
(a)
Interpretation:
The group, period and the metallic character of element should be identified.
Concept introduction:
The periodic table is given below,
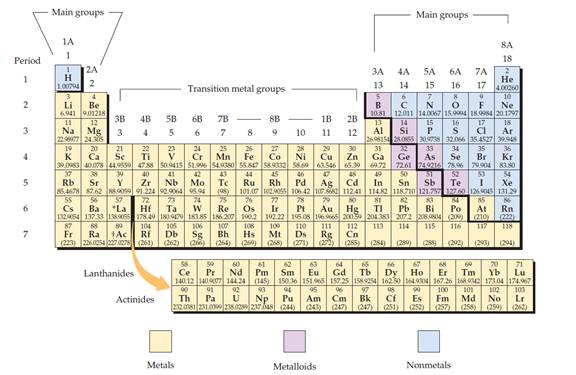
Figure 1
The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbitals.
Metal:
A metal is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, has a shiny appearance. Metal has the capacity to conducts the electricity and heat. Metals are malleable or ductile.
Non-metal:
Non-metal is an element that mostly absences metallic character.
Metalloid:
Metalloid is one of the types of chemical element, which has properties in between, or that are a mixture of metals and nonmetals.
Alkali metals:
Alkali metals are a group (column) in the periodic table is lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr).
Alkaline earth metals:
Alkaline earths metals are group two of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).
(b)
Interpretation:
The group, period and the metallic character of element should be identified.
Concept introduction:
The periodic table is given below,
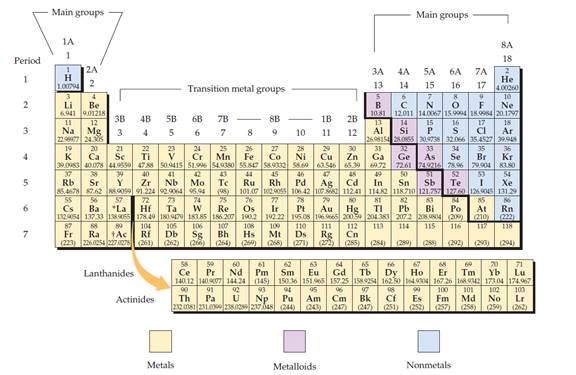
The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbitals.
Metal:
A metal is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, has a shiny appearance. Metal has the capacity to conducts the electricity and heat. Metals are malleable or ductile.
Non-metal:
Non-metal is an element that mostly absences metallic character.
Metalloid:
Metalloid is one of the types of chemical element, which has properties in between, or that are a mixture of metals and nonmetals.
Alkali metals:
Alkali metals are a group (column) in the periodic table is lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr).
Alkaline earth metals:
Alkaline earths metals are group two of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
- Imagine that aldolase can react with the seven carbon molecule Sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphate (below). Use the mechanism to predict the two products generated. Please draw out the stereochemistry in a fischer projection.arrow_forwardSodium borohydride (NaBH4) is a potent inhibitor of aldolase. It is known to ONLY inhibit theenzyme when it is complexed with substrate. Treatment of the enzyme alone has no effect.What is the mechanism for this inhibition? Please draw out the mechanism and show how it inhibits this.arrow_forwardShow the fate of the proton on the 4-Oxygen molecule of F-1,6-BP. Please include a drawing showing the electron flow that occurs.arrow_forward
- 1. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following aldol condensation? O NaOH, H₂O heat A B C D Earrow_forwardAn organic chemist ordered the wrong item. She wanted to obtain 1-hydroxy-2-butanone, butinstead ordered 2-hydroxybutyraldehyde. As a good biochemist, show how the organic chemistcould use biological catalysis to make her desired compound. Please show the mechanism by drawing.arrow_forwardShow the fate of the hydrogen on carbon-2 of glucose. Please draw out the structure using curve arrows to show electron flow.arrow_forward
- 3. Which one of the compounds below is the major product formed by the reaction sequence shown here? CH3 + CH3NO2 NaOH H2, Ni ? nitromethane acetophenone OH OH HO HN- u x x x x Ph A HO -NH2 HO H Ph Ph Ph N- H B Ph NH2 D Earrow_forward4. Only ONE of the five compounds below can be prepared by an aldol condensation in which a single carbonyl compound is treated with base. Which one is it? To solve this problem, reverse the aldol condensation that formed each of these molecules to find out what two molecules came together to make the products. The one in which the two molecules are identical is the answer. Ph Ph ཚིག གནས ག ནཱ ཀ ན ཀནཱ A Ph H B Ph Ph H D Ph. Ph Ph E Harrow_forward5. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence? First, equimolar amounts of cyclopentanone and LDA are mixed at -78°C. Then propionaldehyde (propanal) is added. Addition of aqueous acid completes the process. LDA, -78°C. 1. 2. H₂O* H A B H 0 D H H Earrow_forward
- 2. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction? NaOH, H₂O heat A B C D Earrow_forwardCH3CH2CHO + propanal PhCH2CHO 2-phenylacetaldehyde mixture of four products NaOH 10. In the crossed aldol reaction of propanal and 2-phenylacetaldehyde shown above, a mixture of four products will be formed. Which ONE of the compounds below will NOT be formed in this crossed aldol reaction? OH Ph A H OH OH Ph H B OH OH H H H Ph Ph C Ph D Earrow_forwardAn organic chemist ordered the wrong item. She wanted to obtain 1-hydroxy-2-butanone, butinstead ordered 2-hydroxybutyraldehyde. As a good biochemist, show how the organic chemistcould use biological catalysis to make her desired compound.arrow_forward
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning





