
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 24.4, Problem 1cTH
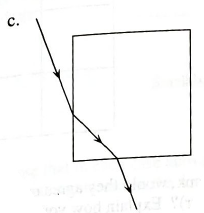
The following are top view diagrams of solid cylinders and cubes. Assume that light travels more slowly through the objects than through the surrounding medium.
Each diagram shows a path for light that is not qualitatively correct; there is at least one flaw, perhaps more, in each diagram. Identify all flaws. Explain your reasoning.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
One well-known image of a prism is the following picture
a. Given the pattern of light on the far side of the prism, is the index of refraction
inside the prism higher or lower than the index of refraction outside the prism?
b. List at least one thing that is wrong with this diagram given what we expect the
dependence of n on the wavelength of light to be (and assuming the prism is
made of a uniform material).
c. List at least one thing that is right with this diagram given what we expect the
dependence of n on the wavelength of light to be (and assuming the prism is
made of a uniform material).
Read the following problem and solve the following questions. Show your complete solutions legibly and concisely in the space provided.
A light is traveling from air into an optic fiber having an index of refraction of 1.44.
a. Which direction should the light bend?
b. Given a 22 degree angle of incidence on the end of the fiber, what is the angle of refraction inside the fiber?
c. Make a sketch of the path of life as the media changes.
Please only answer question 9. I included question 8 as well to give the background of the question. Please give a detailed explanation for why the total internal reflection occurs when the incident angle is greater than the critical angle. Please explain each step carefully with good reasoning.
Chapter 24 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 24.1 - On the diagram, sketch what you would see on the...Ch. 24.1 - The small bulb is replaced by three longfilament...Ch. 24.1 - The three longfilament bulbs are replaced by a...Ch. 24.1 - Predict the size and shape of the shadow that will...Ch. 24.1 - Is it possible to place the bulb in another...Ch. 24.1 - Prob. 2cTHCh. 24.1 - Prob. 2dTHCh. 24.1 - Prob. 3aTHCh. 24.1 - A student is looking at the building shown at...Ch. 24.1 - Prob. 4aTH
Ch. 24.1 - Suppose that this student were walking through the...Ch. 24.2 - The top view diagrams at right were drawn by a...Ch. 24.2 - Draw a ray diagram to determine the location of...Ch. 24.2 - Describe how you could use a ray diagram to...Ch. 24.2 - A pencil is placed in front of a plane mirror as...Ch. 24.2 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 24.3 - Prob. 1aTHCh. 24.3 - A pin is placed in front of a semicylindrical...Ch. 24.3 - Prob. 1cTHCh. 24.3 - Prob. 2aTHCh. 24.3 - A very small, very bright bulb is placed for from...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - Prob. 2THCh. 24.4 - Prob. 3aTHCh. 24.4 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 24.4 - Is the image(s) of the nail real or virtual?...Ch. 24.5 - Suppose that the bulb is placed as shown. Using...Ch. 24.5 - Prob. 1bTHCh. 24.5 - Prob. 1cTHCh. 24.5 - Prob. 1dTHCh. 24.5 - Prob. 2aTHCh. 24.5 - Treat the image produced by lens 1 as an object...Ch. 24.5 - Repeat parts a andb for the case in which lens 2...Ch. 24.6 - Reproduced below is a side view diagram of the...Ch. 24.6 - In section III of the tutorial Magnification, you...Ch. 24.6 - Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged...Ch. 24.6 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 24.6 - Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged...Ch. 24.6 - Prob. 3dTHCh. 24.6 - Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
*Speedomter The speedometer on an automobile measures the rotational speed of the axie and converts that to a l...
College Physics
A small mass measuring device (SMMD) used for research on the biological effects of spaceflight consists of a s...
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
How much energy can be stored in a spring with k = 320 N/m if the maximum allowed stretch is 18 cm?
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
30, (II) A scuba diver and her gear displace a volume of 69.6 L and have a total mass of 72.8 kg. (a) What is t...
Physics: Principles with Applications
An athlete can jump a distance of 8.0 m in the broad jump. What is the maximum distance the athlete can jump, o...
University Physics Volume 1
47. Walking in a boat. A 45.0 kg woman stands up in a 60.0 kg canoe of length 5.00 m. She walks from a point 1....
College Physics (10th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The goal of this exercise is to construct the best rectangular prism containers by a company. 1. The first container they construct will be used to ship baseballs. It will have a width of x ft, a length of (x + 6) ft and a height of (x- 2) ft. Its volume will be 455 ft 3. Write a function V for the volume of the container. Then find one possible width for the container. Explain. 2. Are there any other possible widths for the container? Explain.arrow_forwardFor the next two questions, as seen in the image below, two materials A (na = 1.25) and B ( 1.75) are stacked (ray angles for illustration only). A B 1. Monochromatic light hits A at an angle theta, -30° from the normal. What is the angle of refraction of light that gets to come out from B? A. None (total internal reflection occurs at B) B. 60° C. 30° D. 15° 2. Suppose we want to induce the total internal reflection of light in this system by changing either material A, B or adding another material below material B. Which of the following changes would induce total internal reflection? A. Adding a layer of material A below material B. B. Replacing material A with material B. C. Removing material B. D. None of the above.arrow_forwarda. Given the pattern of light on the far side of the prism, is the index of refraction inside the prism higher or lower than the index of refraction outside the prism? b. List at least one thing that is wrong with this diagram given what we expect the dependence of n on the wavelength of light to be (and assuming the prism is made of a uniform material). c. List at least one thing that is right with this diagram given what we expect the dependence of n on the wavelength of light to be (and assuming the prism is made of a uniform material).arrow_forward
- Please write out equationarrow_forwardPreliminary Questions 1. Is the image projected on a movie screen real or virtual? What about the image of yourself seen in a bathroom mirror? 2. Hold a shiny spoon in front of you. What differences do you notice about the image of your face seen in the convex and concave sides? 3. Where are the images formed by each side of the spoon? In front or behind the spoon? (Try the parallax method. Look at the image of an overhead light. Hold the tip of a pencil where think the image is. Move your head from side to side. If the image and pencil tip appear to you move relative to each other, adjust the position of the pencil back and forth until they appear to move as one.)arrow_forwardLight of wavelength 589x10°m is incident on crown class. Which equation would you use to calculate the frequency of that light? What is the frequency of the light that is incident on the crown glass? Which equation would you use to determine the velocity of light in the crown glass? Calculate the velocity of the light in the crown glass. Refer the to formula sheet for the index of refraction.arrow_forward
- Need Short Answers 1. We have a green object explain what we see when: (a) white light fall on it , blue light falls on it, green light falls on it , yellow light falls on it 2. why does a fisherman aim at the tail of fish, during spear fishing? explain 3. Speed of light again becomes 3x10^8 m/s when it emerges out in air from denser material without the loss of energy. why? 4. why does a ray of light bend when it travels from one medium to another mediumarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements are true? Choose all that apply. O If light from a star passes through an exoplanet's atmosphere, we can look at the absorption spectra to determine what elements & compounds are in the atmosphere. O For a telescope, decreasing f, will increase the actual size of the image seen by the person looking through the telescope. O In crown glass, the index of refraction for blue light is 1.524 and for green light it is 1.519. Thus in crown glass, blue light is slower than green light. O If unpolarized light is incident on a polarizer, 0% will pass through. O The glasses for farsighted people create virtual images for them to see. O The smaller the diameter of an optic is, the larger the minimum angle it can discern is.arrow_forwardUse the dimensions in the figure to estimate the range of values for the radius of curvature of the reflective surface.Express your answers in millimeters in ascending order separated by a comma.arrow_forward
- Problem 3: In the figure below, an image of the object is formed by the following 2 steps: 1. Light from the object first refracts through the diverging lens. 2. This refracted light then refracts through the converging lens. (a) What is g2? The location of the final image, as measured from the converging lens? (b) What is the magnification of the final image? (c) Sketch a ray diagram for this problem. Make sure to include 2 ray diagrams. The first ray diagram is for Step 1 above and the second ray diagram is for Step 2 above. fi = 30 ст f2 = 3 —10 ст Object 50 ст d 3 90 стarrow_forwardGlass is semi circular. I am shining the light through the curved side and then measuring the refraction when it leaves the glass block at the flat side. a.) solve the index of refraction of the glass using table 2 (through the curved side). b.) find the critical angle c.) find the velocity of light inside the glassarrow_forwardTwo flat mirrors are connected to each other such that they make an angle of ψ. A laser enters the system and first reflects off the bottom mirror, then the top mirror. When the beam exits it makes an angle of θ = 106 degrees with respect to the initial beam (see figure). Write an expression for the angle, ψ, between the mirrors.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
AP Physics 2 - Geometric Optics: Mirrors and Lenses - Intro Lesson; Author: N. German;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=unT297HdZC0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY