
(a)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of 2-methyl-1-propanamine has to be given.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the amide, different types of amides can form.
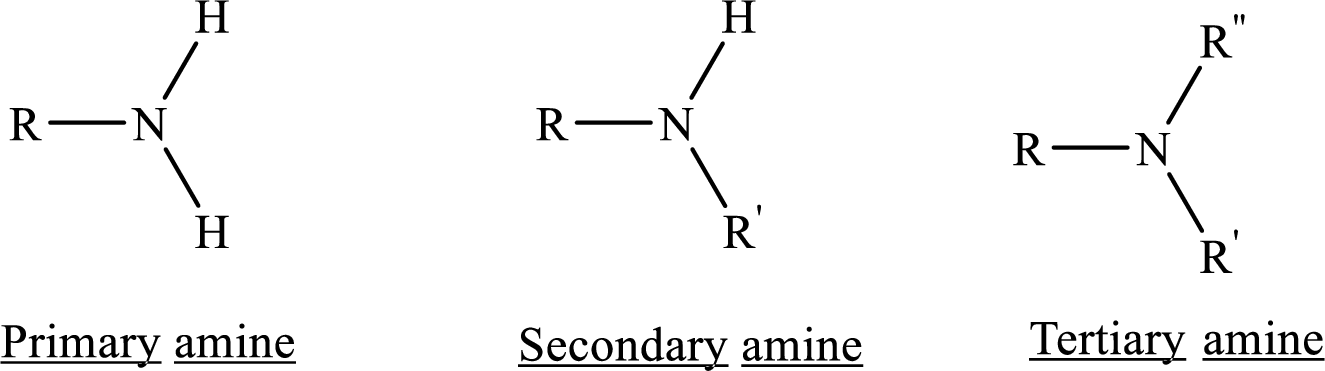
From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
(b)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of cyclohexanamine has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule, specifically which atoms are chemically bonded to what other atoms with what kind of chemical bond.
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the amide, different types of amides can form.
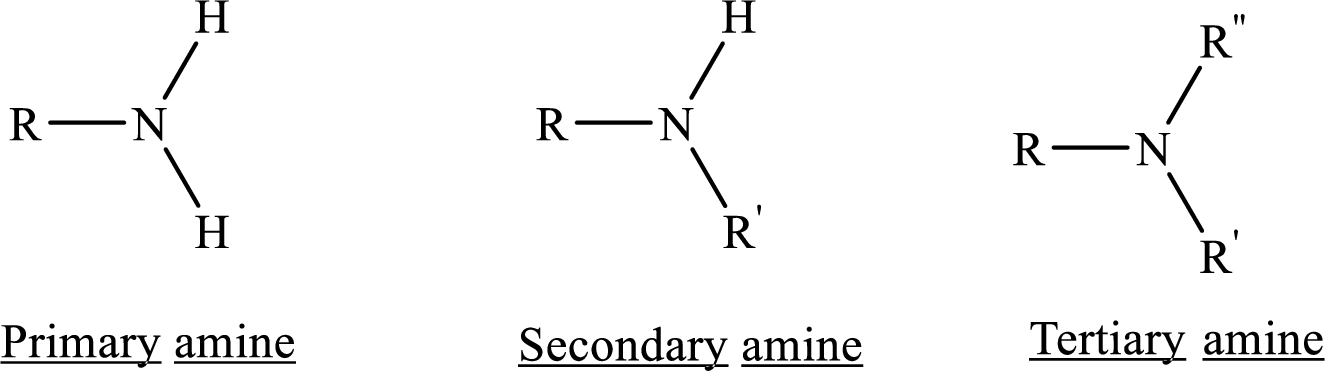
From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
(c)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of (R)-2-butanamine has to be given.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule, specifically which atoms are chemically bonded to what other atoms with what kind of chemical bond.
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the amide, different types of amides can form.
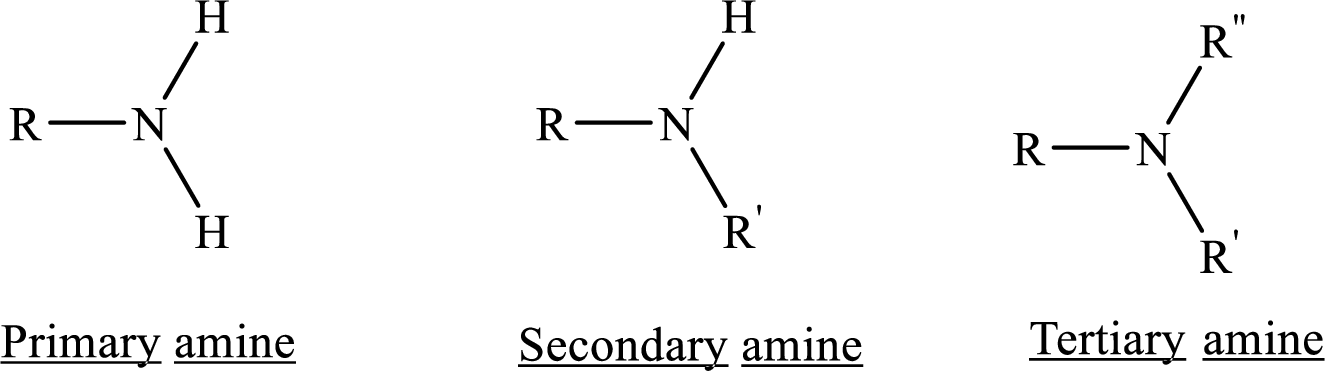
From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
According to Cahn-Ingold-Prelog system,
The group attached to asymmetric center should be ranked based on the
Check the direction of arrow drawn in the direction of decreasing priority. If the arrow points clockwise direction, then the atom has R configuration. If the arrow points counterclockwise direction, then the atom has S configuration. If the group with lowest priority is not bonded by a hatched wedge, then interchange this group (lowest priority) by group bonded to hatched wedge and draw the arrow in priority order but the configuration is assigned as just reverse.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- Please helparrow_forward(a) 21.8 Name the following compounds. & (b) Br (e) O₂N. (h) H (c) Br (d) NH2 ☑N Br H ہیں Ph (g) OMe бл .0-0.e 21.9 Draw a structural formula for each compound. (a) 2,3-Dinitrotoluene (c) Diphenylmethanol (e) p-Nitroaniline (b) 3-Propylanisole (d) m-Propylphenol (f) Pentabromobenzenearrow_forwardIs this the major product of this reaction?arrow_forward
- Help me solve this problem.arrow_forwardDraw a mechanism for the following synthetic transformation including reagents and any isolable intermediates throughout the process. Please clearly indicate bond cleavage/formation using curly arrows. MeO2Carrow_forwardCHEM 310 Quiz 8 Organic Chemistry II Due: Tuesday, April 25th, at 11:59 pm. This quiz is open textbook / open notes - but you must work alone. You cannot use the internet or the solutions manual for the book. Scan in your work and record an explanation of your mechanism. You may record this any way that you like. One way would be to start an individual Zoom meeting, start recording, "share your screen" and then talk through the problem. This will be converted to an .mp4 file that you can upload into Canvas using the "record/upload media" feature. Pyridine, benzoic acid and benzene are dissolved in ethyl acetate. Design and provide a plan / flow chart for separating and isolating each of these components. Pyridine and benzene are liquids at room temperature. Benzoic acid is a solid. You have ethyl acetate, 2M NaOH, 2M HCI and anhydrous MgSO4 available, as well as all the glassware and equipment that you used in the organic lab this year. Provide accurate acid/base reactions for any…arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning

