
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780134015187
Author: John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 25, Problem 25.11UKC
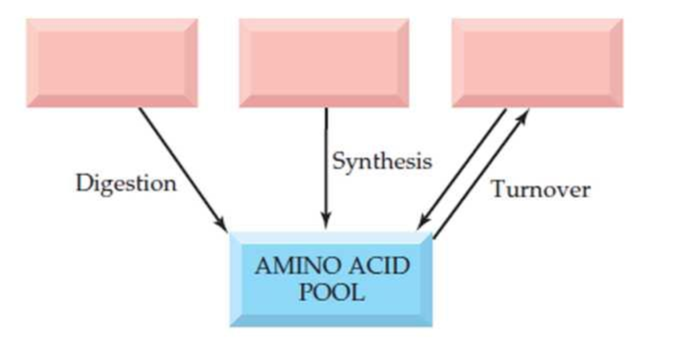
In the diagram shown here, fill in the sources for the amino acid pool.
Expert Solution & Answer
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The missing sources for the amino acids pool has to be filled.
Concept introduction:
- Amino acid had both amino functional group and carboxyl functional group in a molecule.
- Amino acid pool is the entire collection of free amino acids in the whole body.
Explanation of Solution
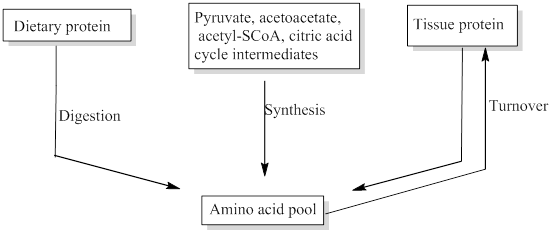
Free amino acids are present throughout the body, in cells and the extracellular fluids. This pool is supplied by few sources include,
- Non-protein nitrogen compounds
- Dietary protein
- Tissue protein etc.
Conclusion
The missing sources for the amino acids pool was filled.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Students have asked these similar questions
Can you help me with question 4
Determine Km and Vmax from the michaelis menten graph
Determine the Km and Vmax from the lineweuver burk graph
Chapter 25 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
Ch. 25.2 - Prob. 25.1PCh. 25.2 - Prob. 25.2KCPCh. 25.3 - Prob. 25.3PCh. 25.3 - Prob. 25.4PCh. 25.3 - Prob. 25.5PCh. 25.3 - Prob. 25.6PCh. 25.4 - Prob. 25.1CIAPCh. 25.4 - Prob. 25.2CIAPCh. 25.4 - Prob. 25.3CIAPCh. 25.4 - Prob. 25.7P
Ch. 25.4 - Prob. 25.8KCPCh. 25.6 - Prob. 25.9PCh. 25.6 - Prob. 25.10KCPCh. 25.6 - What is meant by a conditional amino acid?Ch. 25.6 - Prob. 25.5CIAPCh. 25.6 - Prob. 25.6CIAPCh. 25 - In the diagram shown here, fill in the sources for...Ch. 25 - Prob. 25.12UKCCh. 25 - Prob. 25.13UKCCh. 25 - Prob. 25.14UKCCh. 25 - Prob. 25.15UKCCh. 25 - Prob. 25.16UKCCh. 25 - Prob. 25.17APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.18APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.19APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.20APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.21APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.22APCh. 25 - What is the structure of the -keto acid formed...Ch. 25 - Prob. 25.24APCh. 25 - In general, how does oxidative deamination differ...Ch. 25 - Prob. 25.26APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.27APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.28APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.29APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.30APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.31APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.32APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.33APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.34APCh. 25 - How do essential and nonessential amino acids...Ch. 25 - Prob. 25.36APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.37APCh. 25 - How is tyrosine biosynthesized in the body? What...Ch. 25 - Prob. 25.39APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.40APCh. 25 - Prob. 25.41APCh. 25 - What energy source is used in the formation of...Ch. 25 - Write the equation for the transamination reaction...Ch. 25 - Prob. 25.44CPCh. 25 - Prob. 25.45CPCh. 25 - Prob. 25.46CPCh. 25 - Prob. 25.47CPCh. 25 - Prob. 25.48CPCh. 25 - Prob. 25.49CPCh. 25 - Prob. 25.50CPCh. 25 - Prob. 25.51CPCh. 25 - Prob. 25.52CPCh. 25 - Why might it be a bad idea to take large...Ch. 25 - Prob. 25.54GPCh. 25 - Prob. 25.55GPCh. 25 - Prob. 25.56GP
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
Organic Chemistry
What process causes the Mediterranean intermediate Water MIW to become more dense than water in the adjacent At...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Why do scientists think that all forms of life on earth have a common origin?
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Separate the list P,F,V,,T,a,m,L,t, and V into intensive properties, extensive properties, and nonproperties.
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Identify each of the following reproductive barriers as prezygotic or postzygotic. a. One lilac species lives o...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Do schwann cells produce or act as myelin in the peripheral nervous system? I know that they encase and wrap around axons, but where does the myelin come into play?arrow_forwardThe enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactatein skeletal muscle cells using NAD/NADH during anaerobic “balanced” fermentation.Answer the following questions about this reaction. (a) Write out the two reductive half reactions and indicate the E ̊' for each half reaction. Write out the full balanced reaction for the pyruvate to lactate rxn and indicate the ∆E ̊' for the reaction. (b) What is the free energy change under standard state conditions for thisreaction? Which direction is spontaneous?(c) Assume that in skeletal muscle cells the ratio of [NAD+] to [NADH] is 100, and that the[pyruvate] = 0.40 mM and [lactate] = 4.0 mM. What is the free energy change (∆G')for the conversion of pyruvate to lactate? Indicate the direction in which the reactionis spontaneous under these cellular conditions.arrow_forwardWhy did the authors worry about the temperature-dependent solubility of the carriers in thebilayer? How did the authors determine whether the effect of freezing the lipid bilayer wasto decrease the solubility of the carriers (nonactin and valinomycin) or whether the effectwas to impair their ability to diffuse through the membrane (decrease their mobility)?arrow_forward
- Kranse et. al. measured the temperature dependence of conductance using membranescontaining the phospholipids glyceryl dipalmitate and glyceryl distearate. Describe themodifications in membrane content that you would employ to: (a) shift the temperature of the phase transition (b) make the ion conductance curve for valinomycin andnonactin more like that of gramicidinarrow_forwardObtain the sequence for the 5-HT receptor HTR1A and generate a hydropathy plot usingthe ExPASY tool ProtScale, the appropriate window, and the Kyte-Doolittle weightingalgorithm. How many transmembrane domains are present in this receptor? Attach yourhydropathy plot to your assignment.arrow_forwardCompare and contrast the structural features of the ion carrier valinomycin with those of achannel former like gramicidin. How does structural information help explain the mechanismby which these molecules conduct ions across membranes?arrow_forward
- A typical integral membrane protein has a stretch (or stretches) of ~20 hydrophobic aminoacids that form an α-helix that spans the bilayer (as is found in membrane proteins such asglycophorin A and bacteriorhodopsin). Compare and contrast the molecular and structural features of gramicidin with a membrane-spanning α-helix. Explain how gramicidin can forman ion channel when a typical membrane-spanning α-helix cannot (eg, glycophorin A).arrow_forwardThe titration curve of alanine shows the ionization of two functional groups with pK values of 2.34 and 9.69, corresponding to the ionization of the carboxyl and the protonated amino groups, respectively. The titration of di-, tri-, and larger oligopeptides of alanine also shows the ionization of only two functional groups, although the experimental pK values are different. The table summarizes the trend in pK values. Amino acid or peptide Ala Ala-Ala pKj pk₂ 2.34 9.69 3.12 8.30 Ala-Ala-Ala 3.39 8.03 Ala-(Ala)-Ala, n ≥ 4 3.42 7.94 Modify the molecules to show the oligopeptide Ala-Ala-Ala. You can modify the molecules by moving, adding, deleting, or changing atoms, bonds, or charges. C Select c Draw Templates More H с N 0 S Cl H H | | || H CH3 H CH, H CH₂ Complete the statements about the the pK, values of the Ala-Ala-Ala oligopeptide. The pK₁ value of 3.39 is associated with the -COO group of Ala-Ala-Ala. The pK2 value of 8.03 is associated with the -NH group of Ala-Ala-Ala. Erase Q2 Q…arrow_forwardFacts from the bacterium mals and to dept kan apa in a peptide with antidic properties. This peptide complex with the call membrance of other hacterial species, leading in bacterial death The structure of the peptide has been determined from (a) Cmplete acid hydes of the peptide, followed by amino acid analys, yielded quiar anunt of Lan, Om, Pfx, Prxa, and Wall Cmtiti, an amino acid od prosentin pockets but present in some peptides. Com has the tracture H *H,N-CH-CH-CH, -C- COO (b) The weight of the peptide in approximately 1,200 Th (c) The peptide failed to undergo hydrolysis when treated with the Hydrolysis of the carbonyl-terminal residue of a polypeptide une "NH, the year. This call there Pro or the police does not contain a froz (d) Treatment of the peptide with 1-haw-2,4-dicherer (11N1), followed by complete hydrolysis and ched only from and the derivative NO, Н ON NHCHI CH, CH, C coo +NH, (Hint: The 2,4-diphenyl derivative involves the amino group of a side chain rather than the…arrow_forward
- Electrophoresis Macmillan Learning Chymotrypsin is a protease with a molecular mass of 25.6 kDa. The figure shows a stained SDS polyacrylamide gel with a single band in lane I and three bands of lower molecular weight in lane 2. Lane I contains a preparation of chymotrypsin and lane 2 contains chymotrypsin pre-treated with performic acid. 1 2 Why does performic acid treatment of chymotrypsin generate three bands in lane 2? ° Chymotrypsin self-digests on the carboxyl-terminal side of phenylalanine, tryptophan, or tyrosine residues. The three peptides are impurities in the original chymotrypsin sample. Performic acid cleaves proteins on the carboxyl-terminal side of lysine and arginine residues. Performic acid cleaves the disulfide bonds holding together the three subunits of chymotrypsin. Correct Answerarrow_forwardExtracts from the bacterium Bacillus brevis contain a peptide with antibiotic properties. This peptide forms complexes with metal ions and seems to disrupt ion transport across the cell membranes of other bacterial species, leading to bacterial death. The structure of the peptide has been determined from a series of observations. (a) Complete acid hydrolysis of the peptide, followed by amino acid analysis, yielded equimolar amounts of Leu, Orn, Phe, Pro, and Val. Orn is ornithine, an amino acid not present in proteins but present in some peptides. Orn has the structure H 'H,N-CH, - CH2 CH2 CH2 - C - COO- NH, (b) The molecular weight of the peptide is approximately 1,200 Da. (c) The peptide failed to undergo hydrolysis when treated with the enzyme carboxypeptidase. This enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of the carboxyl-terminal residue of a polypeptide unless the residue is Pro or the peptide does not contain a free carboxyl group. (d) Treatment of the intact peptide with…arrow_forwardAt a pH equal to the isoelectric point (pl) of alanine, the net charge of alanine is zero. Two structures can be drawn that have a net charge of zero, but the predominant form of alanine at its pl is zwitterionic. CH3 H,N CH3 ** H¸N-C H Zwitterionic H Uncharged OH Select statements that explain why alanine is predominantly zwitterionic at its pl. pk of alanine's amino group is more than its pl. pk of alanine's carboxyl group is more than its pl. PK of alanine's carboxyl group is less than its pl. pk of alanine's amino group is less than its pl. Correct Answer What fraction of alanine is in the completely uncharged form at its pl? 1 in 2.2 × 107 1 in 1.6 × 10² 1 in 4680 1 in 9460arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning


Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Cell Membrane; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AsffT7XIXbA;License: Standard youtube license