
Concept explainers
The following equations define the concentrations of threereactants:
If the initial conditions are
To calculate: The concentration for the times from
Initials conditions are
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution:
The concentration of the reactants
The concentration of the reactants
The concentration of the reactants
The concentration of the reactants
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The system of equations,
Initial conditions,
Formula used:
To calculate the values of
Eigen value
Calculation:
Consider the system of first order nonlinear differential equation of reactants
To calculate equilibrium points, consider the equations given below:
Compare the system of first order nonlinear differential equations with the above equations,
Therefore, the equilibrium point is,
Suppose, the system of non-linear differential equations are equal to some functions, that is,
Now, compare these equations with system of non-linear differential equations,
Now, find the Jacobian matrix,
Then, the Jacobian matrix at the equilibrium points
Now, the linearized system corresponding to nonlinear system of differential equation is,
Let,
Suppose,
Thus,
Now calculate the determinant as,
Therefore, the eigenvalues of the matrix are
Now, find the eigenvector corresponding to each eigenvalue of the matrix.
The eigenvector is,
Where,
Substitute the value of X in
Put
Put
Put
Therefore, the eigenvector corresponding to each eigenvalue of the matrix are respectively
Hence, the solution of the system of nonlinear differential equation is,
After solve the above equation,
Then the values of
The initial conditionsgiven as,
Now, apply the initial condition in the above equations,
This imply that,
Then,
Substitute, the value of
The concentration at
Therefore, theconcentration of the reactants
Now, the concentration at
Therefore, the concentration of the reactants
Now, the concentration at
Therefore, the concentration of the reactants
Now, the concentration at
Use the following MATLAB code to plot the concentrationvalues,
Execute the above to obtain the plot as,
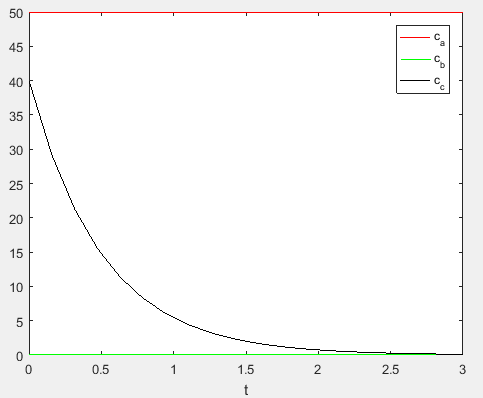
Therefore, the concentration of the reactants
Hence, the concentration of the reactants
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Numerical Methods for Engineers
- 1. Evaluate the following improper integrals: (a) fe-rt dt; (b) fert dt; (c) fi da dxarrow_forward8. Given the rate of net investment I(t) = 9t¹/2, find the level of capital formation in (i) 16 years and (ii) between the 4th and the 8th years.arrow_forward9. If the marginal revenue function of a firm in the production of output is MR = 40 - 10q² where q is the level of output, and total revenue is 120 at 3 units of output, find the total revenue function. [Hints: TR = √ MRdq]arrow_forward
- 6. Solve the following first-order linear differential equations; if an initial condition is given, definitize the arbitrary constant: (a) 2 + 12y + 2et = 0, y(0) = /; (b) dy+y=tarrow_forward4. Let A = {a, b, c, d, e, f}, B = {e, f, g, h} and C = {a, e, h,i}. Let U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k}. • Draw a Venn Diagram to describe the relationships between these sets Find (AB) NC • Find (AC) UB Find AUBUC • Find (BC) N (A - C)arrow_forward7. A consumer lives on an island where she produces two goods x and y according to the production possibility frontier x² + y² < 200 and she consumes all the goods. Her utility function is U(x, y) = x y³. She faces an environmental constraint on her total output of both goods. The environmental constraint is given by x + y ≤20. • (a) Write down the consumer's optimization problem. (b) Write out the Kuhn-Tucker first order conditions. (c) Find the consumer's optimal consumption bundle (x*, y*).arrow_forward
- 3. Answer the following questions: (a) Given the marginal propensity to import M'(Y) = 0.1 and the information that M = 20 when Y = 0, find the import function M(Y). (b) Given a continuous income stream at the constant rate of $1,000 per year, what will be the present value II if the income stream terminates after exactly 3 years and the discount rate is 0.04? (c) What is the present value of a perpetual cash flow of $2,460 per year, discounted at r = 8%?arrow_forward5. Let A and B be arbitrary sets. Prove AnB = AUB.arrow_forward2. Answer the following questions: (a) Given the marginal-revenue function R'(Q) = 28Q - €0.3Q, find the total-revenue function R(Q). What initial condition can you introduce to definitize the constant of integration? = (b) Given the marginal propensity to consume C'(Y) 0.80.1Y-1/2 and the information that C = Y when Y = 100, find the consumption function C(Y).arrow_forward
- 7. Let X, A, and B be arbitrary sets such that ACX and BC X. Prove AUB CX.arrow_forward1. Write out the following sets as a list of elements. If necessary you may use ... in your description. {x EZ: |x|< 10 A x < 0} {x ЄN: x ≤ 20 A x = 2y for some y = N} {n EN: 3 | n^ 1 < n < 20} {y Є Z: y² <0}arrow_forward3. For each statement below, write an equivalent statement using the justification given. = y Є A or yЄ B by the definition of union = y Є A or y Є B by the definition of set complement = x = C and x & D by DeMorgan's Law =Vx (x EnFxЄEUF) by definition of subset. = (X CYUZ)A (YUZ CX) by definition of set equalityarrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
 College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning



