
(a)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Carbohydrates give various reactions. The hydrolysis of acetal group takes place in presence of an acid. The phenyl group will get replaced by the methyl group of methanol and forming phenol as by product. Both
Answer to Problem 24.45AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
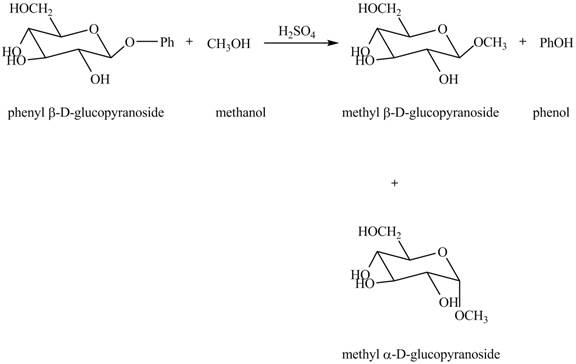
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
In the given reaction, the hydrolysis of compound takes place under acidic conditions. The phenyl acetal group is hydrolyzed to form methyl acetal and phenol. Both anomeric forms of methyl acetal are formed. The complete reaction is shown below in Figure 1.
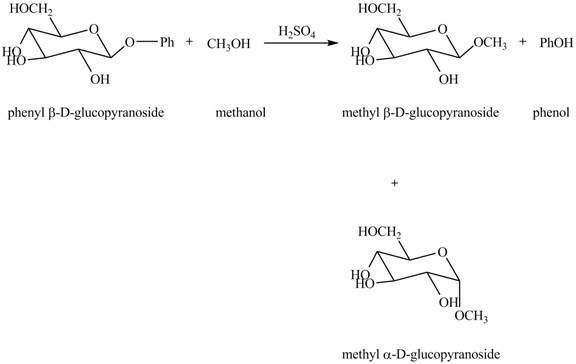
Figure 1
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Carbohydrates give various reactions. In the presence of acid, the compound form cyclic pyranose structure. The hydolysis of acetal group takes place in methanol in presence of an acid to form methyl acetal.
Answer to Problem 24.45AP
The completion of given reaction is shown below.
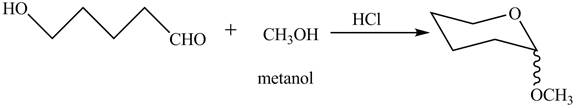
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
The oxygen of hydroxyl group acts as nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon of carbonyl group to form the pyranose structure. In presence of acid the given aldosepentose will form cyclic pyranose structure which will form methyl acetal in presence of methanol. The completion of given reaction is shown in Figure 2.
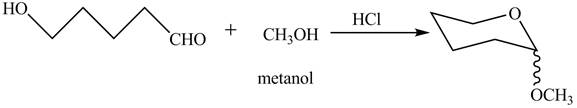
Figure 2
The complete given reaction is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Osmium tetraoxide is an oxidizing agent which oxidizes the double bond. Periodate is also an oxidizing agent used to convert the alcohol group to
Answer to Problem 24.45AP
The complete reaction given is shown below.
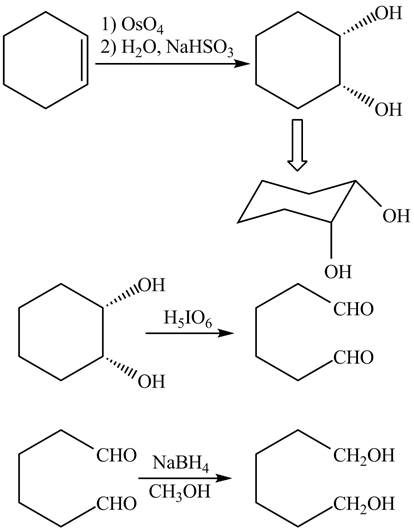
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
Figure 3
The
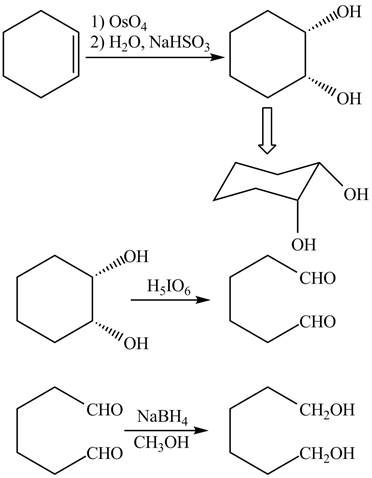
Figure 4
The complete reaction is shown in Figure 4.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Osmium tetraoxide is an oxidizing agent which oxidizes the double bond. On oxidation with osmium tetraoxide vicinal diol is formed. The vicinol diol will react with acetone in presence of an acid to form bicyclo compound. Acetone acts as a protecting group for the vicinal diol, so that it will not undergoes any reaction further.
Answer to Problem 24.45AP
The complete given reaction is shown below.
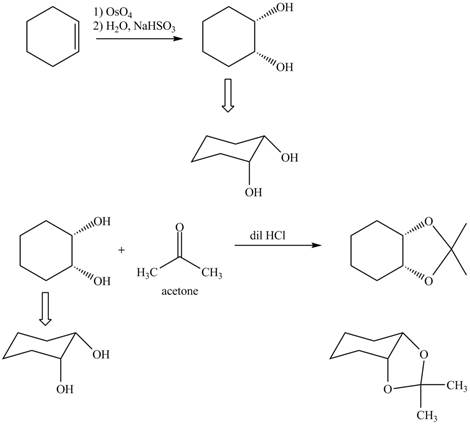
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
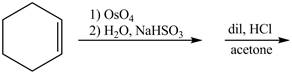
Figure 5
Osmium tetraoxide is oxidizing agent which will oxidize the double bond. The syn dihydroxylation product formed will reacts with acetone. Acetone acts as protecting group which protects the carbonyl functionality from basic conditions. The complete given reaction is shown in Figure 5.
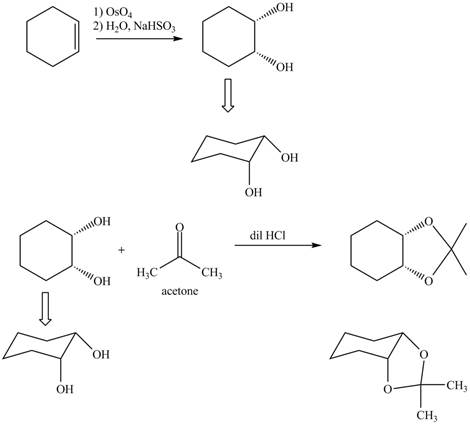
Figure 6
The complete given reaction is shown in Figure 6.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Silver oxide and methyl iodide is used for methylation of all free hydroxyl groups of carbohydrates. Methyl iodide is taken in excess amount to make sure that all hydroxyl groups get methylated.
Answer to Problem 24.45AP
The complete reaction is shown below.
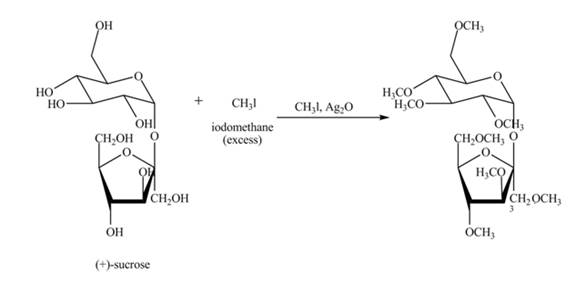
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
Alkylation of carbohydrates is performed using silver oxide and methyl iodide. First the carbohydrate gets oxidized in presence of silver oxide, then alkylation of all hydroxide groups takes place using methyl iodide. Methyl iodide is taken in excess to make sure that all hydroxyl groups get methylated. The complete reaction is shown in Figure 6.

Figure 7
The complete given reaction is shown in Figure 7.
(f)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Disaccharides are hydrolyzed in the presence of an acid. In presence of acid, the glycosidic bond formed between monosaccharides break down to give monosaccharides. Then, in the presence of ethanol both monosaccharides form ethyl acetal.
Answer to Problem 24.45AP
The given reaction is completely shown below.
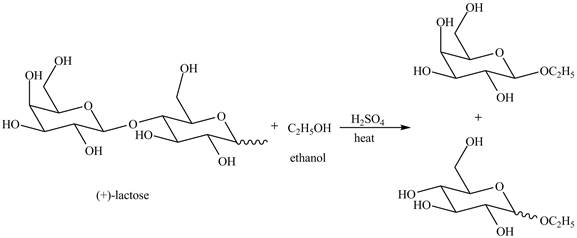
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
The given compound lactose is a disaccharide. A disaccharide is formed by the formation of carbon-oxygen-carbon bond, which is known as glycosidic bond. The hydrolysis of disaccharide takes place in the presence of acid. The glycosidic bond is broken down to form the monosaccharides. Then in presence of ethanol anomeric substitution takes place to form the product. The given reaction is completely shown below.

Figure 8
The complete given reaction is shown in Figure 8.
(g)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Hydrolysis of acetal group of carbohydrate takes place in presence of an acid. The methyl acetal of carbonyl gets hydrolyzed forming methanol as by product Methanol will again react with the carbonyl group to form methyl acetal again.
Answer to Problem 24.45AP
The given reaction is completely shown in below.
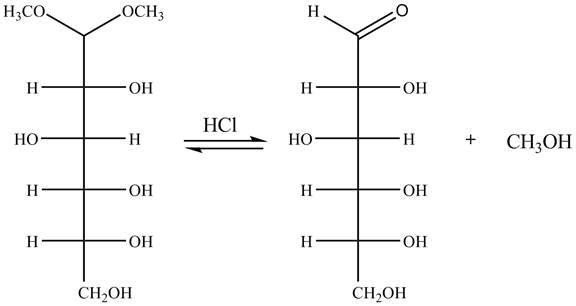
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
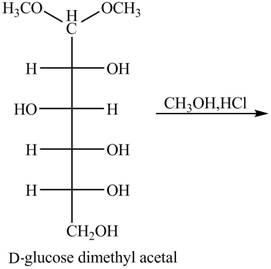
Figure 9
In the presence of an acid hydrolysis of the acetal group of carbohydrate takes place. The acetal group undergoes hydrolysis to form carbonyl group, and methanol is also formed as by product in the reaction.
The given reaction is completely shown in Figure 10.

Figure 10
The complete given reaction is shown in Figure 10.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- What is the total energy cost associated with the compound below adopting the shown conformation? CH3 HH DH CH3arrow_forwardΗΝ, Draw Final Product C cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Edit Enamine H3O+ CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H Edit Iminium Ionarrow_forwardHow many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?arrow_forward
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
- Why isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

