
Concept explainers
Draw the product of each Robinson annulation from the given starting materials using −OH in H2O solution.
a. 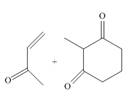 c.
c. 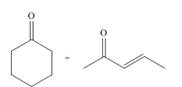
b. 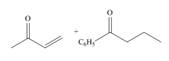 d.
d. 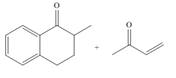
(a)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The combination of the Michael reaction and intramolecular aldol reaction in which the formation of a ring takes place is known as Robinson annulation reaction.
In this reaction, the carbonyl compound is treated with a base which leads to the elimination of a proton from the α−carbon atom. This elimination leads to the formation of an enolate ion. Then, this enolate ion acts as the nucleophile and undergoes conjugate addition reaction with the β−carbon of the α,β−unsaturated carbonyl compound that results in the formation of the new carbon-carbon bond and the desired Robinson annulation product.
Answer to Problem 24.45P
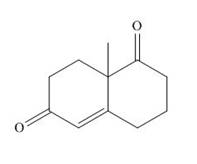
The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is 8a−methyl−3,4,8,8a−tetrahydronaphthalene−1,6(2H,7H)−dione.
Explanation of Solution
The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is shown as,
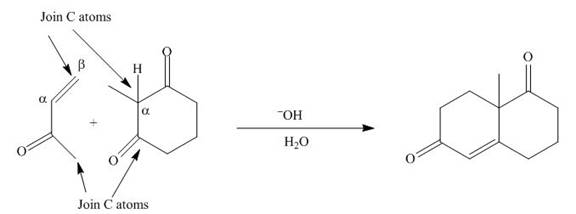
Figure 1
In this reaction, the given dicarbonyl compound is treated with a base, −OH that leads to the elimination of an acidic proton present between the two carbonyl groups. This elimination leads to the formation of an enolate ion. Then, this enolate ion acts as the nucleophile and undergoes conjugate addition reaction with β−carbon of the given α,β−unsaturated carbonyl compound by joining the indicated carbon atoms of both the compounds. The joining of two carbon atoms results in the formation of the new carbon-carbon bond and the desired Robinson annulation product, 8a−methyl−3,4,8,8a−tetrahydronaphthalene−1,6(2H,7H)−dione.
The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The combination of the Michael reaction and intramolecular aldol reaction in which the formation of a ring takes place is known as Robinson annulation reaction.
In this reaction, the carbonyl compound is treated with a base which leads to the elimination of a proton from the α−carbon atom. This elimination leads to the formation of an enolate ion. Then, this enolate ion acts as the nucleophile and undergoes conjugate addition reaction with the β−carbon of the α,β−unsaturated carbonyl compound that results in the formation of the new carbon-carbon bond and the desired Robinson annulation product.
Answer to Problem 24.45P
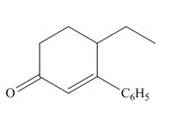
The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is 4−ethyl−3−phenylcyclohex−2−enone.
Explanation of Solution
The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is shown as,
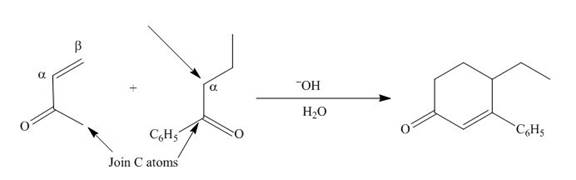
Figure 2
In this reaction, the given carbonyl compound is treated with a base, −OH that leads to the elimination of an acidic proton present between the two carbonyl groups. This elimination leads to the formation of an enolate ion. Then, this enolate ion acts as the nucleophile and undergoes conjugate addition reaction with β−carbon of the given α,β−unsaturated carbonyl compound by joining the indicated carbon atoms of both the compounds. The joining of two carbon atoms results in the formation of the new carbon-carbon bond and the desired Robinson annulation product, 4−ethyl−3−phenylcyclohex−2−enone.
The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The combination of the Michael reaction and intramolecular aldol reaction in which the formation of a ring takes place is known as Robinson annulation reaction.
In this reaction, the carbonyl compound is treated with a base which leads to the elimination of a proton from the α−carbon atom. This elimination leads to the formation of an enolate ion. Then, this enolate ion acts as the nucleophile and undergoes conjugate addition reaction with the β−carbon of the α,β−unsaturated carbonyl compound that results in the formation of the new carbon-carbon bond and the desired Robinson annulation product.
Answer to Problem 24.45P
The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is,
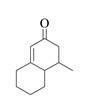
Explanation of Solution
The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is shown as,
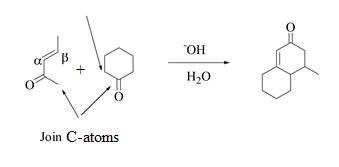
Figure 3
In this reaction, the given carbonyl compound is treated with a base, −OH that leads to the elimination of an acidic proton present between the two carbonyl groups. This elimination leads to the formation of an enolate ion. Then, this enolate ion acts as the nucleophile and undergoes conjugate addition reaction with β−carbon of the given α,β−unsaturated carbonyl compound by joining the indicated carbon atoms of both the compounds. The joining of two carbon atoms results in the formation of the new carbon-carbon bond and the desired Robinson annulation product, 4−methyl−4,4a,5,6,7,8−hexahydronaphthalene−2(3H)−one.
The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The combination of the Michael reaction and intramolecular aldol reaction in which the formation of a ring takes place is known as Robinson annulation reaction.
In this reaction, the carbonyl compound is treated with a base which leads to the elimination of a proton from the α−carbon atom. This elimination leads to the formation of an enolate ion. Then, this enolate ion acts as the nucleophile and undergoes conjugate addition reaction with the β−carbon of the α,β−unsaturated carbonyl compound that results in the formation of the new carbon-carbon bond and the desired Robinson annulation product.
Answer to Problem 24.45P
The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is,
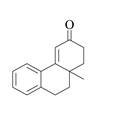
Explanation of Solution
The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is shown as,
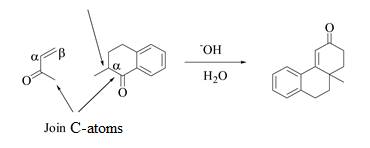
Figure 4
In this reaction, the given carbonyl compound is treated with a base, −OH that leads to the elimination of an acidic proton present between the two carbonyl groups. This elimination leads to the formation of an enolate ion. Then, this enolate ion acts as the nucleophile and undergoes conjugate addition reaction with β−carbon of the given α,β−unsaturated carbonyl compound by joining the indicated carbon atoms of both the compounds. The joining of two carbon atoms results in the formation of the new carbon-carbon bond and the desired Robinson annulation product, 10−methyl−1,2,10,10a−tetrahydrophenanthren−3(9H)−one.
The product that is formed by the Robinson annulation reaction from the given starting materials by using −OH in H2O solution is shown in Figure 4.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- Where are the chiral centers in this molecule? Also is this compound meso yes or no?arrow_forwardA mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forward
- A mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? Farrow_forwardcan someone give the curly arrow mechanism for this reaction written with every intermediate and all the side products pleasearrow_forward
