
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To identify the heme degradation product (1) bilirubin, (2) biliverdin, (3) stercobilin, and (4) urobilin in whose production “ring-opening” occurs.
Concept introduction: Hemoglobin is a heme protein present in the red blood cells. The protein part is called globin and the non-protein part is heme. Heme is the prosthetic group that contains 4 pyrrole groups bonded together and has an iron atom in the center. The structure of the heme group is:
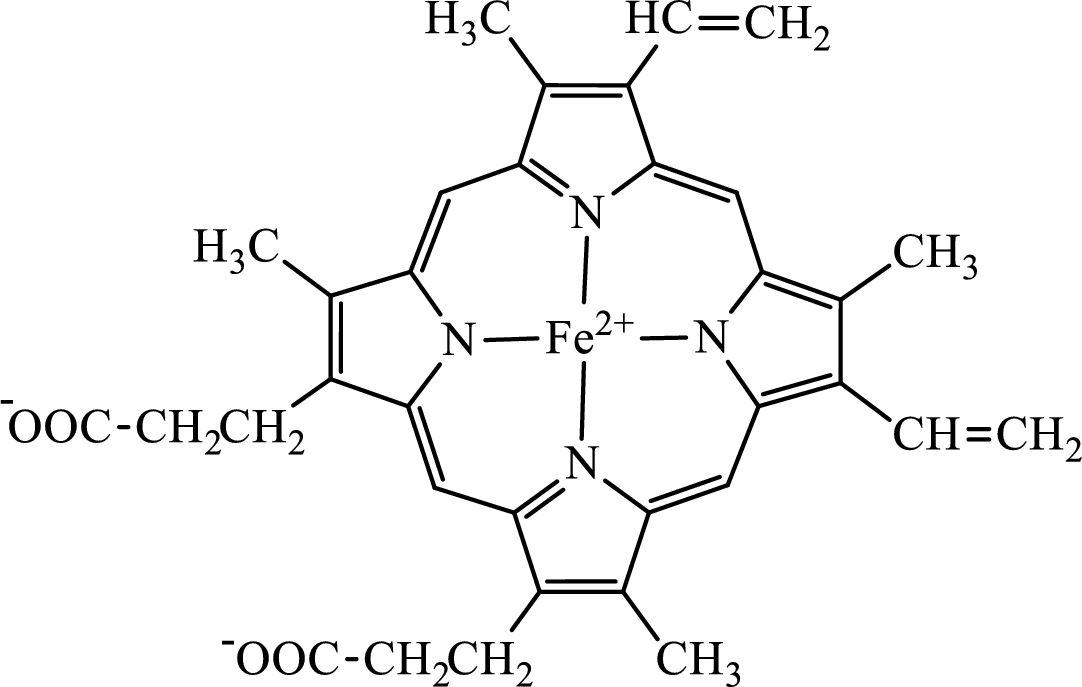
The first step of degradation of heme involves opening of pyrrole ring with the release of the iron atom and production of biliverdin. The iron atom released becomes part of ferritin protein. Biliverdin produced is converted bilirubin in the spleen. Bilirubin is then transported to the liver where attachment of sugar residues to the propionate side chains of the bilirubin occurs to make it more soluble. Then more solubilized bilirubin is excreted in bile and finally to the small intestine. In the small intestine, it is converted into stercobilin for excretion in feces or urobilin for excretion in urine.
(b)
Interpretation: To identify the heme degradation product (1) bilirubin, (2) biliverdin, (3) stercobilin, and (4) urobilin in whose production a carbon-carbon double bond is changed to a carbon-carbon single bond.
Concept introduction: Hemoglobin is a heme protein present in the red blood cells. The protein part is called globin and the non-protein part is heme. Heme is the prosthetic group that contains 4 pyrrole groups bonded together and has an iron atom in the center.
The structure of the heme group is:
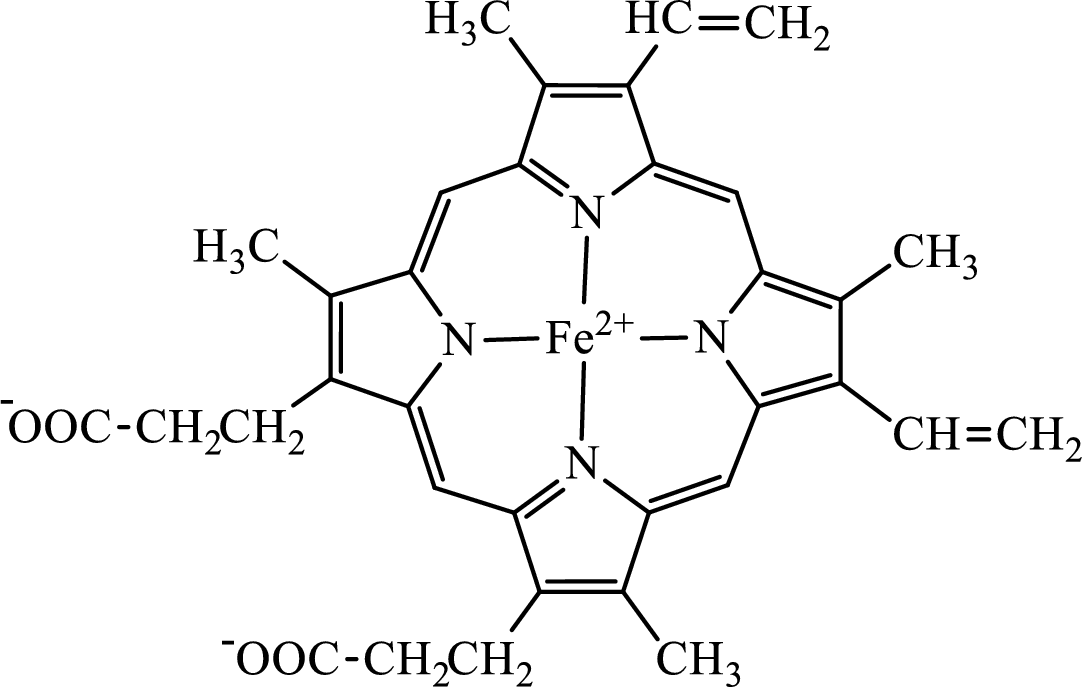
The first step of degradation of heme involves opening of pyrrole ring with the release of the iron atom and production of biliverdin. The iron atom released becomes part of ferritin protein. Biliverdin produced is converted bilirubin in the spleen. Bilirubin is then transported to the liver where attachment of sugar residues to the propionate side chains of the bilirubin occurs to make it more soluble. Then more solubilized bilirubin is excreted in bile and finally to the small intestine. In the small intestine, it is converted into stercobilin for excretion in feces or urobilin for excretion in urine.
(c)
Interpretation: To identify the heme degradation product (1) bilirubin, (2) biliverdin, (3) stercobilin, and (4) urobilin that is rendered more water soluble by use of a glucose derivative.
Concept introduction: Hemoglobin is a heme protein present in the red blood cells. The protein part is called globin and the non-protein part is heme. Heme is the prosthetic group that contains 4 pyrrole groups bonded together and has an iron atom in the center.
The first step of degradation of heme involves opening of pyrrole ring with the release of the iron atom and production of biliverdin. The iron atom released becomes part of ferritin protein. Biliverdin produced is converted bilirubin in the spleen. Bilirubin is then transported to the liver where attachment of sugar residues to the propionate side chains of the bilirubin occurs to make it more soluble. Then more solubilized bilirubin is excreted in bile and finally to the small intestine. In the small intestine, it is converted into stercobilin for excretion in feces or urobilin for excretion in urine.
The structure of the heme group is:
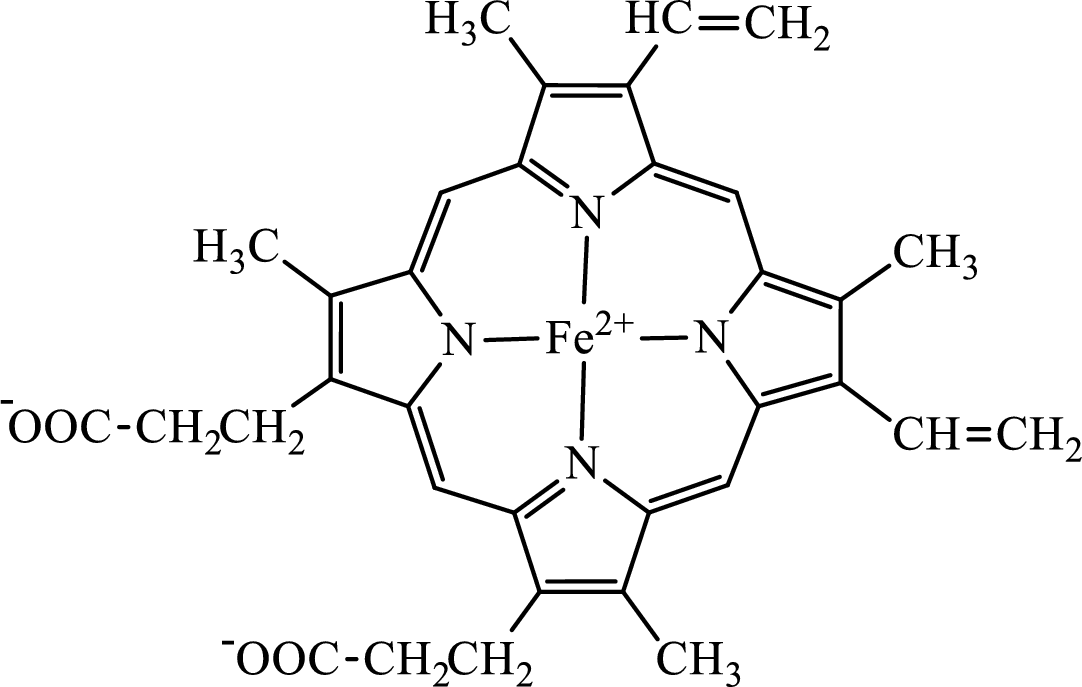
(d)
Interpretation: To identify the heme degradation product (1) bilirubin, (2) biliverdin, (3) stercobilin, and (4) urobilin which is bile pigment and has a yellowish color.
Concept introduction: Hemoglobin is a heme protein present in the red blood cells. The protein part is called globin and the non-protein part is heme. Heme is the prosthetic group that contains 4 pyrrole groups bonded together and has an iron atom in the center.
The structure of the heme group is:
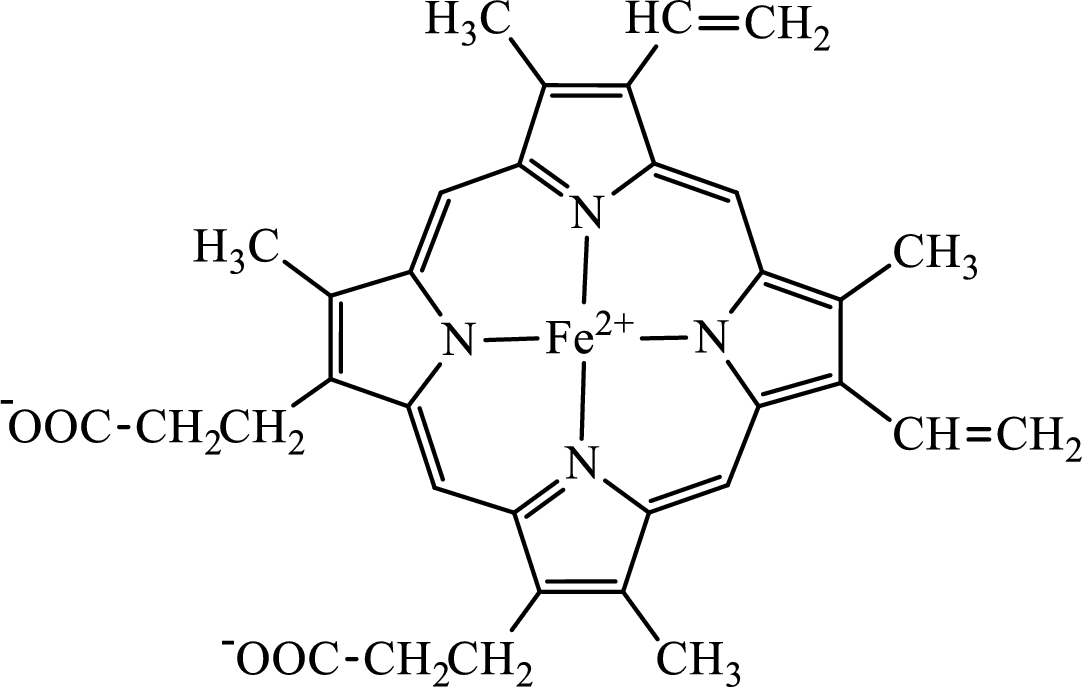
The first step of degradation of heme involves opening of pyrrole ring with the release of the iron atom and production of biliverdin. The iron atom released becomes part of ferritin protein. Biliverdin produced is converted bilirubin in the spleen. Bilirubin is then transported to the liver where attachment of sugar residues to the propionate side chains of the bilirubin occurs to make it more soluble. Then more solubilized bilirubin is excreted in bile and finally to the small intestine. In the small intestine, it is converted into stercobilin for excretion in feces or urobilin for excretion in urine.
Bile pigments are the colored degradation product of tetrapyrrole carbon arrangement of heme portion of hemoglobin. These are excreted in bile and give characteristic color to urine and feces.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 26 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Seventh Edition
- The reaction of solid dimethylhydrazine, (CH3)2N2H2, and liquefied dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4, has been investigated for use as rocket fuel. The reaction produces the gases carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), and water vapor (H2O), which are ejected in the exhaust gases. In a controlled experiment, solid dimethylhydrazine was reacted with excess dinitrogen tetroxide, and the gases were collected in a closed balloon until a pressure of 2.50 atm and a temperature of 400.0 K were reached.(a) What are the partial pressures of CO2, N2, and H2O?(b) When the CO2 is removed by chemical reaction, what are the partial pressures of the remaining gases?arrow_forwardOne liter of chlorine gas at 1 atm and 298 K reacts completely with 1.00 L of nitrogen gas and 2.00 L of oxygen gas at the same temperature and pressure. A single gaseous product is formed, which fills a 2.00 L flask at 1.00 atm and 298 K. Use this information to determine the following characteristics of the product:(a) its empirical formula;(b) its molecular formula;(c) the most favorable Lewis formula based on formal charge arguments (the central atom is N);(d) the shape of the molecule.arrow_forwardHow does the square root mean square velocity of gas molecules vary with temperature? Illustrate this relationship by plotting the square root mean square velocity of N2 molecules as a function of temperature from T=100 K to T=300 K.arrow_forward
- Draw product B, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CF3 NH2 Me O .N. + B OMearrow_forwardBenzimidazole E. State its formula. sState the differences in the formula with other benzimidazoles.arrow_forwardDraw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CN CF3 K2CO3, DMSO, H₂O2 Aarrow_forward
- 19) Which metal is most commonly used in galvanization to protect steel structures from oxidation? Lead a. b. Tin C. Nickel d. Zinc 20) The following molecule is an example of a: R₁ R2- -N-R3 a. Secondary amine b. Secondary amide c. Tertiary amine d. Tertiary amidearrow_forwardpls helparrow_forwardIndicate the product of the reaction OH OH CH3-CC- Ph + H2SO4 a 20°C | CH3 Pharrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



