directions respectively. Part (a) The thrust force is equal to 101,855 ☑ lbs. The lift force is equal to 141,282 ☑ lbs. Part (b) The trajectory angle 0 is equal to 7.31 ✓ deg. The lift force is equal to 143,005 ☑ lbs.arrow_forwardsimply supported beam has a concentrated moment M, applied at the left support and a concentrated force F applied at the free end of the overhang on the right. Using superposition, determine the deflection equations in regions AB and BC.arrow_forwardwhat is heat exchanger, what are formulas, and their importance, define the diagram, and give me a script on how to explain the design of heat exchanger, and how did values end up in that number. based on standards . what is dshellarrow_forward
- FIGURE P1.37 1.38 WP As shown in Figure P1.38, an inclined manometer is used to measure the pressure of the gas within the reservoir, (a) Using data on the figure, determine the gas pressure, in lbf/in.² (b) Express the pressure as a gage or a vacuum pressure, as appropriate, in lbf/in.² (c) What advantage does an inclined manometer have over the U-tube manometer shown in Figure 1.7? Patm = 14.7 lbf/in.² L I C i Gas a Oil (p = 54.2 lb/ft³) 140° 8=32.2 ft/s² 15 in.arrow_forwardwhat is an low pressure Heater, what are formulas, and their importance, define the diagram, and give me a script on how to explain the design of an air preheater, and how did values end up in that number. based on standardsarrow_forwardwhat is an air preheater, what are formulas, and their importance, define the diagram, and give me a script on how to explain the design of an air preheater, and how did values end up in that number. based on standardsarrow_forward
- Qf, Qa,Qm, Qcon,Qfg, Qbd, Qref,Qloss ( meaning, formula, percentage, and importance of higher value na qf, qa etc)arrow_forwardThe beam is supported by a fixed support at point C and a roller at point A. It also has an internal hinge at point B. The beam supports a point load at point D, a moment at point A and a distributed load on segment BC. a. calculate the support reactions at points A and C b. calculate the internal resultant loadings (N, V, M) at points E and F, which lies in the middle between points A and D P = 4 kip Ma = 5 kip-ft w1 = 3 kip/ft and w2 = 4 kip/ft a = 3 ftarrow_forwardFrom the image of the pyramid, I want to find what s1 hat, s2 hat, and s3 hat are. I think s3 hat is just equal to e3 hat right? What about the others?arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
