
Concept explainers
Identify the more stable stereoisomer in each of the following pairs, and give the reason for your choice:

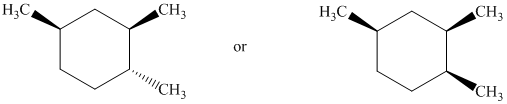
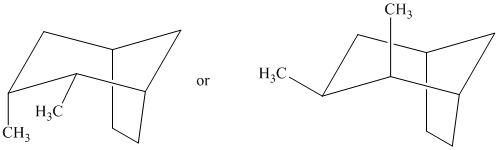
Interpretation:
The most stable stereoisomer in each of the given pairs is to be identified and the reason for it is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
The most stable conformation is the one that has the largest number of substituents in the equatorial orientation.
An axial substituent in the molecule is said to be crowded because of
Crowding causes increase in the potential energy of an isomer, which decreases its stability.
The basic chair conformation of cyclohexane is shown below:
Stereoisomers are isomers having the same constitution but differ in the arrangement of atoms in space. Cis-trans isomers are stereoisomers.
Two substituents are cis to each other if they are on the same side of the ring.
Two substituents are trans to each other if they are on the opposite side of the ring.
Answer to Problem 40P
Solution:
a)
In the cis isomer, the methyl substituent is in the axial orientation while in the trans isomer, the methyl substituent is in the equatorial orientation. The axial methyl group experiences
Thus, the trans isomer (B) is more stable than the cis isomer (A).
b)
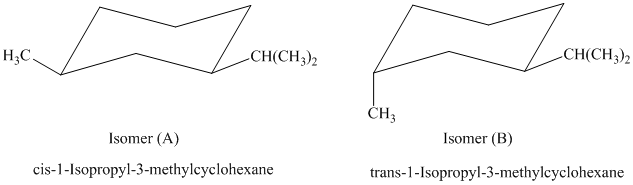
In isomer (A), the methyl substituent is in the equatorial orientation while in isomer (B), the methyl substituent is in the axial orientation. The axial methyl group in isomer (B) experiences
Thus, isomer (A) is more stable than isomer (B).
c)
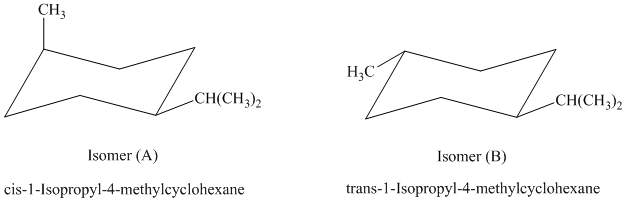
In isomer (A), the methyl substituent is in the axial orientation while in isomer (B), the methyl substituents is in the equatorial orientation. The axial methyl group in isomer (A) experiences
Thus, isomer (B) is more stable than isomer (A).
d)
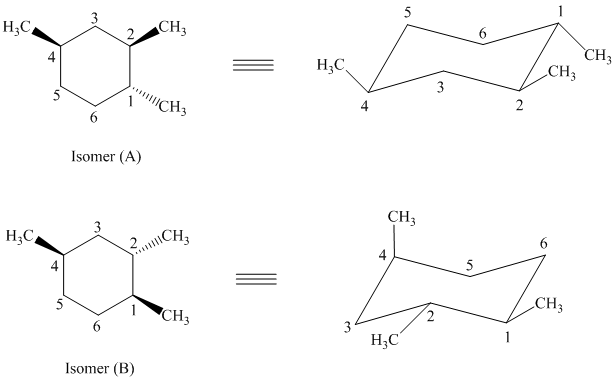
In isomer (A), all three methyl substituents are in an equatorial orientation while in isomer (B), one methyl substituent
Thus, isomer (A) is more stable than isomer (B).
e)
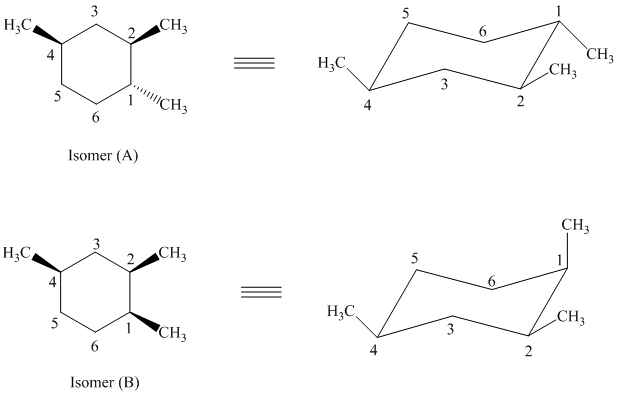
In isomer (A) all three methyl substituents are in an equatorial orientation while in isomer (B), one methyl substituent is in the axial orientation. The axial methyl group in isomer (B) experiences
Thus, isomer (A) is more stable than isomer (B).
f)
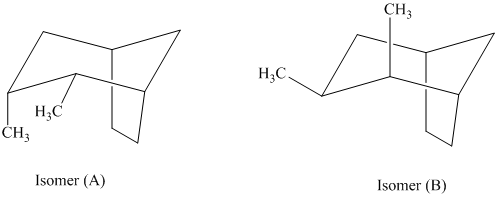
In isomer (A), the two methyl groups are on the same side as the cyclopentane ring and its hydrogen atoms. In isomer (B), the two methyl groups are on the opposite side of the cyclopentane ring and its hydrogen atoms. Isomer (A) is more crowded than isomer (B). Crowding increases the potential energy of the molecule and makes the molecule less stable.
Thus, isomer (B) is more stable than isomer (A).
Explanation of Solution
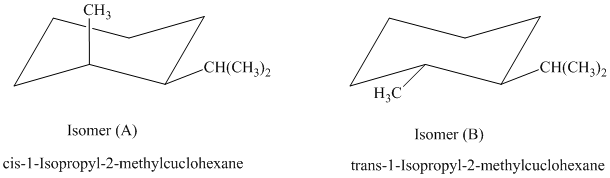
a) The given name of the compound shown below is
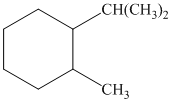
For cis and trans isomers of this compound, two substituents, an isopropyl and methyl groups at
The most stable cis and trans isomers for this compound are shown below:
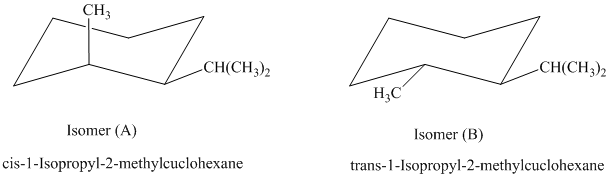
In isomer (A), the methyl substituent is in the axial orientation while in isomer (B), the methyl substituents is in the equatorial orientation. The axial methyl group experiences
Thus, isomer (B) is more stable than isomer (A).
b) The given name of the compound shown below is
For cis and trans isomers of
The most stable cis and trans isomers for this compound are shown below:
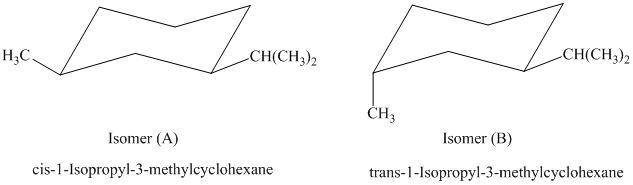
In isomer (A), the methyl substituent is in the equatorial orientation while in isomer (B), the methyl substituent is in the axial orientation. The axial methyl group in isomer (B) experiences
Thus, isomer (A) is more stable than isomer (B).
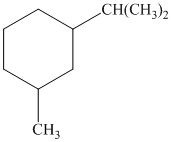
c) The given name of the compound shown below is
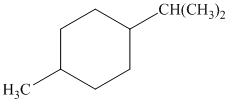
For cis and trans isomers of this compound, two substituents, an isopropyl and methyl groups at
The most stable cis and trans isomers for this compound are shown below:
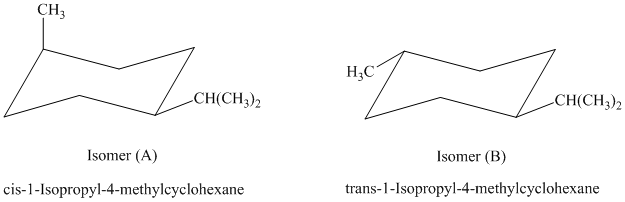
In isomer (A), the methyl substituent is in the axial orientation while in isomer (B), the methyl substituents is in the equatorial orientation. The axial methyl group in isomer (A) experiences
Thus, isomer (B) is more stable than isomer (A).
d) The given structures for two stereoisomers are as follows:
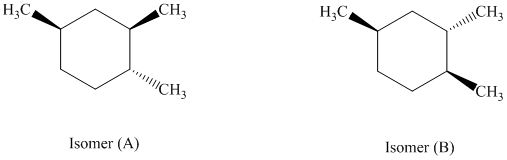
Both of the given isomers have three methyl groups attached to the cyclohexane. Their most stable conformations are shown below:
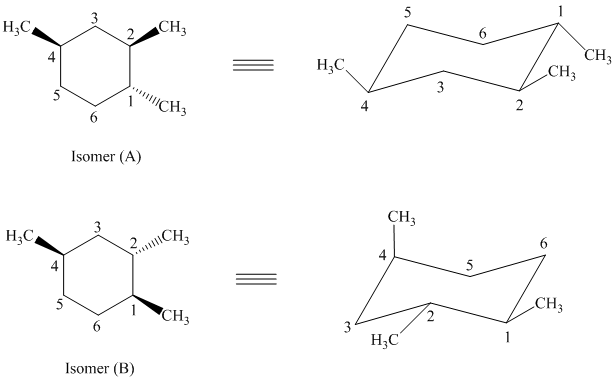
In isomer (A), all three methyl substituents are in an equatorial orientation while in isomer (B), two methyl substituenst at
Thus, isomer (A) is more stable than isomer (B).
e) The given structures for two stereoisomers are as follows:
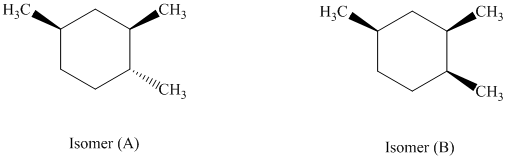
Both of the given isomers have three methyl groups attached to the cyclohexane. Their most stable conformations are shown below:
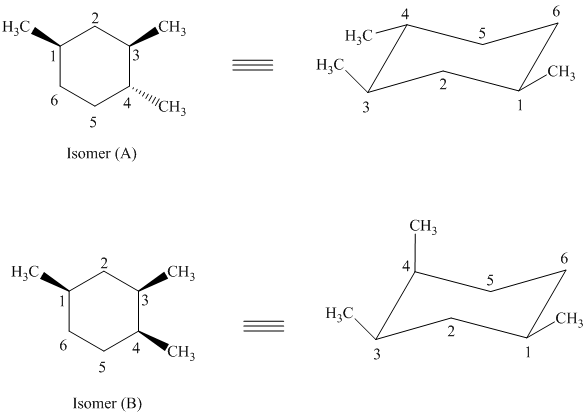
In isomer (A), all three methyl substituents are in an equatorial orientation while in isomer (B), two methyl substituents are in axial orientation. The axial methyl group in isomer (B) experiences
Thus, isomer (A) is more stable than isomer (B).
f) The given structures for two stereoisomers are as follows:
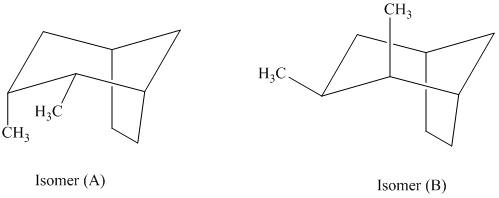
Both of the conformations represent two different cis conformations of the same compound. In isomer (A), the two methyl groups and hydrogen atoms on the cyclopentane ring are on the same side. In isomer (B), the two methyl groups and hydrogen atoms on the cyclopentane rings are on the opposite side. Isomer (A) is more crowded than isomer (B). Crowding increases potential energy of the molecule and makes the molecule less stable.
Thus, isomer (B) is more stable than isomer (A).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- helparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forward
- pressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward
- 6.arrow_forward0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning



