
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The enolates that are formed by the reaction of the given
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one
The bulky base like LDA always abstracts the proton from the side of less substituted
Answer to Problem 23.9P
The enolates that are formed by the reaction of the given ketone with LDA present in the THF solution and with
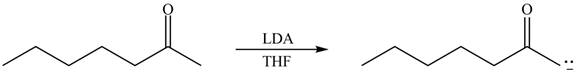

Explanation of Solution
The enolate that is formed by the reaction of the given ketone with LDA present in the THF solution is shown is shown as,

Figure 1
In this reaction, the given ketone is treated with LDA in the presence of THF solution to form an enolate ion. The strong base, LDA abstracts a proton from the less substituted carbon atom of the compound.
The enolate that is formed by the reaction of the given ketone with
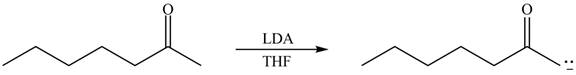
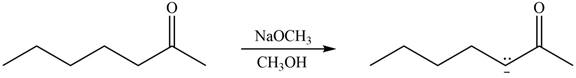
Figure 2
In this reaction, the given ketone is treated with
The enolates that are formed by the reaction of the given ketone with LDA present in the THF solution and with
(b)
Interpretation: The enolates that are formed by the reaction of the given ketone with LDA present in the THF solution and with
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
The bulky base like LDA always abstracts the proton from the side of less substituted
Answer to Problem 23.9P
The enolates that are formed by the reaction of the given ketone with LDA present in the THF solution and with
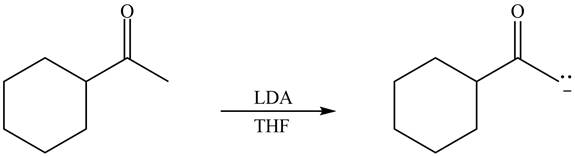
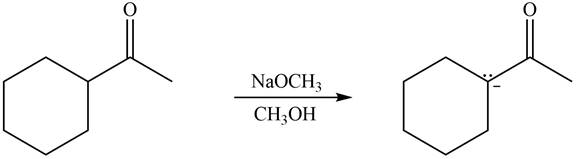
Explanation of Solution
The enolate that is formed by the reaction of the given ketone with LDA present in the THF solution is shown is shown as,

Figure 3
In this reaction, the given ketone is treated with LDA in the presence of THF solution to form an enolate ion. The strong base, LDA abstracts a proton from the less substituted carbon atom of the compound.
The enolate that is formed by the reaction of the given ketone with

Figure 4
In this reaction, the given ketone is treated with
The enolates that are formed by the reaction of the given ketone with LDA present in the THF solution and with
(c)
Interpretation: The enolates that are formed by the reaction of the given ketone with LDA present in the THF solution and with
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
The bulky base like LDA always abstracts the proton from the side of less substituted
Answer to Problem 23.9P
The enolates that are formed by the reaction of the given ketone with LDA present in the THF solution and with
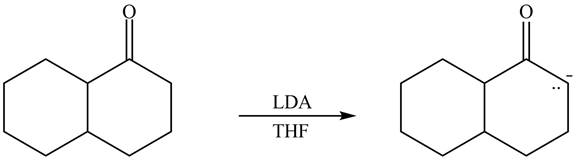
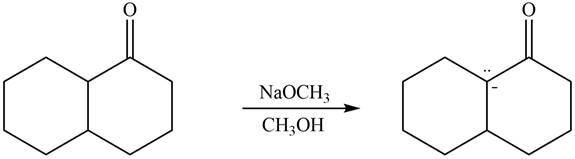
Explanation of Solution
The enolate that is formed by the reaction of the given ketone with LDA present in the THF solution is shown is shown as,
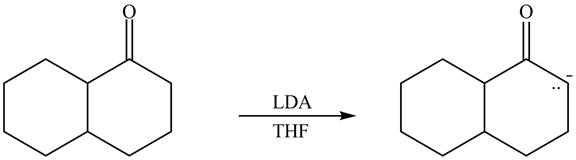
Figure 5
In this reaction, the given ketone is treated with LDA in the presence of THF solution to from an enolate ion. The strong base, LDA abstracts a proton from the less substituted carbon atom of the compound.
The enolate that is formed by the reaction of the given ketone with
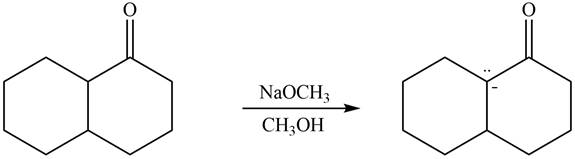
Figure 6
In this reaction, the given ketone is treated with
The enolates that are formed by the reaction of the given ketone with LDA present in the THF solution and with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- I need the most help figuring out how to find [I^-] mol/ L, [S2O8^2-] mol/L. 1st and 2nd Blank columns.arrow_forwardCan someone help me whats the issue?arrow_forwarda. The change in the Gibbs energy of a certain constant pressure process is found to fit the expression: AG-85.1 J mol −1 +36.5 J mol ¹K-1 × T A. Calculate the value of AS for the process. B. Next, use the Gibbs-Helmholtz equation: (a(AG/T)) ΔΗ - T2 to calculate the value of AH for the process.arrow_forward
- Consider the structure of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane. Part 1 of 2 Draw the Newman projection for the anti conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. ✡ ぬ Part 2 of 2 H H F Br H H ☑ Draw the Newman projection for the gauche conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. H F Br H Harrow_forwardPlease help me answer this question. I don't understand how or where the different reagents will attach and it's mostly due to the wedge bond because I haven't seen a problem like this before. Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how it can happen and what the final product will look like.arrow_forwardWhich of the following compounds is the most acidic in the gas phase? Group of answer choices H2O SiH4 HBr H2Sarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





