
(a)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one
The bulky base like LDA always abstracts the proton from the side of less substituted
Answer to Problem 23.15P
The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
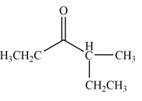
Explanation of Solution
The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
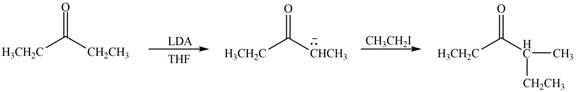
Figure 1
In this reaction, the given compound is treated with LDA in the presence of THF solution to form an enolate ion. The strong base, LDA abstracts a proton from the less substituted carbon atom of the compound. Then methyl iodide reacts with the enolte ion to form the desired product.
The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
(b)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
The bulky base like LDA always abstracts the proton from the side of less substituted
Answer to Problem 23.15P
The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
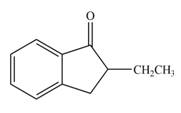
Explanation of Solution
The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
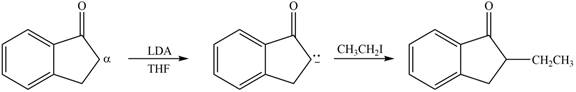
Figure 2
In this reaction, the given compound is treated with LDA in the presence of THF solution to form an enolate ion. The strong base, LDA abstracts a proton from the less substituted carbon atom or
The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
(c)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
The bulky base like LDA always abstracts the proton from the side of less substituted
Answer to Problem 23.15P
The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
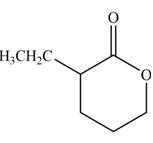
Explanation of Solution
The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
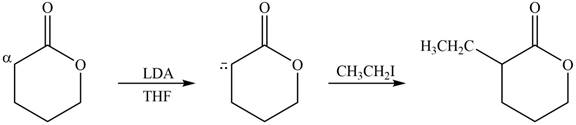
Figure 3
In this reaction, the given compound is treated with LDA in the presence of THF solution to form an enolate ion. The strong base, LDA abstracts a proton from the less substituted carbon atom or
The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
(d)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
The bulky base like LDA always abstracts the proton from the side of less substituted
Answer to Problem 23.15P
The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
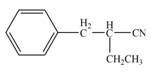
Explanation of Solution
The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
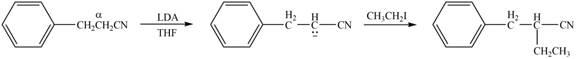
Figure 4
In this reaction, the given compound is treated with LDA in the presence of THF solution to form an enolate ion. The strong base, LDA abstracts a proton from the less substituted carbon atom or
The product that is formed by the reaction of the given compound with LDA in the presence of THF solution at low temperature, followed by
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- answer thisarrow_forwardplease add appropriate arrows and tell me in detail where to add which or draw itarrow_forwardPart 1. Draw monomer units of the following products and draw their reaction mechanism (with arrow pushing) Temporary cross-linked polymer Using: 4% polyvinyl alcohol+ methyl red + 4% sodium boratearrow_forward
- can you please answer both these questions and draw the neccesaryarrow_forwardcan you please give the answer for both these pictures. thankyouarrow_forwardPart 1. Draw monomer units of the following products and draw their reaction mechanism (with arrow pushing) | Bakelite like polymer Using: Resorcinol + NaOH + Formalinarrow_forward
- Question 19 0/2 pts 3 Details You have a mixture of sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium chloride (KCl) dissolved in water and want to separate out the Cl- ions by precipitating them out using silver ions (Ag+). The chemical equation for the net ionic reaction of NaCl and KCl with silver nitrate, AgNO3, is shown below. Ag+(aq) + Cl(aq) → AgCl(s) The total mass of the NaCl/KCl mixture is 1.299 g. Adding 50.42 mL of 0.381 M solution precipitates out all of the Cl-. What are the masses of NaCl and KCl in the mixture? Atomic masses: g: Mass of NaCl g: Mass of KCL Ag = 107.868 g mol- 1 Cl = 35.453 g mol- 1 K = 39.098 g mol- N = 14.007 g mol−1 Na = 22.99 g mol−1 0 = 15.999 g mol 1 Question Help: ✓ Message instructor Submit Questionarrow_forwardPart 1. Draw monomer units of the following products and draw their reaction mechanism (with arrow pushing) Polyester fiber Using a) pthalic anhydride + anhydrous sodium acetate + ethylene glycol B)pthalic anhydride + anhydrous sodium acetate + glycerolarrow_forwardIdentify the missing starting materials/ reagents/ products in the following reactions. Show the stereochemistry clearly in the structures, if any. If there is a major product, draw the structures of the major product with stereochemistry clearly indicated where applicable. Show only the diastereomers (you do not have to draw the pairs of enantiomers). If you believe that multiple products are formed in approximately equal amounts (hence neither is the major product), draw the structures of the products, and show the detailed mechanism of these reactions to justify the formation of the multiple products. If you believe no product is formed, explain why briefly. (6 mark for each, except f and g, which are 10 mark each)arrow_forward
- 3. What starting material would you use to synthesize 3-hydroxypentanoic acid using a NaBH4 reduction?arrow_forward1. Give stereochemical (Fischer projection) formulas for all (but no extras) the stereoisomers that could theoretically form during the reduction of a. the carbonyl group of 2-methyl-3--pentanone b. both carbonyl groups of 2,4-pentanedione (careful!) 2. Predict the products of the reduction of O=CCH2CH2CH2C=O with a. LiAlH4 b. NaBH4 CH3 OHarrow_forwardWhich of the following compounds can be synthesized using one reaction from any alkene, as a major product? If it can be synthesized, propose a route, and you may use any other starting materials, reagents and solvents as needed. If you do not think that it can be synthesized as a major product from an alkene, explain in detail why.arrow_forward

 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

