
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
8th Edition
ISBN: 8220102744127
Author: Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 23.3, Problem 9P
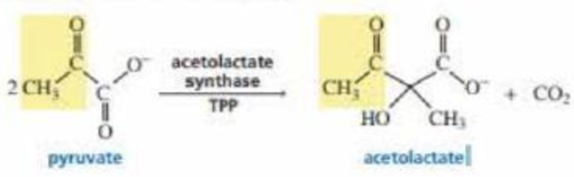
Acetolactate synthase is another TPP-requiring enzyme. It transfers the acyl group to another molecule of pyruvate, forming acetolactate. This is the first step in the biosynthesis of the amino acids valine and leucine. Propose a mechanism for this reaction.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Consider this step in a radical reaction:
Br
N
O
hv
What type of step is this? Check all that apply.
Draw the products of the step on the right-hand side of the drawing area
below. If more than one set of products is possible, draw any set.
Also, draw the mechanism arrows on the left-hand side of the drawing
area to show how this happens.
O primary
Otermination
O initialization
O electrophilic
O none of the above
×
☑
None
Can I get a drawing of what is happening with the orbitals (particularly the p orbital) on the O in the OH group? Is the p orbital on the O involved in the ring resonance? Why or why not?
Chapter 23 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 23.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 23.1 - Prob. 3PCh. 23.2 - How many conjugated double bonds are there in a....Ch. 23.2 - Instead of adding to the 4a position and...Ch. 23.2 - Prob. 7PCh. 23.3 - Prob. 8PCh. 23.3 - Acetolactate synthase is another TPP-requiring...Ch. 23.3 - Acetolactate synthase transfers the acyl group of...Ch. 23.3 - Prob. 12PCh. 23.5 - Which compound is more easily decarboxylated?
Ch. 23.5 - Prob. 14PCh. 23.5 - Explain why the ability of PLP to catalyze an...Ch. 23.5 - Explain why the ability of PLP to catalyze an...Ch. 23.5 - The enzyme that catalyzes the C C bond cleavage...Ch. 23.5 - Propose a mechanism for the ,-elimination reaction...Ch. 23.6 - Ethanolamine ammonia lyase, a coenzyme...Ch. 23.6 - Prob. 20PCh. 23.7 - How do the structure of tetrahydrofolate and...Ch. 23.7 - What is the source of the methyl group in...Ch. 23.8 - Thiols such as ethanethiol and propanethiol can be...Ch. 23 - How does the metal ion in carboxypeptidase A...Ch. 23 - Prob. 24PCh. 23 - Prob. 25PCh. 23 - For each of the following reactions, name both the...Ch. 23 - Prob. 27PCh. 23 - When transaminated, the three branched-chain amino...Ch. 23 - What acyl groups have we seen transferred by...Ch. 23 - Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:Ch. 23 - Draw the products of the following reaction, where...Ch. 23 - When UMP is dissolved in T2O, exchange of T for H...Ch. 23 - Dehydratase is a PLP-requiring enzyme that...Ch. 23 - In addition to the reaction mentioned in Section...Ch. 23 - PLP can catalyze both ,-elimination reactions...Ch. 23 - The glycine cleavage system is a group of four...Ch. 23 - Prob. 37PCh. 23 - FADH2 reduces , -unsaturated thioesters to...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1) How many monochlorination products-including stereochemistry- are there for the molecule below:arrow_forwardSelect an amino acid that has and N-H or O-H bond in its R-group (you have 8 to choose from!). Draw at least two water molecules interacting with the R-group of the amino acid.arrow_forwardIs this aromatic?arrow_forward
- CHEM2323 E Tt PS CH03 Draw and name all monobromo derivatives of pentane, C5H11Br. Problem 3-33 Name: Draw structures for the following: (a) 2-Methylheptane (d) 2,4,4-Trimethylheptane Problem 3-35 (b) 4-Ethyl-2,2-dimethylhexane (e) 3,3-Diethyl-2,5-dimethylnonane (c) 4-Ethyl-3,4-dimethyloctane 2 (f) 4-Isopropyl-3-methylheptane KNIE>arrow_forwardProblem 3-42 Consider 2-methylbutane (isopentane). Sighting along the C2-C3 bond: (a) Draw a Newman projection of the most stable conformation. (b) Draw a Newman projection of the least stable conformation. Problem 3-44 Construct a qualitative potential-energy diagram for rotation about the C-C bond of 1,2-dibromoethane. Which conformation would you expect to be most stable? Label the anti and gauche conformations of 1,2- dibromoethane. Problem 3-45 Which conformation of 1,2-dibromoethane (Problem 3-44) would you expect to have the largest dipole moment? The observed dipole moment of 1,2-dibromoethane is µ = 1.0 D. What does this tell you about the actual conformation of the molecule?arrow_forwardGas Law Studies 1. Mass of zinc Determination of 0.899 2) Moles of zinc 0.01361 mol 3.) Moles of hydrogen 00? ← I was told to calculate this number from mole of zinc. 350m So does that mean it will be 0.01361 mol too? 4 Volume of water collected (mL) 5) VL of water collected (Liters) 0.350 L 6) Temp of water collected (°C) 7) Temp of water collected (°K) 8) Atmospheric pressure (mm) 9) Vapor pressure of water (mm) 10) Corrected pressure of hydrogen 20% 29°C 764.0mm Hg (mm) 17.5mm 11) Corrected pressure of hydrogen (atm) 12) Experimentally calculated value of 19 13. Literature value of R 14) % Error 15) Suggest reasons for the % error (#14)arrow_forward
- No wedge or dashes. Do proper structure. Provide steps and explanation.arrow_forward10 Question (1 point) Draw curved arrow notation to indicate the proton transfer between NaOH and CH3CO₂H. 2nd attempt :0- H See Periodic Table See Hint Draw the products of the proton transfer reaction. Don't add a + sign between the products.arrow_forwardProvide steps and explanation please.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic And Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305081079
Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)
Publisher:Cengage Learning,


Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning
DIGESTER-35 | VITAMINS AND THEIR RELATED COENZYMES| GPAT | NIPER | PHARMACIST| DI; Author: GPAT DISCUSSION CENTER;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CGrdNYmho0s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY