
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To indicate whether the statement “
Concept introduction: Glucose is a monosaccharide with the molecular formula
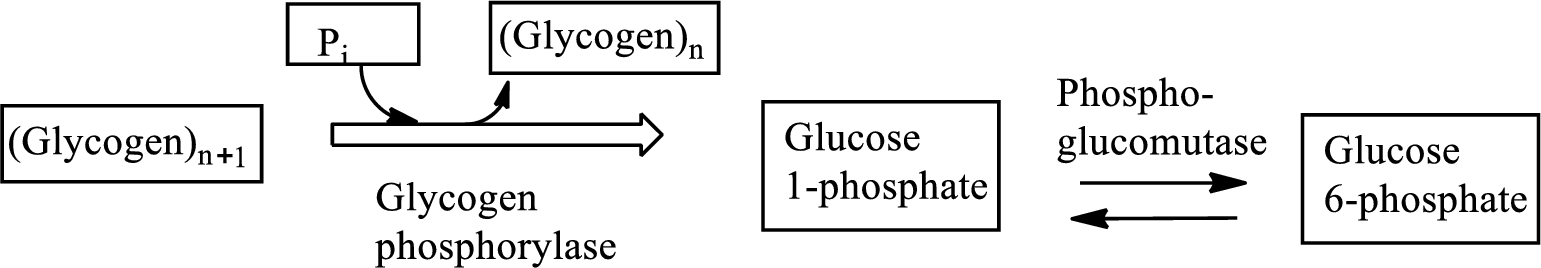
Glycogenolysis is the
An intermediate is defined as the transient species that is formed from the reactants in the preceding step and gets consumed in the subsequent steps to generate the products. An intermediate is formed within a multi-step reaction mechanism.
In the isomerization reaction, a molecule transformed itself to another molecule, having the same number of atoms with a different arrangement.
(b)
Interpretation: To indicate whether the statement “an isomerization reaction changes
Concept introduction: Glucose is a monosaccharide with the molecular formula
Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
In the isomerization reaction, a molecule transformed itself to another molecule, having the same number of atoms with a different arrangement.
(c)
Interpretation: To indicate whether the statement “an ATP molecule is used to activate a
Concept introduction: Glucose is a monosaccharide with the molecular formula
Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency of life that provides energy to carry out the metabolic processes in the living cells.
(d)a
Interpretation: To indicate whether the statement “the equivalent of two ATP molecules are consumed” relating to glycogenolysis is true or false.
Concept introduction: Glucose is a monosaccharide with the molecular formula
Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
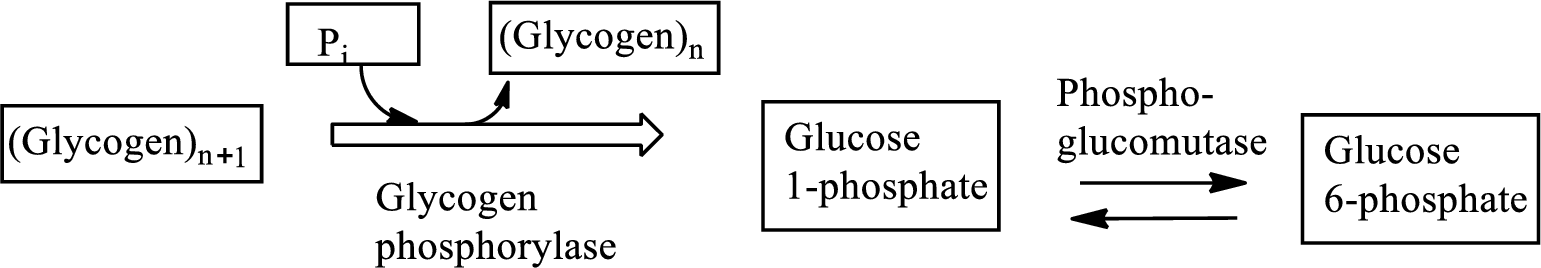
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency of life that provides energy to carry out the metabolic processes in the living cells.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 24 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC,+BIO.CHEM.-MINDTAP
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
- Question 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are reacted with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning




