
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure for the product of each of the given Lewis acid-base association reactions is to be derived by using curved-arrow notation. The formal charge on each species is to be assigned. The Lewis acid and the Lewis base is to be labeled. The atom that donates electrons in each case is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Lewis acid-base association reaction involves the transfer of a proton from a base to an acid. Lewis acid accepts an electron pair and acts as an electrophile. Lewis base donates an electron pair and acts as a nucleophile.
Answer to Problem 3.1P
The Lewis acid and Lewis base are
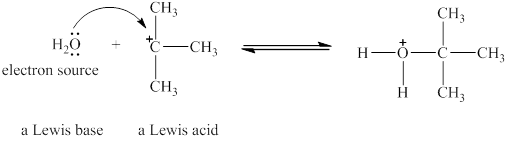
Explanation of Solution
Lewis acids are electron donor, whereas Lewis bases are electron pair accepter. In water molecule oxygen consists of a lone pair. Thus, it will act a Lewis base and oxygen atom has tendnecy to donate its electrons. The
The oxygen in
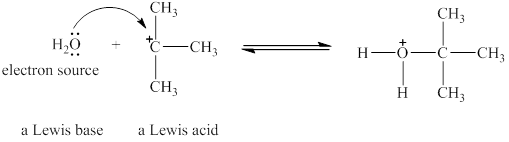
Figure 1
The Lewis acid and Lewis base are
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure for the product of each of the given Lewis acid-base association reactions is to be derived by using curved-arrow notation. The formal charge on each species is to be assigned. The Lewis acid and the Lewis base is to be labeled. The atom that donates electrons in each case is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Lewis acid-base association reaction involves the transfer of a proton from a base to an acid. Lewis acid accepts an electron pair. It acts as an electrophile Lewis base donates an electron pair. It acts as nucleophile.
Answer to Problem 3.1P
The Lewis acid and Lewis base are
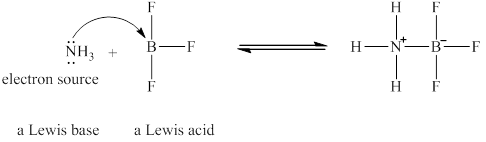
Explanation of Solution
Lewis acids are electron donor, whereas Lewis bases are electron accepter. In
The nitrogen in
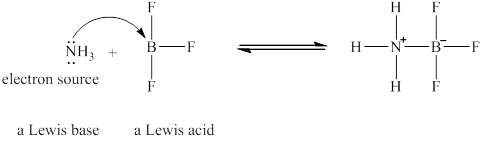
Figure 2
The Lewis acid and Lewis base are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. :0: :0 H. 0:0 :0: :6: S: :0: Select to Edit Arrows ::0 Select to Edit Arrows H :0: H :CI: Rotation Select to Edit Arrows H. < :0: :0: :0: S:arrow_forward3:48 PM Fri Apr 4 K Problem 4 of 10 Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Mg. :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: :Br: Mg :0: :0: Select to Add Arrows Mg. Br: :0: 0:0- Br -190 H 0:0 Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows neutralizing workup H CH3arrow_forwardIarrow_forward
- Draw the Markovnikov product of the hydrobromination of this alkene. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for this problem. + Explanation Check 1 X E 4 1 1 1 1 1 HBr Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 80 LE #3 @ 2 $4 0 I அ2 % 85 F * K M ? BH 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center & 6 27 FG F10 8 9 R T Y U D F G H P J K L Z X C V B N M Q W A S H option command H command optiarrow_forwardBe sure to use wedge and dash bonds to show the stereochemistry of the products when it's important, for example to distinguish between two different major products. Predict the major products of the following reaction. Explanation Q F1 A Check F2 @ 2 # 3 + X 80 F3 W E S D $ 4 I O H. H₂ 2 R Pt % 05 LL ee F6 F5 T <6 G Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 27 & A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Acce Y U H DII 8 9 F10 4 J K L Z X C V B N M T H option command F11 P H commandarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the arrows to draw the intermediate and product in this reaction or mechanistic step(s). Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H :0: CH3 O: OH Q CH3OH2+ Draw Intermediate protonation CH3OH CH3OH nucleophilic addition H Draw Intermediate deprotonation :0: H3C CH3OH2* protonation H 0: H CH3 H.arrow_forward
- Predicting the reactants or products of hemiacetal and acetal formation uentify the missing organic reactants in the following reaction: H+ X+Y OH H+ за Note: This chemical equation only focuses on the important organic molecules in the reaction. Additional inorganic or small-molecule reactants or products (like H2O) are not shown. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactants X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ? olo 18 Ar © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardcan someone please answer thisarrow_forwardPlease, please help me figure out the the moles, molarity and Ksp column. Step by step details because I've came up with about three different number and have no idea what I'm doing wrong.arrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


