
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of benzylamine from the given starting material has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Preparation of imine:
An imine is a compound having
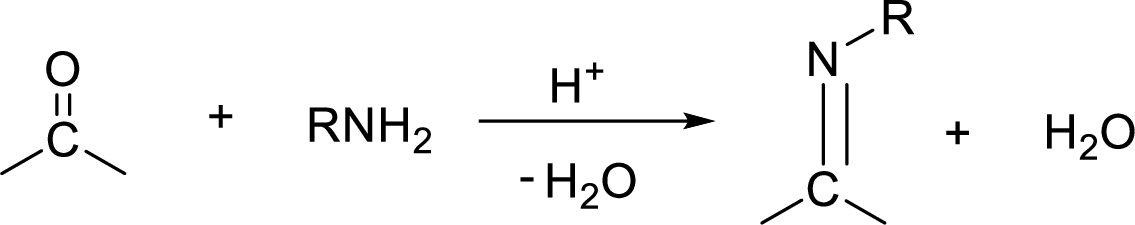
Reduction: If electrons are gained to a species or hydrogen atoms are added to a species or oxygen atom gets removed from a species during a
(b)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of benzylamine from the given starting material has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Amide Hydrolysis: In presence of base, amide reacts with water to form the corresponding amine and
(c)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of benzylamine from the given starting material has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
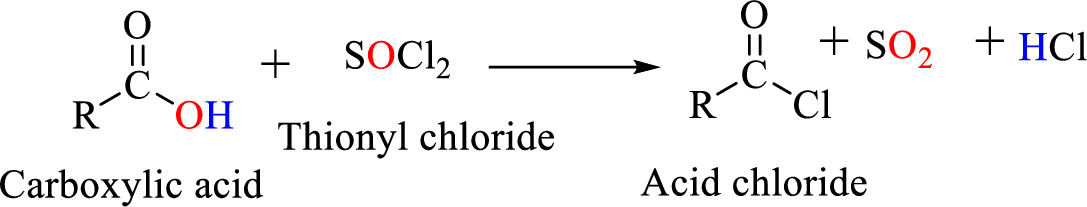
Preparation of amine: A primary amine is formed when an
Thionyl chloride:
(d)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of benzylamine from the given starting material has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Thionyl chloride:
(e)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of benzylamine from the given starting material has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Acid chlorides are most often prepared by treating a carboxylic acid with thionyl chloride.
Amide Formation: Amide is formed when an acid chloride reacts with an amine or ammonia.
Here, the chlorine atom that is attached to the carbonyl carbon atom of the acid chloride is being replaced by
Reduction: If electrons are gained to a species or hydrogen atoms are added to a species or oxygen atom gets removed from a species during a chemical reaction is known as reduction. In a reaction,
(f)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of benzylamine from the given starting material has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Preparation of amide: An amide is formed when an ester is reacted with ammonia.
Reduction: If electrons are gained to a species or hydrogen atoms are added to a species or oxygen atom gets removed from a species during a chemical reaction is known as reduction. In a reaction,
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- 1. Using radii from Resource section 1 (p.901) and Born-Lande equation, calculate the lattice energy for PbS, which crystallizes in the NaCl structure. Then, use the Born-Haber cycle to obtain the value of lattice energy for PbS. You will need the following data following data: AH Pb(g) = 196 kJ/mol; AHƒ PbS = −98 kJ/mol; electron affinities for S(g)→S¯(g) is -201 kJ/mol; S¯(g) (g) is 640kJ/mol. Ionization energies for Pb are listed in Resource section 2, p.903. Remember that enthalpies of formation are calculated beginning with the elements in their standard states (S8 for sulfur). The formation of S2, AHF: S2 (g) = 535 kJ/mol. Compare the two values, and explain the difference. (8 points)arrow_forwardIn the answer box, type the number of maximum stereoisomers possible for the following compound. A H H COH OH = H C Br H.C OH CHarrow_forward7. Magnesium is found in nature in the form of carbonates and sulfates. One of the major natural sources of zinc is zinc blende (ZnS). Use relevant concepts of acid-base theory to explain this combination of cations and anions in these minerals. (2 points)arrow_forward
- 6. AlF3 is insoluble in liquid HF but dissolves if NaF is present. When BF3 is added to the solution, AlF3 precipitates. Write out chemical processes and explain them using the principles of Lewis acid-base theory. (6 points)arrow_forward5. Zinc oxide is amphoteric. Write out chemical reactions for dissolution of ZnO in HCl(aq) and in NaOH(aq). (3 points)arrow_forwardDraw the product(s) formed when alkene A is reacted with ozone, followed by Zn and H₂O. If no second product is formed, do not draw a structure in the second box. Higher Molecular Weight Product A Lower Molecular Weight Product draw structure ... draw structure ...arrow_forward
- Rank A - D in order of increasing rate of reaction with H2 and Pd/C. ب ب ب ب A B с Which option correctly ranks the alkenes in order of increasing rate of reaction with H₂ and Pd/C? О Barrow_forwardDraw the product of the following Sharpless epoxidation, including stereochemistry. Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. -OH (CH3)3C-OOH Ti[OCH(CH3)2]4 (+)-DET draw structure ... Guidarrow_forwardWhat alkyne (or diyne) yields the following oxidative cleavage products? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ... CO₂ + OHarrow_forwardlighting discharges in the atmosphere catalyze the conversion of nitrogen to nitric oxide. How many grams of nitrogen would be required to make 25.0 g of nitric oxide in this way ?arrow_forwardThe electron of a hydrogen atom is excited to the 4d orbital. Calculate the energy of the emitted photon if the electron were to move to each of the following orbitals: (a) 1s; (b) 2p; (c) 2s; (d) 4s. (e) Suppose the outermost electron of a potassium atom were excited to a 4d orbital and then moved to each of these same orbitals. Describe qualitatively the differences that would be found between the emission spectra of potassium and hydrogen (do not perform calculations). Explain your answer.arrow_forwardImagine a four-dimensional world. In it, atoms would have one s orbital and four p orbitals in a given shell. (a) Describe the shape of the Periodic Table of the first 24 elements. (b) What elements would be the first two noble gases (use the names from our world that correspond to the atomic numbers).arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


