
(a)
Interpretation:
An explanation regarding the arrangement of the compounds in order of their decreasing
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 3.47AP
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
Figure 1
Compounds shown in Figure 1 are alcohols that mean acidic proton is bonded to oxygen.
Compound B contains two chlorine atoms which are electron-withdrawing group. Due to
Compound C contains only one chlorine atom which is an electron-withdrawing group Due to
Compound A contains one methyl group which is an electron-donating group. Due to
Therefore, the order of acidity of the compounds is shown below.
Figure 2
The
Therefore, the order of decreasing
Figure 3
The order of decreasing
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
(b)
Interpretation:
An explanation regarding the arrangement of the compounds in order of their decreasing
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 3.47AP
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
Figure 4
According to the elemental effect, the acidity increases as the
Compound A contains only chlorine atom which is an electron-withdrawing group. Due to
Compound C contains
Therefore, the order of acidity of the compounds is shown below.
Figure 5
The
Therefore, the order of decreasing
Figure 6
The order of decreasing
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
(c)
Interpretation:
An explanation regarding the arrangement of the compounds in order of their decreasing
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 3.47AP
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
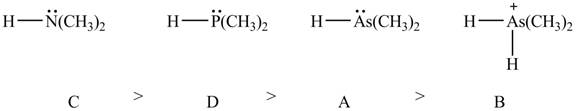
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
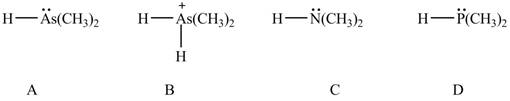
Figure 7
According to the elemental effect, the acidity increases as the atomic number attached to the acidic hydrogen also increases. The element
The atomic number of arsenic is higher than nitrogen and phosphorus. The
The atomic number of phosphorus is higher than nitrogen. The
According to the charge effect, the acidity increases with the presence of positive charge on atom attached to acidic hydrogen. Compound B contains a positive charge. Therefore, compound B is more acidic than compound A.
Therefore, the order of acidity of the compounds is shown below.
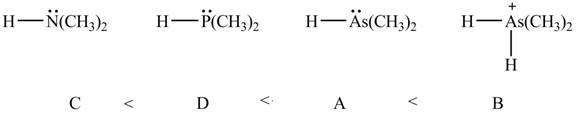
Figure 8
The
Therefore, the order of decreasing
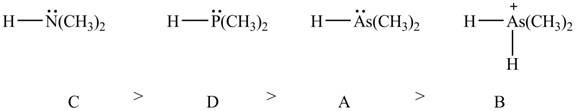
Figure 9
The order of decreasing
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
(d)
Interpretation:
An explanation regarding the arrangement of the compounds in order of their decreasing
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 3.47AP
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
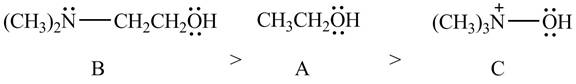
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
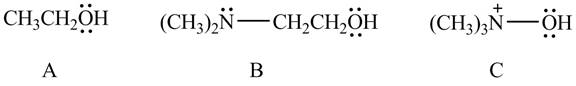
Figure 10
According to the charge effect, the acidity increases with the presence of positive charge on atom attached to acidic hydrogen. Compound C contains a positive charge. Therefore, compound C is more acidic than compound A and B.
Compound B contains only
Therefore, the order of acidity of the compounds is shown below.
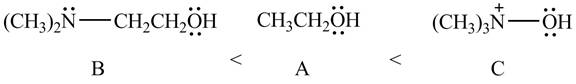
Figure 11
The
Therefore, the order of decreasing
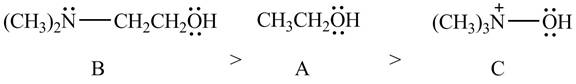
Figure 12
The order of decreasing
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Please predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forwardin the scope of ontario SCH4U grade 12 course, please show ALL workarrow_forwardIs the chemical reaction CuCl42-(green) + 4H2O <==> Cu(H2O)42+(blue) + 4Cl- exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forward
- If we react tetraethoxypropane with hydrazine, what is the product obtained (explain its formula). State the reason why the corresponding dialdehyde is not used.arrow_forwarddrawing, no aiarrow_forwardIf CH3COCH2CH(OCH3)2 (4,4-dimethoxy-2-butanone) and hydrazine react, two isomeric products are formed. State their structure and which will be the majority.arrow_forward
- + Reset Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. 4-methylhept-2-ene (Z)- (E)- 1-6-5-2-3-4- cyclo iso tert- sec- di tri hept hex oct meth eth pent ane yne ene ylarrow_forward+ Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. Reset H3C H H C CH3 CH-CH3 1-3-methylpent ene trans- cis- 5-6-3-1-2-4- tert- tri sec- di cyclo iso but pent hex meth prop eth yl ane ene yne ☑arrow_forwarddrawing, no aiarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
