
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The peptide
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are classified as acidic, basic and neutral according to the
Answer to Problem 27.10P
The peptide
There will be no charge on the peptide,
Explanation of Solution
Peptides are classified as acidic, basic, or neutral according to the amino acids they contain. If they contain unbalanced basic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptide and if they contain unbalanced acidic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptides. If the basic and acidic amino acids are balanced or not at all present in the peptide then it is considered as neutral peptide.
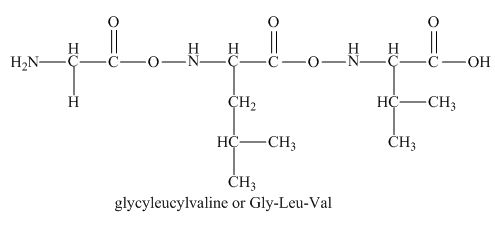
The given peptide

Figure 1
This tripeptide contains one amino group and one carboxylic group. So, this amino acid is neutral in nature. The
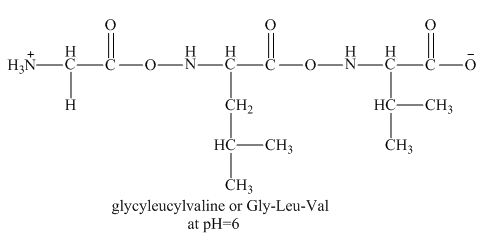
Figure 2
Therefore, the net charge on the peptide,
The peptide
(b)
Interpretation:
The peptide,
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are classified as acidic, basic and neutral according to the functional group they possesses. Acidic amino acids are those which have one more than one carboxylic acid group in its side chain and basic amino acids are those which have one or more amino group present in their side chain. Isoelectric point of the amino acids is the pH of the dilute aqueous solution of the amino acid at which the total charge on all molecules of amino acid is zero.
Answer to Problem 27.10P
The peptide,
The net charge on the peptide,
Explanation of Solution
Peptides are classified as acidic, basic, or neutral according to the amino acids they contain. If they contain unbalanced basic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptide and if they contain unbalanced acidic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptides. If the basic and acidic amino acids are balanced or not at all present in the peptide then it is considered as neutral peptide.
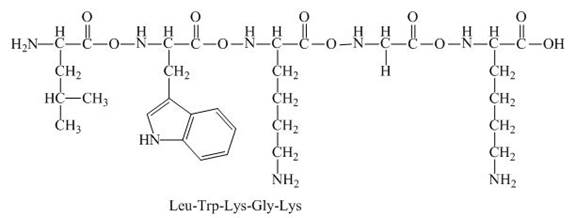
The given peptide,

Figure 3
This given peptide contains three amino group in its chain and one carboxylic group. So, this amino acid is basic in nature. All the amine group of the given peptide having value of
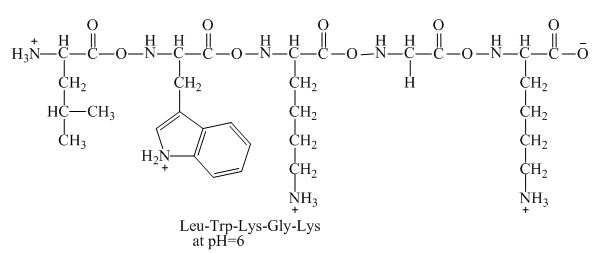
Figure 4
Therefore, the net charge of
The peptide,
(c)
Interpretation:
The peptide,
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are classified as acidic, basic and neutral according to the functional group they possesses. Acidic amino acids are those which have one more than one carboxylic acid group in its side chain and basic amino acids are those which have one or more amino group present in their side chain. Isoelectric point of the amino acids is the pH of the dilute aqueous solution of the amino acid at which the total charge on all molecules of amino acid is zero.
Answer to Problem 27.10P
The peptide
There will be no charge on the peptide,
Explanation of Solution
Peptides are classified as acidic, basic, or neutral according to the amino acids they contain. If they contain unbalanced basic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptide and if they contain unbalanced acidic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptides. If the basic and acidic amino acids are balanced or not at all present in the peptide then it is considered as neutral peptide.
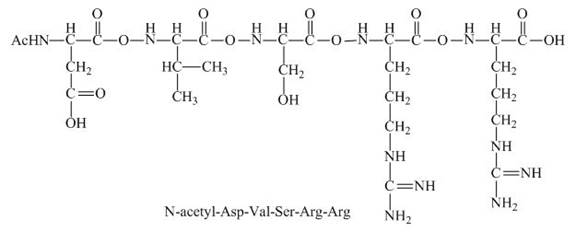
The given peptide

Figure 5
This given peptide contains two amino groups in the side chain and two carboxylic groups. So, this amino acid is neutral in nature. All the amine groups of this peptide having
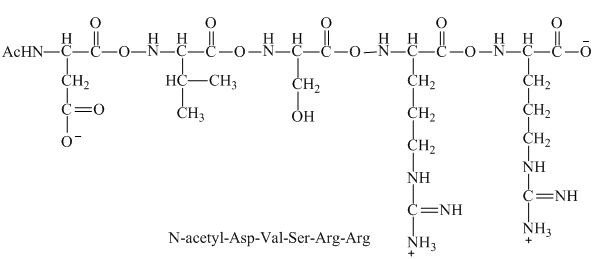
Figure 6
Therefore, the net charge on the peptide,
The peptide
(d)
Interpretation:
The peptide
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are classified as acidic, basic and neutral according to the functional group they possesses. Acidic amino acids are those which have one more than one carboxylic acid group in its side chain and basic amino acids are those which have one or more amino group present in their side chain. Isoelectric point of the amino acids is the pH of the dilute aqueous solution of the amino acid at which the total charge on all molecules of amino acid is zero.
Answer to Problem 27.10P
The peptide
The charge present on the peptide,
Explanation of Solution
Peptides are classified as acidic, basic, or neutral according to the amino acids they contain. If they contain unbalanced basic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptide and if they contain unbalanced acidic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptides. If the basic and acidic amino acids are balanced or not at all present in the peptide then it is considered as neutral peptide.
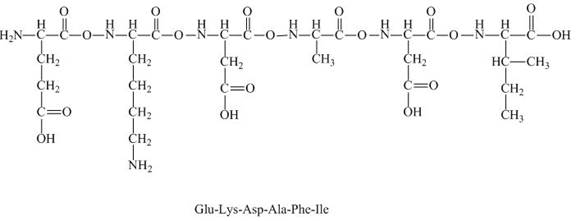
The given peptide

Figure 7
This given peptide contains two amino groups in the side chain and four carboxylic groups. So, this amino acid is acidic in nature. All the amine groups of this peptide having
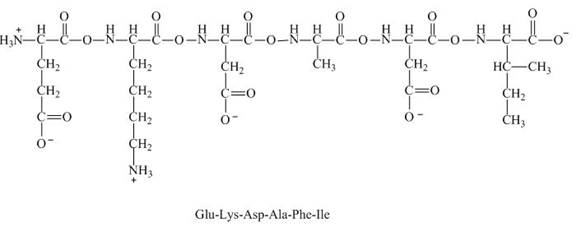
Figure 8
Therefore, the net charge on the peptide,
The peptide
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Organic Functional Groups entifying positions labeled with Greek letters in acids and derivatives 1/5 ssible, replace an H atom on the a carbon of the molecule in the drawing area with a ce an H atom on the ẞ carbon with a hydroxyl group substituent. ne of the substituents can't be added for any reason, just don't add it. If neither substi er the drawing area. O H OH Oneither substituent can be added. Check D 1 Accessibility ado na witharrow_forwardDifferentiate between electrophilic and nucleophilic groups. Give examples.arrow_forwardAn aldehyde/ketone plus an alcohol gives a hemiacetal, and an excess of alcohol gives an acetal. The reaction is an equilibrium; in aldehydes, it's shifted to the right and in ketones, to the left. Explain.arrow_forward
- Draw a Haworth projection or a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H- -OH H- OH H- -OH CH₂OHarrow_forwardAnswer the question in the first photoarrow_forwardGgggffg2258555426855 please don't use AI Calculate the positions at which the probability of a particle in a one-dimensional box is maximum if the particle is in the fifth energy level and in the eighth energy level.arrow_forward
- Draw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. NH2 F3C CF3 NH OMe NH2-NH2, ACOH Aarrow_forwardPhotochemical smog is formed in part by the action of light on nitrogen dioxide. The wavelength of radiation absorbed by NO2 in this reaction is 197 nm.(a) Draw the Lewis structure of NO2 and sketch its π molecular orbitals.(b) When 1.56 mJ of energy is absorbed by 3.0 L of air at 20 °C and 0.91 atm, all the NO2 molecules in this sample dissociate by the reaction shown. Assume that each absorbed photon leads to the dissociation (into NO and O) of one NO2 molecule. What is the proportion, in parts per million, of NO2 molecules in this sample? Assume that the sample behaves ideally.arrow_forwardCorrect each molecule in the drawing area below so that it has the skeletal ("line") structure it would have if it were dissolved in a 0.1 M aqueous solution of HCI. If there are no changes to be made, check the No changes box under the drawing area. No changes. HO Explanation Check NH, 2 W O :□ G ©2025 M unter Accessibilityarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





