
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 24.6, Problem 2TH
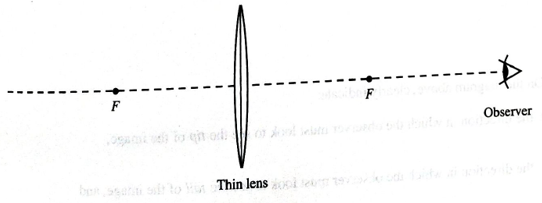
In section III of the tutorial Magnification, you used a convex lens as a magnifying glass.
Is the expression that you derived in problem 1 above for the lateral magnification, m, also valid in this case? If not, what expression holds in this case? Draw a diagram below to support your answer.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In the movie Fast X, a 10100 kg round bomb is set rolling in Rome. The bomb gets up to 17.6 m/s. To try to stop the bomb, the protagonist Dom swings the counterweight of a crane, which has a mass of 354000 kg into the bomb at 3.61 m/s in the opposite direction. Directly after the collision the crane counterweight continues in the same direction it was going at 2.13 m/s. What is the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the bomb right after the collision?
Don't use ai
Make sure to draw a sketch with scale please
Chapter 24 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 24.1 - On the diagram, sketch what you would see on the...Ch. 24.1 - The small bulb is replaced by three longfilament...Ch. 24.1 - The three longfilament bulbs are replaced by a...Ch. 24.1 - Predict the size and shape of the shadow that will...Ch. 24.1 - Is it possible to place the bulb in another...Ch. 24.1 - Prob. 2cTHCh. 24.1 - Prob. 2dTHCh. 24.1 - Prob. 3aTHCh. 24.1 - A student is looking at the building shown at...Ch. 24.1 - Prob. 4aTH
Ch. 24.1 - Suppose that this student were walking through the...Ch. 24.2 - The top view diagrams at right were drawn by a...Ch. 24.2 - Draw a ray diagram to determine the location of...Ch. 24.2 - Describe how you could use a ray diagram to...Ch. 24.2 - A pencil is placed in front of a plane mirror as...Ch. 24.2 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 24.3 - Prob. 1aTHCh. 24.3 - A pin is placed in front of a semicylindrical...Ch. 24.3 - Prob. 1cTHCh. 24.3 - Prob. 2aTHCh. 24.3 - A very small, very bright bulb is placed for from...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - Prob. 2THCh. 24.4 - Prob. 3aTHCh. 24.4 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 24.4 - Is the image(s) of the nail real or virtual?...Ch. 24.5 - Suppose that the bulb is placed as shown. Using...Ch. 24.5 - Prob. 1bTHCh. 24.5 - Prob. 1cTHCh. 24.5 - Prob. 1dTHCh. 24.5 - Prob. 2aTHCh. 24.5 - Treat the image produced by lens 1 as an object...Ch. 24.5 - Repeat parts a andb for the case in which lens 2...Ch. 24.6 - Reproduced below is a side view diagram of the...Ch. 24.6 - In section III of the tutorial Magnification, you...Ch. 24.6 - Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged...Ch. 24.6 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 24.6 - Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged...Ch. 24.6 - Prob. 3dTHCh. 24.6 - Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The bond angles in a regular polygon with n sides are equal to 180360n a. What are the bond angles in a regular...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
19. A car starts from rest at a stop sign. It accelerates at 4.0 m/s2 for 6.0 s, coasts for 2.0s, and then slow...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
28. The maximum allowed leakage of microwave radiation from a microwave oven is 5.0 mW/cm2. If microwave radiat...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Which coastal area experiences the smallest tidal range? ____________
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
2. Define equilibrium population. Outline the conditions that must be met for a population to stay in genetic e...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
All of the following processes are involved in the carbon cycle except: a. photosynthesis b. cell respiration c...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Make sure to draw a sketch with scalearrow_forwardUltimate Byleth and Little Mac fight. Little Mac, who is a boxer, dashes forward at 26.6 m/s, fist first. Byleth moves in the opposite direction at 3.79 m/s, where they collide with Little Mac’s fist. After the punch Byleth flies backwards at 11.1 m/s. How fast, and in what direction, is Little Mac now moving? Little Mac has a mass of 48.5 kg and Byleth has a mass of 72.0 kg.arrow_forwardMake sure to draw a sketch with scale as wellarrow_forward
- Make sure to draw a sketch with scale pleasearrow_forwardKirby jumps towards his enemy/ally, Meta Knight, at 2.06 m/s while Meta Knight glides in the opposite direction (toward Kirby) at 5.06 m/s. Kirby then begins to inhale, swallowing Meta Knight. What is Kirby/Meta Knight’s velocity immediately after being swallowed? Please put the magnitude of the velocity and then mark direction using dropdown menu. Kirby has a mass of 0.283 kg and Meta Knight has a mass of 0.538 kg.arrow_forwardNo Aiarrow_forward
- Can someone help mearrow_forwardNeed help on the following questions on biomechanics. (Please refer to images below)A gymnast weighing 68 kg attempts a handstand using only one arm. He plants his handat an angle resulting in the reaction force shown.A) Find the resultant force (acting on the Center of Mass)B) Find the resultant moment (acting on the Center of Mass)C) Draw the resultant force and moment about the center of mass on the figure below. Will the gymnast rotate, translate, or both? And in which direction?arrow_forwardPlease help me on the following question (Please refer to image below)An Olympic lifter (m = 103kg) is holding a lift with a mass of 350 kg. The barexerts a purely vertical force that is equally distributed between both hands. Each arm has amass of 9 kg, are 0.8m long and form a 40° angle with the horizontal. The CoM for each armis 0.5 m from hand. Assuming the lifter is facing us in the diagram below, his right deltoidinserts 14cm from the shoulder at an angle of 13° counter-clockwise from the humerus.A) You are interested in calculating the force in the right deltoid. Draw a free body diagramof the right arm including the external forces, joint reaction forces, a coordinate system andstate your assumptions.B) Find the force exerted by the right deltoidC) Find the shoulder joint contact force. Report your answer using the magnitude and directionof the shoulder force vector.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Convex and Concave Lenses; Author: Manocha Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CJ6aB5ULqa0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY