
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with
Concept introduction:
The chemical compounds in which carbon is bonded with the acidic and basic group along with hydrocarbon side chain are known as amino acids. The amino acids are classified into acidic, basic, polar, non-polar, essential, and non-essential categories. The three-word abbreviation or one-word abbreviation is used for amino acids.
Answer to Problem 27.43AP
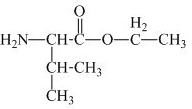
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with
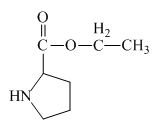
The structure of the product expected when proline would react with
Explanation of Solution
The valine has a carboxylic group in it. This carboxylic group can undergo esterification with ethanol in the presence of sulfuric acid. The corresponding
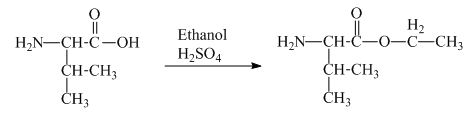
Figure 1
The proline has a carboxylic group in it. This carboxylic group can undergo esterification with ethanol in the presence of sulfuric acid. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
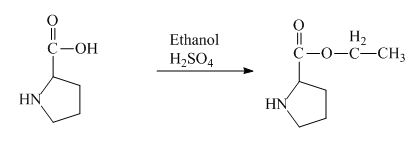
Figure 2
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with benzoyl chloride and
Concept introduction:
The chemical compounds in which carbon is bonded with the acidic and basic group along with hydrocarbon side chain are known as amino acids. The amino acids are classified into acidic, basic, polar, non-polar, essential, and non-essential categories. The three-word abbreviation or one-word abbreviation is used for amino acids.
Answer to Problem 27.43AP
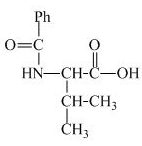
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with benzoyl chloride and ![]() is shown below.
is shown below.
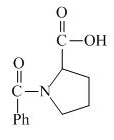
The structure of the product expected when proline would react with benzoyl chloride and
Explanation of Solution
The valine has a basic
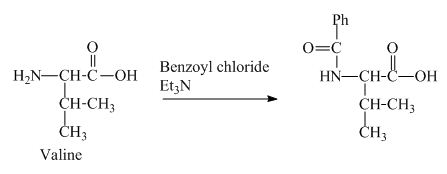
Figure 3
The proline has a basic amine group in it. This group can react with benzoyl chloride to form amide bond. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
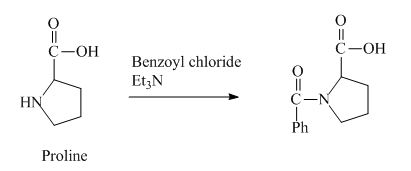
Figure 4
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with benzoyl chloride and
The structure of the product expected when proline would react with benzoyl chloride and
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with an aqueous
Concept introduction:
The chemical compounds in which carbon is bonded with the acidic and basic group along with hydrocarbon side chain are known as amino acids. The amino acids are classified into acidic, basic, polar, non-polar, essential, and non-essential categories. The three-word abbreviation or one-word abbreviation is used for amino acids.
Answer to Problem 27.43AP
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with an aqueous
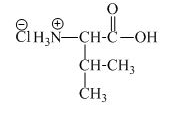
The structure of the product expected when proline would react with an aqueous
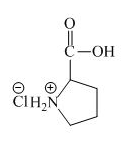
Explanation of Solution
The valine has a basic amine group in it. This amine group can react with acid to form an ammonium base. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
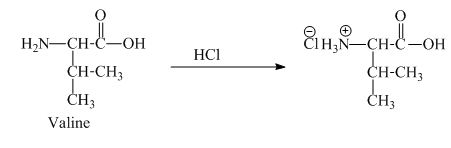
Figure 5
The proline has a basic amine group in it. This amine group can react with acid to form an ammonium base. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
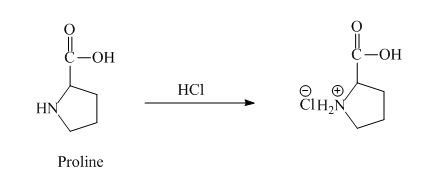
Figure 6
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with an aqueous
The structure of the product expected when proline would react with an aqueous
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with an aqueous
Concept introduction:
The chemical compounds in which carbon is bonded with the acidic and basic group along with hydrocarbon side chain are known as amino acids. The amino acids are classified into acidic, basic, polar, non-polar, essential, and non-essential categories. The three-word abbreviation or one-word abbreviation is used for amino acids.
Answer to Problem 27.43AP
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with an aqueous
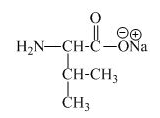
The structure of the product expected when proline would react with an aqueous
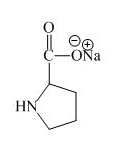
Explanation of Solution
The valine has an acidic carboxylic group in it. This group can react with a base such as sodium hydroxide to form a sodium salt of
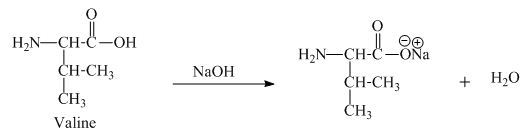
Figure 7
The proline has an acidic carboxylic group in it. This group can react with a base such as sodium hydroxide to form a sodium salt of carboxylic acid. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
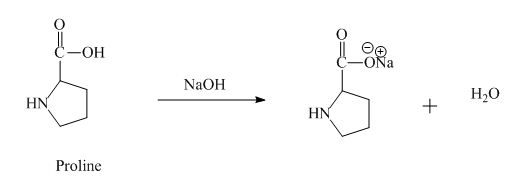
Figure 8
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with an aqueous
The structure of the product expected when proline would react with an aqueous
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with aqueous benzaldehyde and
Concept introduction:
The chemical compounds in which carbon is bonded with the acidic and basic group along with hydrocarbon side chain are known as amino acids. The amino acids are classified into acidic, basic, polar, non-polar, essential, and non-essential categories. The three-word abbreviation or one-word abbreviation is used for amino acids.
Answer to Problem 27.43AP
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with aqueous benzaldehyde and
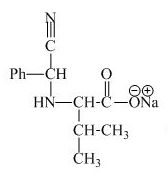
The structure of the product expected when proline would react with aqueous benzaldehyde and
Explanation of Solution
The valine has a basic group in it. This group can be attacked by the benzaldehyde in the presence of sodium cyanide to form the final product. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
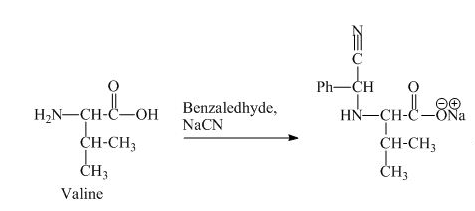
Figure 9
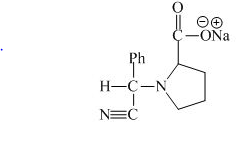
The proline has a basic group in it. This group can be attacked by the benzaldehyde in the presence of sodium cyanide to form the final product. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
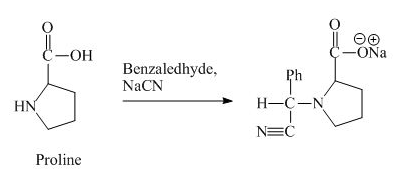
Figure 10
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with aqueous benzaldehyde and
The structure of the product expected when proline would react with aqueous benzaldehyde and
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with aqueous Fmoc-![]() followed by neutralizing with
followed by neutralizing with
Concept introduction:
The chemical compounds in which carbon is bonded with the acidic and basic group along with hydrocarbon side chain are known as amino acids. The amino acids are classified into acidic, basic, polar, non-polar, essential, and non-essential categories. The three-word abbreviation or one-word abbreviation is used for amino acids.
Answer to Problem 27.43AP
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with aqueous Fmoc-
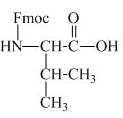
The structure of the product expected when proline would react with aqueous Fmoc-
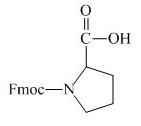
Explanation of Solution
The valine has an amine group. This group can be protected by the reaction of valine with aqueous Fmoc-
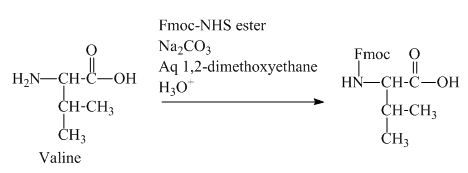
Figure 11
The proline has an amine group. This group can be protected by the reaction of proline with aqueous Fmoc-
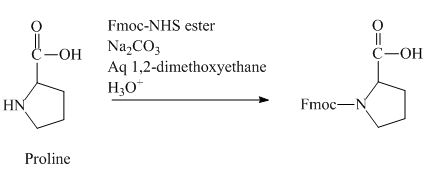
Figure 12
The structure of the product expected when valine would react with aqueous Fmoc-
The structure of the product expected when proline would react with aqueous Fmoc-
(g)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of valine would react with ![]() butyl ester is to be predicted. The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of proline would react with
butyl ester is to be predicted. The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of proline would react with ![]() butyl ester is to be predicted.
butyl ester is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The chemical compounds in which carbon is bonded with the acidic and basic group along with hydrocarbon side chain are known as amino acids. These
Answer to Problem 27.43AP
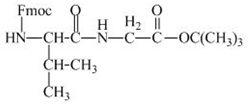
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of valine would react with ![]() butyl ester is shown below.
butyl ester is shown below.
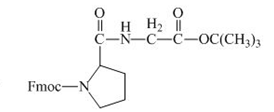
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of proline would react with ![]() butyl ester is below.
butyl ester is below.
Explanation of Solution
The valine has an amine group. This group can be protected by the reaction of valine with aqueous Fmoc-![]() butyl ester. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
butyl ester. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
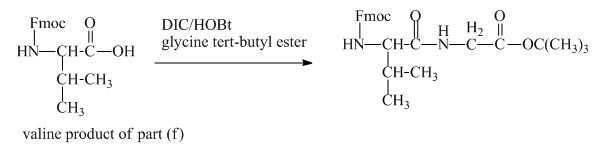
Figure 13
The carboxylic group of the derivative of proline can be protected with the help of reagent with ![]() butyl ester. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
butyl ester. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
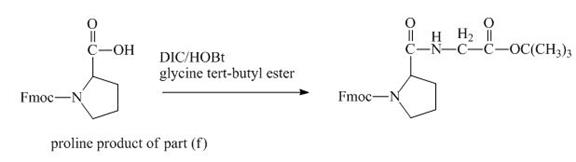
Figure 14
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of valine would react with ![]() butyl ester is shown in Figure 13.
butyl ester is shown in Figure 13.
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of proline would react with ![]() butyl ester is shown in Figure 14.
butyl ester is shown in Figure 14.
(h)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of valine would react with anhydrous
Concept introduction:
The chemical compounds in which carbon is bonded with the acidic and basic group along with hydrocarbon side chain are known as amino acids. These functional groups can be protected by different reagent to synthesize peptide chains. The protecting groups can be removed by hydrolysis.
Answer to Problem 27.43AP
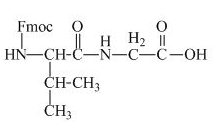
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of valine would react with anhydrous
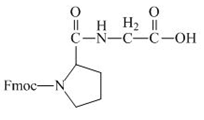
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of proline would react with anhydrous
Explanation of Solution
The derivative of valine has an ester linkage in it. The acid,
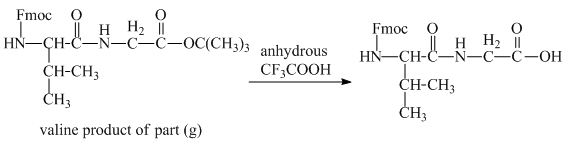
Figure 15
The derivative of proline has an ester linkage in it. The acid,
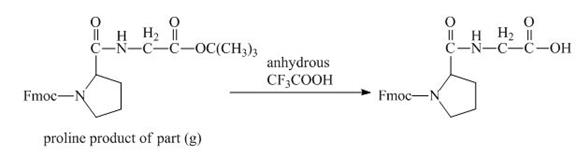
Figure 16
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of valine would react with anhydrous
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of proline would react with anhydrous
(i)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of valine would react with
Concept introduction:
The chemical compounds in which carbon is bonded with the acidic and basic group along with hydrocarbon side chain are known as amino acids. These functional groups can be protected by different reagent to synthesize peptide chains. The protecting groups can be removed by hydrolysis.
Answer to Problem 27.43AP
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of valine would react with
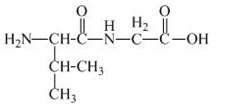
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of proline would react with
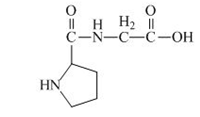
Explanation of Solution
The solution of
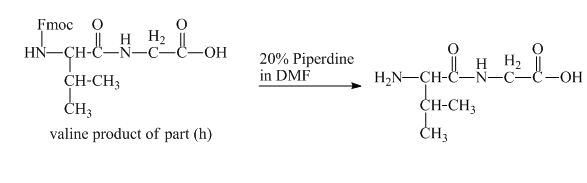
Figure 17
The solution of
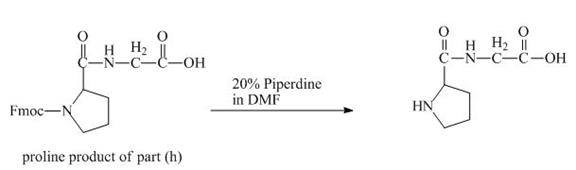
Figure 18
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of valine would react with
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of proline would react with
(j)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of valine would react with
Concept introduction:
The chemical compounds in which carbon is bonded with the acidic and basic group along with hydrocarbon side chain are known as amino acids. These functional groups can be protected by different reagent to synthesize peptide chains. The protecting groups can be removed by hydrolysis.
Answer to Problem 27.43AP
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of valine would react with
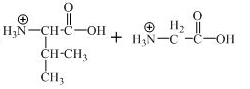
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of proline would react with
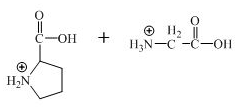
Explanation of Solution
The derivative of valine has amide linkage in it. This amide linkage can be hydrolysis by heating with a strong acid such as
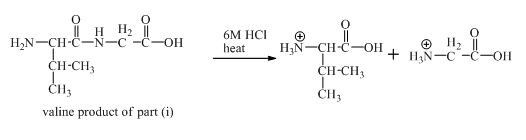
Figure 19
The derivative of valine has amide linkage in it. This amide linkage can be hydrolysis by heating with a strong acid such as
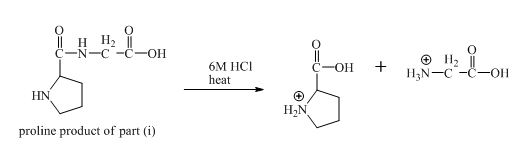
Figure 20
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of valine would react with
The structure of the product expected when the given derivative of proline would react with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Polymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. Draw three repeat units (trimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. Assume there are hydrogen atoms there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the trimer. Ignore inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwardDraw a tetramer if this alternating copolymer pleasearrow_forwardDraw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer.arrow_forward
- Draw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer.arrow_forward8:44 PM Sun Apr 13 Earn Freecash.com O Measurement and Matter =1 Setting up a unit conversion 110 Eddie says... ✰ www-awu.aleks.com A student sets up the following equation to convert a measurement. (The ? stands for a number the student is going to calculate.) Fill in the missing part of this equation. Note: your answer should be in the form of one or more fractions multiplied together. (- 4 J kJ -7.0 × 10 ☐ = ? mmol.°C mol °C x10 μ Explanation Check □·□ torox.io Grey Hill LLC. All Rightsarrow_forwardPolymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. Draw three repeat units (trimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. Assume there are hydrogen atoms there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the trimer. Ignore inorganic byproducts please.arrow_forward
- i need help on how to complete the followingarrow_forwardno AI walkthrough current image is wrong answerarrow_forwarda. Determine whether each of the Followery Molecules is in the R- On the y- Configuration 1-01"/ 1-6-4 Br 4 I el Br b. Draw The Fisher projection For all the Meso compounds that can exist FOR The Following molenlearrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


