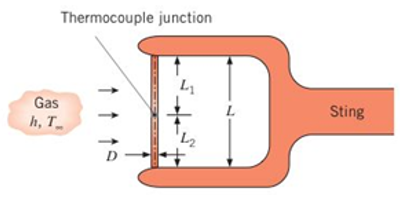
Problem 3.1P: Consider the plane wall of Figure 3.1, separating hot and cold fluids at temperatures T,1 and T,2,... Problem 3.2P: A new building to be located in a cold climate is being designed with a basement that has an... Problem 3.3P: The rear window of an automobile is defogged by passing warm air over its inner surface. If the warm... Problem 3.4P: The rear window of an automobile is defogged by attaching a thin, transparent, film-type heating... Problem 3.5P: A dormitory at a large university, built 50 years ago, has exterior walls constructed of... Problem 3.6P: In a manufacturing process, a transparent film is being bonded to a substrate as shown in the... Problem 3.7P: The walls of a refrigerator are typically constructed by sandwiching a layer of insulation between... Problem 3.8P: A t=10-mm -thick horizontal layer of water has a top surface temperature of Tc=4C and a bottom... Problem 3.9P: A technique for measuring convection heat transfer coefficients involves bonding one surface of a... Problem 3.10P: The wind chill, which is experienced on a cold, windy day, is related to increased heat transfer... Problem 3.11P: Determine the thermal conductivity of the carbon nanotube of Example 3.4 when the heating island... Problem 3.12P: A thermopane window consists of two pieces of glass 7 mm thick that enclose an air space 7 mm thick.... Problem 3.13P: A house has a composite wall of wood, fiberglass insulation. and plaster board. as indicated in the... Problem 3.14P: Consider the composite wall of Problem 3.13 under conditions for which the inside air is still... Problem 3.15P: Consider a composite wall that includes an 8-mm-thick hardwood siding, 40-rnm by 130-mm hardwood... Problem 3.16P: Work Problem 3.15 assuming surfaces parallel to the x-direction are adiabatic. Problem 3.17P: Consider the oven of Problem 1.54. The walls of the oven consist of L=30-mm -thick layers of... Problem 3.18P: The composite wall of an oven consists of three materials, two of which are of known thermal... Problem 3.19P: The wall of a drying oven is constructed by sandwiching an insulation material of thermal... Problem 3.20P: The t=4-mm-thick glass windows of an automobile have a surface area of A=2.6m2. The outside... Problem 3.21P: The thermal characteristics of a small, dormitory refrigerator are determined by performing two... Problem 3.22P: In the design of buildings, energy conservation requirements dictate that the exterior surface area,... Problem 3.23P: When raised to very high temperatures. many conventional liquid fuels dissociate into hydrogen and... Problem 3.24P: A firefighter's protective clothing, referred to as a turnout coat. is typically constructed as an... Problem 3.25P: A particular thermal system involves three objects of fixed shape with conduction resistances of... Problem 3.26P: A composite wall separates combustion gases at 2600C from a liquid coolant at 100C, with gas-and... Problem 3.27P: Approximately 106 discrete electrical components can be placed on a single integrated circuit... Problem 3.28P: Two stainless steel plates 10 mm thick are subjected to a contact pressure of I bar under vacuum... Problem 3.29P: Consider a plane composite wall that is composed of two materials of thermal conductivities... Problem 3.30P: The performance of gas turbine engines may be improved by increasing the tolerance of the turbine... Problem 3.31P: A commercial grade cubical freezer, 3 m on a side, has a composite wall consisting of an exterior... Problem 3.32P: Physicists have determined the theoretical value of the thermal conductivity of a carbon nanotube to... Problem 3.33P: Consider a power transistor encapsulated in an aluminum case that is attached at its base to a... Problem 3.34P: Ring-porous woods, such as oak, are characterized by grains. dark grains consist of very low-density... Problem 3.35P: A batt of glass fiber insulation is of density =28kg/m3. Determine the maximum and minimum possible... Problem 3.36P: Air usually constitutes up to half of the volume of commercial ice creams and takes the form of... Problem 3.37P: Determine the density, specific heat, and thermal conductivity of a lightweight aggregate concrete... Problem 3.38P: A one-dimensional plane wall of thickness L is constructed of a solid material with a linear,... Problem 3.39P: The diagram shows a conical section fabricated from pure aluminum. It is of circular cross section... Problem 3.40P: A truncated solid cone is of circular cross section, and its diameter is related to the axial... Problem 3.41P: From Figure 2.5 it is evident that, over a wide temperature range, the temperature dependence of the... Problem 3.42P: Consider a tube wall of inner and outer radii ri and ro, whose temperatures are maintained at Ti and... Problem 3.43P: Measurements show that steady-state conduction through a plane wall without heat generation produced... Problem 3.44P: A device used to measure the surface temperature of an object to within a spatial resolution of... Problem 3.45P: A steam pipe of 0.12-m outside diameter is insulated with a layer of calcium silicate. If the... Problem 3.46P: Consider the water heater described in Problem 1.48. We now wish to determine the energy needed to... Problem 3.47P: To maximize production and minimize pumping costs. crude oil is heated to reduce its viscosity... Problem 3.48P: A thin electrical heater is wrapped around the outer surface of a long cylindrical tube whose inner... Problem 3.50P: A stainless steel (AISI 304) tube used to transport a chilled pharmaceutical has an inner diameter... Problem 3.52P: A thin electrical heater is inserted between a long circular rod and a concentric tube with inner... Problem 3.54P: A 2-mm-diameter electrical wire is insulated by a 2-mm-thick rubberized sheath (k=0.13W/mK), and the... Problem 3.55P: Electric current flows through a long rod generating thermal energy at a uniform volumetric rate of... Problem 3.57P: A composite cylindrical wall is composed of two materials of thermal conductivity kA and kB, which... Problem 3.58P: An electrical current of 700 A flows through a stainless steel cable having a diameter of 5 mm and... Problem 3.59P: A 0.20-m-diameter. thin-walled steel pipe is used to transport saturated steam at a pressure of 20... Problem 3.60P: An uninsulated. thin-walled pipe of 100-mm diameter is used to transport water to equipment that... Problem 3.61P: Steam flowing through a long. thin-walled pipe maintains the pipe wall at a uniform temperature of... Problem 3.63P: A storage tank consists of a cylindrical section that has a length and inner diameter of L=2m and... Problem 3.64P: Consider the liquid oxygen storage system and the laboratory environmental conditions of Problem... Problem 3.65P: A spherical Pyrex glass shell has inside and outside diameters of D1=0.1m and D2=0.2m, respectively.... Problem 3.66P: In Example 3.6. an expression was derived for the critical insulation radius of an insulated,... Problem 3.67P: A hollow aluminum sphere. with an electrical heater in the center. is used in tests to determine the... Problem 3.68P: A spherical tank for storing liquid oxygen on the space shuttle is to be made from stainless steel... Problem 3.69P: A spherical, cryosurgical probe may be imbedded in diseased tissue for the purpose of freezing, and... Problem 3.70P Problem 3.71P Problem 3.72P: A composite spherical shell of inner radius r1=0.25m is constructed from lead of outer radius... Problem 3.73P: The energy transferred from the anterior chamber of the eye through the cornea varies considerably... Problem 3.74P: The outer surface of a hollow sphere of radius r2 is subjected to a uniform heat flux q2n. The inner... Problem 3.75P: A spherical shell of inner and outer radii r1 and ro, respectively, is filled with a heat-generating... Problem 3.76P Problem 3.77P Problem 3.78P Problem 3.79P: The air inside a chamber at T,i=50C is heated convectively with hi=20W/m2K by a 200-mm-thick wall... Problem 3.80P Problem 3.81P: A plane wall of thickness 0.1 m and thermal conductivity 25W/mK having uniform volumetric heat... Problem 3.82P: Large, cylindrical bales of hay used to feed livestock in the winter months are D=2m in diameter and... Problem 3.83P Problem 3.84P: Consider one-dimensional conduction in a plane composite wall. The outer surfaces are exposed to a... Problem 3.85P: Consider a plane composite wall that is composed of three materials (materials A, B, and C are... Problem 3.86P: An air heater may be fabricated by coiling Nichrome wire and passing air in cross flow over the... Problem 3.87P Problem 3.88P: Consider uniform thermal energy generation inside a one-dimensional plane wall of thickness L with... Problem 3.89P: A plane wall of thickness and thermal conductivity k experiences a uniform volumetric generation... Problem 3.90P: A nuclear fuel element of thickness 21, is covered with a steel cladding of thickness b. Heat... Problem 3.92P: In Problem 3.79 the strip heater acts to guard against heat losses from the wall to the outside, and... Problem 3.93P: The exposed surface (x=0) of a plane wall of thermal conductivity k is subjected to microwave... Problem 3.94P: A quartz window of thickness L serves as a viewing port in a furnace used for annealing steel. The... Problem 3.95P: For the conditions described in Problem 1.44. determine the temperature distribution, T(r), in the... Problem 3.96P: A cylindrical shell of inner and outer radii, ri and ro, respectively, is filled with a... Problem 3.97P: The cross section of a long cylindrical fuel element in a nuclear reactor is shown. Energy... Problem 3.101P: A long cylindrical rod of diameter 200 mm with thermal conductivity of 0.5W/mK experiences uniform... Problem 3.102P: A radioactive material of thermal conductivity k is cast as a solid sphere of radius ro and placed... Problem 3.103P: Radioactive wastes are packed in a thin-walled spherical container. The wastes generate thermal... Problem 3.104P: Radioactive wastes (ktw=20W/mK) are stored in a spherical, stainless steel (kss=15W/mK) container of... Problem 3.105P: Unique characteristics of biologically active materials such as fruits, vegetables, and other... Problem 3.106P: Consider the plane wall, long cylinder, and sphere shown schematically, each with the same... Problem 3.109P: One method that is used to grow nanowires (nanotubes with solid cores) is to initially deposit a... Problem 3.110P: Consider the manufacture of photovoltaic silicon, as described in Problem 1.42. The thin sheet of... Problem 3.111P: Copper tubing is joined to a solar collector plate of thickness t, and the working fluid maintains... Problem 3.112P: A thin flat plate of length L thickness t. and width WL is thermally joined to two large heat sinks... Problem 3.114P: The temperature of a flowing gas is to be measured with a thermocouple junction and wire stretched... Problem 3.116P: A thin metallic wire of thermal conductivity k, diameter D, and length 2L is annealed by passing an... Problem 3.117P: A motor draws electric power Pelec from a supply line and delivers mechanical power Pmech to a pump... Problem 3.118P: Consider the fuel cell stack of Problem 158. The t=0.42 -mm-thick membranes have a nominal thermal... Problem 3.119P: Consider a rod of diameter D, thermal conductivity k, and length 2L that is perfectly insulated over... Problem 3.120P: A carbon nanotube is suspended across a trench of width s=5m that separates two islands, each at... Problem 3.121P: A probe of overall length L=200mm and diameter D=12.5mm is inserted through a duct wall such that a... Problem 3.123P: A metal rod of length 2L diameter D, and thermal conductivity k is inserted into a perfectly... Problem 3.124P: A very long rod of 5-mm diameter and uniform thermal conductivity k=25W/mK is subjected to a heat... Problem 3.125P: From Problem 1.71, consider the wire leads connecting the transistor to the circuit board. The leads... Problem 3.126P: Turbine blades mounted to a rotating disc in a turbine engine are exposed to a gas stream that is at... Problem 3.127P Problem 3.128P Problem 3.129P Problem 3.130P: A brass rod 100 mm long and 5 mm in diameter extends horizontally from a casting at 200C. The rod is... Problem 3.131P: The extent to which the tip condition affects the thermal performance of a tin depends on the fin... Problem 3.132P: A pin fin of uniform. cross-sectional area is fabricated of an aluminum alloy (k=160W/mK). The fin... Problem 3.133P: The extent to which the tip condition affects the thermal performance of a tin depends on the fin... Problem 3.134P: A straight tin fabricated from 2024 aluminum alloy (k=185W/mK) has a base thickness of t=3mm and a... Problem 3.135P: Triangular and parabolic straight tins are subjected to the same thermal conditions as the... Problem 3.136P: Two long copper rods of diameter D=10mm are soldered together end to end. with solder having a... Problem 3.137P: Circular copper rods of diameter D=1mm and length L=25mm are used to enhance heat transfer from a... Problem 3.138P: During the initial stages of the growth of the nanowire of Problem 3.109, a slight perturbation of... Problem 3.139P: Consider two long, slender rods of the same diameter but different materials. One end of each rod is... Problem 3.140P: A 40-mm-long, 2-mm-diameter pin fin is fabricated of an aluminum alloy (k=140W/mK). Determine the... Problem 3.141P: An experimental arrangement for measuring the thermal conductivity of solid materials involves the... Problem 3.142P: Finned passages are frequently formed between parallel plates to enhance convection heat transfer in... Problem 3.143P: The fin array of Problem 3.142 is commonly found in compact heat exchangers. Whose function is to... Problem 3.144P: An isothermal silicon chip of width W=20mm on a side is soldered to an aluminum heat sink... Problem 3.145P: As seen in Problem 3.109, silicon carbide nanowires of diameter D=15nm can be grown onto a solid... Problem 3.147P: A homeowner's wood stove is equipped with a top burner for cooking. The D=200-mm -diameter burner is... Problem 3.149P: Water is heated by submerging 50-mm-diameter, thin-walled copper tubes in a tank and passing hot... Problem 3.150P: As a means of enhancing heat transfer from high-performance logic chips, it is common to attach a... Problem 3.152P: Consider design B of Problem 3.151. Over time. dust can collect in the fine grooves that separate... Problem 3.155P: Determine the percentage increase in heat transfer associated with attaching aluminum fins of... Problem 3.157P: Aluminum fins of triangular profile are attached to a plane wall whose surface temperature is 250C.... Problem 3.158P: An annular aluminum fin of rectangular profile is attached to a circular tube having an outside... Problem 3.159P: Annular aluminum fins of rectangular profile are attached to a circular tube having an outside... Problem 3.160P: It is proposed to air-cool the cylinders of a combustion chamber by joining an aluminum casing with... Problem 3.165P Problem 3.166P Problem 3.168P Problem 3.173P Problem 3.174P Problem 3.175P Problem 3.177P: A nanolaminated material is fabricated with an atomic layer deposition process, resulting in a... format_list_bulleted


 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning