
Concept explainers
Draw the organic products formed in each reaction.
a.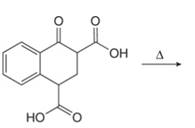 e.
e.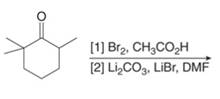
b.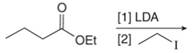 f.
f.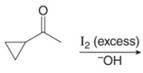
c.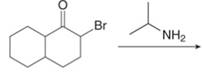 g.
g.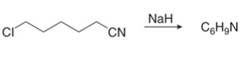
d.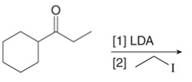 h.
h.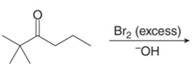
(a)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Decarboxylation occurs in carboxylic acids.[a1] It involves a cleavage of alpha carbon with loss of carbon dioxide along with heating.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
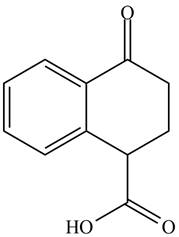
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
Decarboxylation occurs when a carboxyl group is attached to alpha carbon of another carbonyl group. It removes the carboxylic group from the alpha carbon of the carbonyl group. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
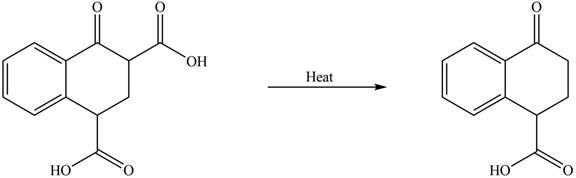
Figure 2
Hence, the organic product formed in given reaction is
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) is a sterically hindered strong base. In an unsymmetrical ketone, it abstracts hydrogen from least substituted carbon to form kinetic product.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
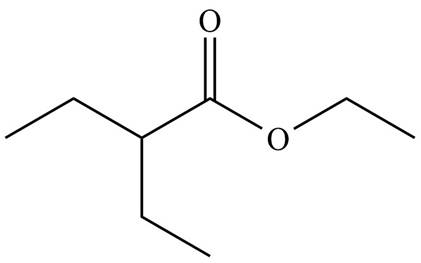
Figure 3
Explanation of Solution
LDA abstracts a proton from the alpha carbon of ethylbutanoate to form enolate. This enolate ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks on electrophilic centre of iodoethane and forms
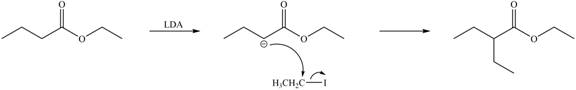
Figure 4
Hence, the organic product formed in given reaction is
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 3.
(c)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Alkyl amines are formed by the reaction of alkyl halides with amines. This reaction is known as alkylation of amines.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
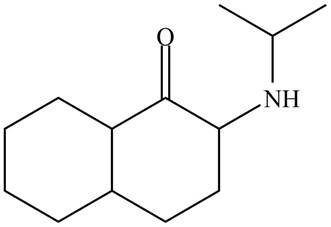
Figure 5
Explanation of Solution
In the first step,
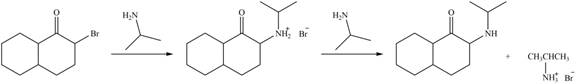
Figure 6
Hence, the organic product formed in given reaction is
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 5.
(d)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) is a sterically hindered strong base. In an unsymmetrical ketone, it abstracts hydrogen from least substituted carbon to form kinetic product.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
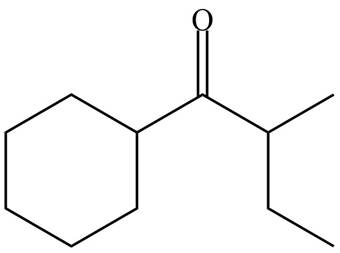
Figure 7
Explanation of Solution
LDA abstracts a proton from the less hindered alpha carbon of
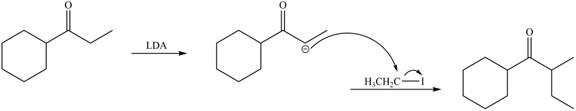
Figure 8
Hence, the organic product formed in given reaction is
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 7.
(e)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Monobromo product is formed by the reaction of carbonyl compounds with bromine in the presence of acetic acid and further treatment of monobromo with base yield alkenes.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
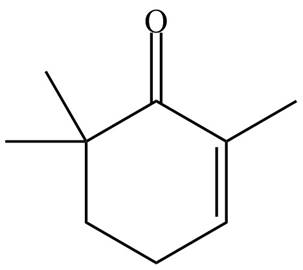
Figure 9
Explanation of Solution
Monobromo product is formed by the reaction of
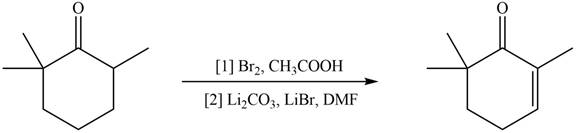
Figure 10
Hence, the organic product formed in given reaction is
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 9.
(f)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Haloform is produced by the halogenation of a methyl ketone in the presence of a base. This reaction is also known as haloform reaction.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
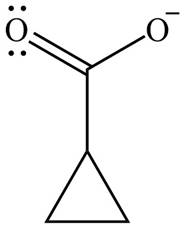
Figure 11
Explanation of Solution
The enolate ion reacts with iodine and form
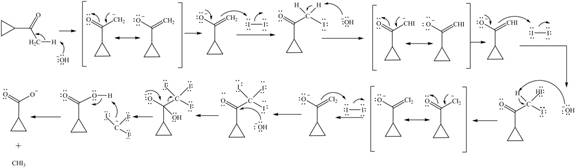
Figure 12
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 11.
(g)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Sodium hydride is a strong base. It abstracts a proton and forms carbanion. This carbanion acts as a nucleophile and attacks on the electrophilic centre of alkyl halide.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
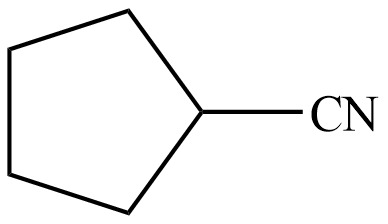
Figure 13
Explanation of Solution
Sodium hydride abstracts a proton from the carbon which is attached to cyanide and forms secondary carbanion. The next step is intra molecular cyclization. Now this carbanion acts as nucleophile and attack to the carbon (electrophile) which is directly attach to the electronegative atom i.e. chlorine. The corresponding chemical reaction of given organic compound with a strong base is shown below
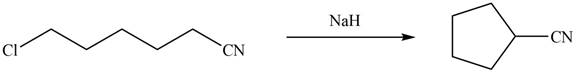
Figure 14
Hence, the organic product formed in given reaction is cyclopentanecarbonitrile.
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 13.
(h)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Bromination is a type of radical substitution reaction. It is highly specific reaction. In this reaction, an alkyl halide is formed by the replacement of hydrogen atom from highly substituted carbon by
Answer to Problem 23.50P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
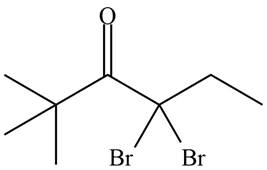
Figure 15
Explanation of Solution
An alkyl halide is formed by the replacement of hydrogen atom from highly substituted carbon by
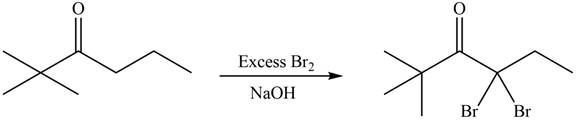
Figure 16
Hence, the organic product formed in given reaction is
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 15.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardThe vibrational contribution isa) temperature independent for internal energy and heat capacityb) temperature dependent for internal energy and heat capacityc) temperature independent for heat capacityd) temperature independent for internal energyarrow_forward
- Quantum mechanics. Explain the basis of approximating the summation to an integral in translational motion.arrow_forwardQuantum mechanics. In translational motion, the summation is replaced by an integral when evaluating the partition function. This is correct becausea) the spacing of the translational energy levels is very small compared to the product kTb) the spacing of the translational energy levels is comparable to the product kTc) the spacing of the translational energy levels is very large compared to the product kTarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raiting don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardIf the viscosity of hydrogen gas (at 0oC and 1 atm) is 8.83x10-5 P. If we assume that the molecular sizes are equal, calculate the viscosity of a gas composed of deuterium.arrow_forwardIf the viscosity of hydrogen gas (at 0oC and 1 atm) is 8.83x10-5 P. If we assume that the molecular sizes are equal, calculate the viscosity of a gas composed of deuterium.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
