
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether there is any chiral carbon atom present in the following compound opr not should be determined:
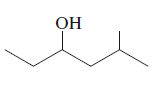
Concept introduction:
Chiral carbon atoms are the species in which a carbon is attached to all different groups.
Since, the valency of a carbon atom is four. So, every chiral carbon atom will be attached to four different groups. A chiral atom is non-superimposable on its mirror image and it is unsymmetrical in nature.
Whereas a carbon atom that is superimposable on its mirror image is called an achiral carbon atom. It is symmetrical in nature.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether there is any chiral carbon atom present in the following compound opr not should be determined:
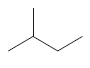
Concept introduction:
Chiral carbon atoms are the species in which a carbon is attached to all different groups.
Since, the valency of a carbon atom is four. So, every chiral carbon atom will be attached to four different groups. A chiral atom is non-superimposable on its mirror image and it is unsymmetrical in nature.
Whereas a carbon atom that is superimposable on its mirror image is called an achiral carbon atom. It is symmetrical in nature.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether there is any chiral carbon atom present in the following compound opr not should be determined:
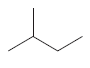
Concept introduction:
Chiral carbon atoms are the species in which a carbon is attached to all different groups.
Since, the valency of a carbon atom is four. So, every chiral carbon atom will be attached to four different groups. A chiral atom is non-superimposable on its mirror image and it is unsymmetrical in nature.
Whereas a carbon atom that is superimposable on its mirror image is called an achiral carbon atom. It is symmetrical in nature.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 26 Solutions
EBK GENERAL CHEMISTRY
- help 20arrow_forwardProvide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





