
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 29, Problem 1PQ
Study the symbols in Table 29.2. Then, without looking at the table, draw the symbols for these circuit elements:
a. a wire,
b. a switch,
c. a resistor,
d. an emf device, and
e. a lightbulb.
(a)
Expert Solution
To determine
The symbol of a wire.
Explanation of Solution
The wire is represented by the symbol shown below:
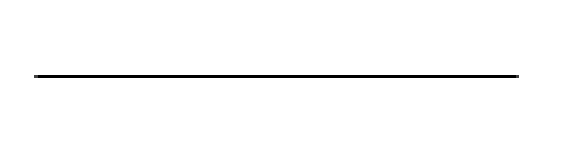
(b)
Expert Solution
To determine
The symbol of a switch.
Explanation of Solution
The switch is represented by the symbol shown below:
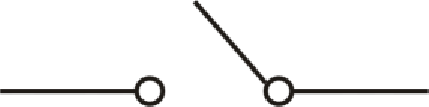
(c)
Expert Solution
To determine
The symbol a resistor.
Explanation of Solution
The resistor is represented by the symbol shown below:
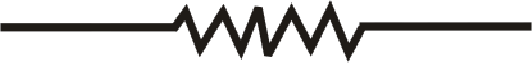
(d)
Expert Solution
To determine
The symbol of an emf device.
Explanation of Solution
An emf device is represented by the symbol shown below:

(e)
Expert Solution
To determine
The symbol of a light bulb.
Explanation of Solution
The lightbulb is represented by the symbol as shown below:
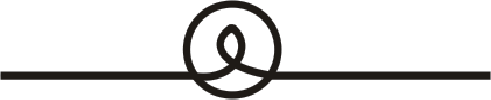
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Students have asked these similar questions
Please solve and answer the problem step by step with explanations along side each step stating what's been done correctly please. Thank you!! ( preferably type out everything)
Answer this
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 29 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
Ch. 29.1 - What are the SI units of ?Ch. 29.1 - Prob. 29.2CECh. 29.2 - Prob. 29.3CECh. 29.4 - Prob. 29.5CECh. 29.4 - Prob. 29.6CECh. 29.5 - Prob. 29.7CECh. 29 - Study the symbols in Table 29.2. Then, without...Ch. 29 - Prob. 2PQCh. 29 - Prob. 3PQCh. 29 - Suppose you need to measure the potential...
Ch. 29 - Prob. 5PQCh. 29 - Prob. 6PQCh. 29 - A real battery (modeled as an ideal emf device in...Ch. 29 - Prob. 8PQCh. 29 - Two circuits made up of identical ideal emf...Ch. 29 - Prob. 10PQCh. 29 - Prob. 11PQCh. 29 - Prob. 12PQCh. 29 - Eight real batteries, each with an emf of 5.00 V...Ch. 29 - Prob. 14PQCh. 29 - Prob. 15PQCh. 29 - Prob. 16PQCh. 29 - Prob. 17PQCh. 29 - Prob. 18PQCh. 29 - Prob. 19PQCh. 29 - An ideal emf device with emf is connected to two...Ch. 29 - Prob. 21PQCh. 29 - Prob. 22PQCh. 29 - Prob. 23PQCh. 29 - Prob. 24PQCh. 29 - Prob. 25PQCh. 29 - Prob. 26PQCh. 29 - Determine the currents through the resistors R2,...Ch. 29 - The emf devices in the circuits shown in Figure...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29PQCh. 29 - Prob. 30PQCh. 29 - Prob. 31PQCh. 29 - Prob. 32PQCh. 29 - Prob. 33PQCh. 29 - Prob. 34PQCh. 29 - A Figure P29.35 shows a combination of six...Ch. 29 - A Each resistor shown in Figure P29.36 has...Ch. 29 - Each resistor shown in Figure P29.36 has a...Ch. 29 - Prob. 38PQCh. 29 - Prob. 39PQCh. 29 - The emf in Figure P29.40 is 4.54 V. The...Ch. 29 - Figure P29.41 shows three resistors (R1 = 14.0 ,...Ch. 29 - Figure P29.42 shows five resistors and two...Ch. 29 - The emfs in Figure P29.43 are 1 = 6.00 V and 2 =...Ch. 29 - Prob. 44PQCh. 29 - Figure P29.45 shows five resistors connected...Ch. 29 - Figure P29.46 shows a circuit with a 12.0-V...Ch. 29 - Two ideal emf devices are connected to a set of...Ch. 29 - Two ideal emf devices are connected to a set of...Ch. 29 - Three resistors with resistances R1 = R/2 and R2 =...Ch. 29 - Prob. 51PQCh. 29 - Prob. 52PQCh. 29 - Prob. 53PQCh. 29 - Prob. 55PQCh. 29 - At time t = 0, an RC circuit consists of a 12.0-V...Ch. 29 - A 210.0- resistor and an initially uncharged...Ch. 29 - Prob. 58PQCh. 29 - A real battery with internal resistance 0.500 and...Ch. 29 - Figure P29.60 shows a simple RC circuit with a...Ch. 29 - Prob. 61PQCh. 29 - Prob. 62PQCh. 29 - Prob. 63PQCh. 29 - Ralph has three resistors, R1, R2, and R3,...Ch. 29 - Prob. 65PQCh. 29 - An ideal emf device is connected to a set of...Ch. 29 - Prob. 67PQCh. 29 - An ideal emf device (24.0 V) is connected to a set...Ch. 29 - Prob. 69PQCh. 29 - What is the equivalent resistance between points a...Ch. 29 - A capacitor with initial charge Q0 is connected...Ch. 29 - Prob. 73PQCh. 29 - Prob. 74PQCh. 29 - Prob. 75PQCh. 29 - Prob. 76PQCh. 29 - Figure P29.77 shows a circuit with two batteries...Ch. 29 - In the RC circuit shown in Figure P29.78, an ideal...Ch. 29 - Prob. 79PQCh. 29 - Calculate the equivalent resistance between points...Ch. 29 - In Figure P29.81, N real batteries, each with an...Ch. 29 - Prob. 82PQCh. 29 - Prob. 83PQCh. 29 - Prob. 84PQCh. 29 - Figure P29.84 shows a circuit that consists of two...Ch. 29 - Prob. 86PQCh. 29 - Prob. 87PQCh. 29 - Prob. 88PQCh. 29 - Prob. 89PQCh. 29 - Prob. 90PQCh. 29 - Prob. 91PQCh. 29 - Prob. 92PQCh. 29 - Prob. 93PQCh. 29 - Prob. 94PQCh. 29 - Prob. 95PQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvote instantarrow_forwardKirchoff's Laws. A circuit contains 3 known resistors, 2 known batteries, and 3 unknown currents as shown. Assume the current flows through the circuit as shown (this is our initial guess, the actual currents may be reverse). Use the sign convention that a potential drop is negative and a potential gain is positive. E₂ = 8V R₁₁ = 50 R₂ = 80 b с w 11 www 12 13 E₁ = 6V R3 = 20 a) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop abefa in the clockwise direction starting at point a. (2 pt). b) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop bcdeb in the clockwise direction starting at point b. (2 pt). c) Apply Kirchoff's Junction Rule at junction b (1 pt). d) Solve the above 3 equations for the unknown currents I1, 12, and 13 and specify the direction of the current around each loop. (5 pts) I1 = A 12 = A 13 = A Direction of current around loop abef Direction of current around loop bcde (CW or CCW) (CW or CCW)arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 4.) The diagram shows the electric field lines of a positively charged conducting sphere of radius R and charge Q. A B Points A and B are located on the same field line. A proton is placed at A and released from rest. The magnitude of the work done by the electric field in moving the proton from A to B is 1.7×10-16 J. Point A is at a distance of 5.0×10-2m from the centre of the sphere. Point B is at a distance of 1.0×10-1 m from the centre of the sphere. (a) Explain why the electric potential decreases from A to B. [2] (b) Draw, on the axes, the variation of electric potential V with distance r from the centre of the sphere. R [2] (c(i)) Calculate the electric potential difference between points A and B. [1] (c(ii)) Determine the charge Q of the sphere. [2] (d) The concept of potential is also used in the context of gravitational fields. Suggest why scientists developed a common terminology to describe different types of fields. [1]arrow_forward3.) The graph shows how current I varies with potential difference V across a component X. 904 80- 70- 60- 50- I/MA 40- 30- 20- 10- 0+ 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 VIV Component X and a cell of negligible internal resistance are placed in a circuit. A variable resistor R is connected in series with component X. The ammeter reads 20mA. 4.0V 4.0V Component X and the cell are now placed in a potential divider circuit. (a) Outline why component X is considered non-ohmic. [1] (b(i)) Determine the resistance of the variable resistor. [3] (b(ii)) Calculate the power dissipated in the circuit. [1] (c(i)) State the range of current that the ammeter can measure as the slider S of the potential divider is moved from Q to P. [1] (c(ii)) Describe, by reference to your answer for (c)(i), the advantage of the potential divider arrangement over the arrangement in (b).arrow_forward1.) Two long parallel current-carrying wires P and Q are separated by 0.10 m. The current in wire P is 5.0 A. The magnetic force on a length of 0.50 m of wire P due to the current in wire Q is 2.0 × 10-s N. (a) State and explain the magnitude of the force on a length of 0.50 m of wire Q due to the current in P. [2] (b) Calculate the current in wire Q. [2] (c) Another current-carrying wire R is placed parallel to wires P and Q and halfway between them as shown. wire P wire R wire Q 0.05 m 0.05 m The net magnetic force on wire Q is now zero. (c.i) State the direction of the current in R, relative to the current in P.[1] (c.ii) Deduce the current in R. [2]arrow_forward
- 2.) A 50.0 resistor is connected to a cell of emf 3.00 V. The voltmeter and the ammeter in the circuit are ideal. V A 50.00 (a) The current in the ammeter is 59.0 mA. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell. The circuit is changed by connecting another resistor R in parallel to the 50.0 resistor. V A 50.00 R (b) Explain the effect of this change on R is made of a resistive wire of uniform cross-sectional area 3.1 × 10-8 m², resistivity 4.9 × 10-70m and length L. The resistance of R is given by the equation R = KL where k is a constant. (b.i) the reading of the ammeter. [2] (b.ii) the reading of the voltmeter. [2] (c) Calculate k. State an appropriate unit for your answer. [3] [2]arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- A rod 12.0 cm long is uniformly charged and has a total charge of -20.0 μc. Determine the magnitude and direction of the electric field along the axis of the rod at a point 32.0 cm from its center. 361000 ☑ magnitude What is the general expression for the electric field along the axis of a uniform rod? N/C direction toward the rodarrow_forwardA certain brand of freezer is advertised to use 730 kW h of energy per year. Part A Assuming the freezer operates for 5 hours each day, how much power does it require while operating? Express your answer in watts. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? P Submit Request Answer Part B W If the freezer keeps its interior at a temperature of -6.0° C in a 20.0° C room, what is its theoretical maximum performance coefficient? Enter your answer numerically. K = ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer Part C What is the theoretical maximum amount of ice this freezer could make in an hour, starting with water at 20.0°C? Express your answer in kilograms. m = Ο ΑΣΦ kgarrow_forwardDescribe the development of rational choice theory in sociology. Please includearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
DC Series circuits explained - The basics working principle; Author: The Engineering Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VV6tZ3Aqfuc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY