
Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged as shown below. Two rays from the tip of the object are drawn in order to determine the location of the image produced by lens 1. Lens 2 is placed so that one of its focal points coincides with the location of the image produced by lens 1.
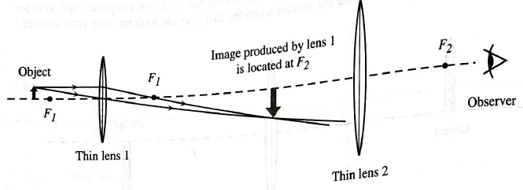
c. On the diagram above, clearly indicate:
• the direction in which the observer must look to see the tip of the image,
• the direction in which the observer must look to See the tail of the image, and
• an angle that represents the angular size of the entire image seen by the observer.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 24 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- A block of mass m₁ = 10.0 kg is connected to a block of mass m₂ = 34.0 kg by a massless string that passes over a light, frictionless pulley. The 34.0-kg block is connected to a spring that has negligible mass and a force constant of k = 200 N/m as shown in the figure below. The spring is unstretched when the system is as shown in the figure, and the incline is frictionless. The 10.0-kg block is pulled a distance h = 22.0 cm down the incline of angle 0 = 40.0° and released from rest. Find the speed of each block when the spring is again unstretched. m/s Vm1 Vm2 m/s mi m2 k iarrow_forwardTruck suspensions often have "helper springs" that engage at high loads. One such arrangement is a leaf spring with a helper coil spring mounted on the axle, as in the figure below. The helper spring engages when the main leaf spring is compressed by distance yo, and then helps to support any additional load. Consider a leaf spring constant of 5.45 × 105 N/m, helper spring constant of 3.60 × 105 N/m, and y = 0.500 m. Truck body Dyo Axle (a) What is the compression of the leaf spring for a load of 4.90 × 105 N? m (b) How much work is done compressing the springs? ]arrow_forwardA skier of mass 75 kg is pulled up a slope by a motor-driven cable. (a) How much work is required to pull him 50 m up a 30° slope (assumed frictionless) at a constant speed of 2.8 m/s? KJ (b) What power (expressed in hp) must a motor have to perform this task? hparrow_forward
- A block of mass 1.4 kg is attached to a horizontal spring that has a force constant 900 N/m as shown in the figure below. The spring is compressed 2.0 cm and is then released from rest. a x = 0 x b (a) A constant friction force of 4.4 N retards the block's motion from the moment it is released. Using an energy approach, find the position x of the block at which its speed is a maximum. cm (b) Explore the effect of an increased friction force of 13.0 N. At what position of the block does its maximum speed occur in this situation? cmarrow_forwardA block of mass m = 3.00 kg situated on a rough incline at an angle of 0 = 37.0° is connected to a spring of negligible mass having a spring constant of 100 N/m (see the figure below). The pulley is frictionelss. The block is released from rest when the spring is unstretched. The block moves 11.0 cm down the incline before coming to rest. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between block and incline. k=100 N/m Ө marrow_forward23. What is the velocity of a beam of electrons that goes undeflected when passing through perpendicular electric and magnetic fields of magnitude 8.8 X 103 V/m and 7.5 X 10-3 T. respectively? What is the radius of the electron orbit if the electric field is turned off?arrow_forward
- 10. A light bulb emits 25.00 W of power as visible light. What are the average electric and magnetic fields from the light at a distance of 2.0 m?arrow_forward9. Some 1800 years ago Roman soldiers effectively used slings as deadly weapons. The length of these slings averaged about 81 cm and the lead shot that they used weighed about 30 grams. If in the wind up to a release, the shot rotated around the Roman slinger with a period of .15 seconds. Find the maximum acceleration of the shot before being released in m/s^2 and report it to two significant figures.arrow_forwardIn the movie Fast X, a 10100 kg round bomb is set rolling in Rome. The bomb gets up to 17.6 m/s. To try to stop the bomb, the protagonist Dom swings the counterweight of a crane, which has a mass of 354000 kg into the bomb at 3.61 m/s in the opposite direction. Directly after the collision the crane counterweight continues in the same direction it was going at 2.13 m/s. What is the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the bomb right after the collision?arrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





