
Concept explainers
(a)
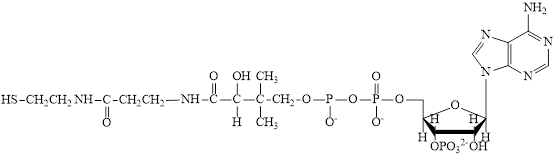
Interpretation: To identify the subunit that involves a B vitamin in the six-subunit block diagram for CoA.
Concept introduction: Coenzymes are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. Coenzymes cannot perform on their own alone. CoA is also an example of the coenzyme.
Coenzyme A (CoA) is utilized in various
(b)
Interpretation: To identify the subunit that is the “active” subunit in
Concept introduction: Coenzymes are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. Coenzymes cannot perform on their own alone. CoA is also an example of the coenzyme.
Coenzyme A (CoA) is utilized in various metabolic reactions. The functions of coenzyme A include oxidation of pyruvate in the citric cycle and fatty acid oxidation. The main function of coenzyme A is to transfer the acetyl group in various metabolic pathways. The structure of coenzyme A is:

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
Study Guide with Selected Solutions for Stoker's General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



