
(a)
Interpretation:
The R or S configuration to each of the chiral C atom in the given structure is to be assigned.
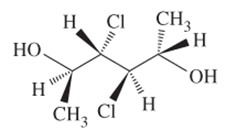
Concept introduction:
Enantiomers are optical isomers which can rotate the plane polarized light either clockwise or anticlockwise. These molecules must have at least one chiral C atom which is bonded with four different groups. They are assigned by R and S configuration. The R/S naming follows the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rules for naming the enantiomer as R or S-enantiomer. According to Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rules assign the numbers from 1 to 4 to the groups bonded with chiral C atom on the basis of their molar mass. The essential condition is that the 4th group or atom must be below the plane means with dash line. If 1(2(3 is clockwise it will be R-configuration and if it is anticlockwise it will be S-configuration.
If the 4th number group is in plane then follow these steps.
- Swap the 4 group with the group with dash line
- Assign R/S configuration with clockwise or anticlockwise movement
- Flip the configuration to get the real configuration.
If the 4th number group is in above the plane shown by wedge line then follow these steps.
- Swap the 4 group with the group with dash line.
- Assign R/S configuration with clockwise or anticlockwise movement.
(b)
Interpretation:
The R or S configuration to each of the chiral C atom in the given structure should be assigned.
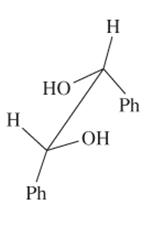
Concept introduction:
Enantiomers are optical isomers which can rotate the plane polarized light either clockwise or anticlockwise. These molecules must have at least one chiral C atom which is bonded with four different groups. They are assigned by R and S configuration. The R/S naming follows the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rules for naming the enantiomer as R or S-enantiomer. According to Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rules assign the numbers from 1 to 4 to the groups bonded with chiral C atom on the basis of their molar mass. The essential condition is that the 4th group or atom must be below the plane means with dash line. If 1(2(3 is clockwise it will be R-configuration and if it is anticlockwise it will be S-configuration.
If the 4th number group is in plane then follow these steps.
- Swap the 4 group with the group with dash line
- Assign R/S configuration with clockwise or anticlockwise movement
- Flip the configuration to get the real configuration.
If the 4th number group is in above the plane shown by wedge line then follow these steps.
- Swap the 4 group with the group with dash line.
- Assign R/S configuration with clockwise or anticlockwise movement.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 26 Solutions
EBK GENERAL CHEMISTRY
- Can you please explain why the answer is structures 2 and 3? Please include a detailed explanation and show how the synthesis can be done with those two structures.arrow_forwardCan you please explain why the correct answer to this question is option 2? I am having trouble understanding how and why. Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing of how the diene and dienophile would create the product in the question.arrow_forwardCan you please explain why the correct answer is molecules 2 and 4? Base your explanation off of the rules for aromaticity and well as the principles of the Huckel rule of aromaticity. Please give a detailed explanation of what Hucekl's rule is.arrow_forward
- Can you please explain why the answer is B and not A? I chose A because I thought the thermodynamic product was a 1,4-addition. Please give a detailed explanation to this problem and include a drawing of how the reaction works.arrow_forwardLabel the diagram according to the components and processes of an alkaline batteryarrow_forwardCan you please explain why the answer to the question is option 4? Please include the aromaticity rules as well as Huckel's rule. Please label molecules 1, 2, 3, and 5 with their respective labels of aromatic or nonaromatic and why.arrow_forward
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardCan you please explain why the correct answer is molecules 2 and 4? Please provide a detailed explanation as well as the two molecules drawn showing what and where it is conjugated.arrow_forwardCan you please explain why the correct answer is (2E, 4Z, 6Z)-2,4,6-Nonatriene? Please include a detailed explanation and a drawing of the structure, with the corresponding parts of the answer labeled. I'm confused why 6 is Z and why it is Nonatriene.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





