
Organic Chemistry
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781118875766
Author: T. W. Graham Solomons, Craig B. Fryhle, Scott A. Snyder
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 26P
Designate the Lewis acid and Lewis base in each of the following reactions:
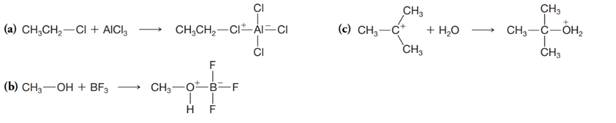
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Question 4
Determine the rate order and rate constant for sucrose hydrolysis.
Time (hours)
[C6H12O6]
0
0.501
0.500
0.451
1.00
0.404
1.50
0.363
3.00
0.267
First-order, k = 0.210 hour 1
First-order, k = 0.0912 hour 1
O Second-order, k =
0.590 M1 hour 1
O Zero-order, k = 0.0770 M/hour
O Zero-order, k = 0.4896 M/hour
O Second-order, k = 1.93 M-1-hour 1
10 pts
Determine the rate order and rate constant for sucrose hydrolysis.
Time (hours)
[C6H12O6]
0
0.501
0.500
0.451
1.00
0.404
1.50
0.363
3.00
0.267
Draw the products of the reaction shown below. Use wedge and dash bonds
to indicate stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts.
OSO4 (cat)
(CH3)3COOH
Select to Draw
ઘ
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 3 - Prob. 1PPCh. 3 - PRACTICE PROBLEM 3.2
Write equations showing the...Ch. 3 - PRACTICE PROBLEM 3.3 Which of the following are...Ch. 3 - Prob. 4PPCh. 3 - PRACTICE PROBLEM 3.5 Formic acid (HCO2H) has...Ch. 3 - Prob. 6PPCh. 3 - Prob. 7PPCh. 3 - Prob. 8PPCh. 3 - PRACTICE PROBLEM 3.9 Predict the outcome of the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 10PP
Ch. 3 - Prob. 11PPCh. 3 - Prob. 12PPCh. 3 - Prob. 13PPCh. 3 - Prob. 14PPCh. 3 - PRACTICE PROBLEM 3.15 Nitro groups have a large...Ch. 3 - PRACTICE PROBLEM 3.16
Your laboratory instructor...Ch. 3 - Prob. 17PPCh. 3 - Prob. 18PPCh. 3 - Prob. 19PPCh. 3 - What is the conjugate base of each of the...Ch. 3 - List the bases you gave as answers to Problem 3.20...Ch. 3 - 3.22 What is the conjugate acid of each of the...Ch. 3 - List the acids you gave as answers to Problem 3.22...Ch. 3 - Rank the following in order of increasing acidity.Ch. 3 - Without consulting tables, select the stronger...Ch. 3 - Designate the Lewis acid and Lewis base in each of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 27PCh. 3 - Prob. 28PCh. 3 - Write an equation, using the curved-arrow...Ch. 3 - 3.30 What reaction will take place if ethyl...Ch. 3 - 3.31 (a) The of formic acid. What is the? (b)...Ch. 3 - Acid HA has pKa=20; acid HB has pKa=10. (a) Which...Ch. 3 - Prob. 33PCh. 3 - 3.34 (a) Arrange the following compounds in order...Ch. 3 - 3.35 Arrange the following compounds in order of...Ch. 3 - 3.36 Arrange the following in order of increasing...Ch. 3 - Prob. 37PCh. 3 - 3.38 Supply the curved arrows necessary for the...Ch. 3 - Glycine is an amino acid that can be obtained from...Ch. 3 - 3.40 Malonic acid, , is a diprotic acid. The for...Ch. 3 - 3.41 The free-energy change, , for the ionization...Ch. 3 - 3.42 At the enthalpy change, , for the ionization...Ch. 3 - The compound at right has (for obvious reasons)...Ch. 3 - 3.44.
(a) Given the above sequence of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 45PCh. 3 - Prob. 46PCh. 3 - 3.47 As noted in Table 3.1, the of acetone, , is...Ch. 3 - Formamide (HCONH2) has a pKa of approximately 25....Ch. 3 - List all the chemical species likely to be present...Ch. 3 - Prob. 2LGPCh. 3 - Prob. 3LGPCh. 3 - Prob. 4LGP
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
How does the organism Prochlorococcus contribute to both the carbon and oxygen cycles in the oceans?
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
In what ways does connective tissue differ from epithelial tissue?
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
A piston motion moves a 50-lbm hammerhead vertically down 3 ft from rest to a velocity of 150 ft/s in a stampin...
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
What two body structures contain flexible elastic cartilage?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
All of the following processes are involved in the carbon cycle except: a. photosynthesis b. cell respiration c...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
11.57 Draw the cis and trans isomers for each of the following: (11.6)
a. 2-pentene
b. 3-hexene
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate the reaction rate for selenious acid, H2SeO3, if 0.1150 M I-1 decreases to 0.0770 M in 12.0 minutes. H2SeO3(aq) + 6I-1(aq) + 4H+1(aq) ⟶ Se(s) + 2I3-1(aq) + 3H2O(l)arrow_forwardProblem 5-31 Which of the following objects are chiral? (a) A basketball (d) A golf club (b) A fork (c) A wine glass (e) A spiral staircase (f) A snowflake Problem 5-32 Which of the following compounds are chiral? Draw them, and label the chirality centers. (a) 2,4-Dimethylheptane (b) 5-Ethyl-3,3-dimethylheptane (c) cis-1,4-Dichlorocyclohexane Problem 5-33 Draw chiral molecules that meet the following descriptions: (a) A chloroalkane, C5H11Cl (c) An alkene, C6H12 (b) An alcohol, C6H140 (d) An alkane, C8H18 Problem 5-36 Erythronolide B is the biological precursor of erythromycin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic. How H3C CH3 many chirality centers does erythronolide B have? OH Identify them. H3C -CH3 OH Erythronolide B H3C. H3C. OH OH CH3arrow_forwardPLEASE HELP! URGENT! PLEASE RESPOND!arrow_forward
- 2. Propose a mechanism for this reaction. ہلی سے ملی N H (excess)arrow_forwardSteps and explanationn please.arrow_forwardProblem 5-48 Assign R or S configurations to the chirality centers in ascorbic acid (vitamin C). OH H OH HO CH2OH Ascorbic acid O H Problem 5-49 Assign R or S stereochemistry to the chirality centers in the following Newman projections: H Cl H CH3 H3C. OH H3C (a) H H H3C (b) CH3 H Problem 5-52 Draw the meso form of each of the following molecules, and indicate the plane of symmetry in each: OH OH (a) CH3CHCH2CH2CHCH3 CH3 H3C. -OH (c) H3C CH3 (b) Problem 5-66 Assign R or S configurations to the chiral centers in cephalexin, trade-named Keflex, the most widely prescribed antibiotic in the United States. H2N H IHH S Cephalexin N. CH3 CO₂Harrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning  Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry | Acids & Bases; Author: Ninja Nerd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AOr_5tbgfQ0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY