![OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook for Ebbing/Gammon's General Chemistry, 11th Edition, [Instant Access], 4 terms (24 months)](https://www.bartleby.com/isbn_cover_images/9781305864900/9781305864900_largeCoverImage.jpg)
Concept explainers
In the models shown here, C atoms are black and H atoms are light blue:
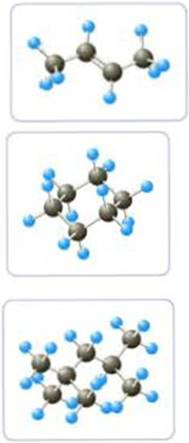
- a Write the molecular formula of each molecule.
- b Write the condensed structural formula for each molecule.
- c Give the IUPAC name of each molecule.
(a)
Interpretation:
Molecular formula for the given set of compounds has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular formula of a compound represents the total number of atoms that is present in it. It does not give any other information about the functional group, etc present in the compound. Simply it gives how many number of atoms are present for each element that is present in the compound.
To Write: The molecular formula for the given ball-stick models.
Answer to Problem 23.24QP
The molecular formula for the first structure is
The molecular formula for the second structure is
The molecular formula for the third structure is
Explanation of Solution
For First structure:
In the given ball-stick model, the black spheres are carbon atoms, light blue spheres are hydrogen atoms and dark blue spheres are nitrogen atoms. The total number of black spheres is 4, while that of light blue spheres is 8 and a double bond is present between the second and third carbon atom. Hence we arrive at the molecular formula of
For Second structure:
In the given ball-stick model, the black spheres are carbon atoms, light blue spheres are hydrogen atoms and red spheres are oxygen atoms. The total number of black spheres is 6, while that of light blue spheres is 12 and the given structure is a cyclic one. Hence we arrive at the molecular formula of
For Third structure:
In the given ball-stick model, the black spheres are carbon atoms, light blue spheres are hydrogen atoms and red spheres are oxygen atoms. The total number of black spheres is 8, while that of light blue spheres is 18. Hence we arrive at the molecular formula of
The molecular formula for the given ball-stick model compounds are written.
(b)
Interpretation:
Condensed structural formula for the given ball-stick model compounds has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structural formula is representation of the organic compound. In this the lengthy carbon chain is shown only with the carbon atoms (along with the hydrogen) without any bonds. The additional branches are shown with explicit bonds.
To Write: The condensed structural formula for the given set of ball-stick model compounds.
Answer to Problem 23.24QP
The condensed structural formula of First structure is
The condensed structural formula for the Second structure is,
![OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook for Ebbing/Gammon's General Chemistry, 11th Edition, [Instant Access], 4 terms (24 months), Chapter 23, Problem 23.24QP , additional homework tip 1](https://content.bartleby.com/tbms-images/9781305580343/Chapter-23/images/80343-23-23.24qp_image001.png)
The condensed structural formula for the Third structure is,
![OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook for Ebbing/Gammon's General Chemistry, 11th Edition, [Instant Access], 4 terms (24 months), Chapter 23, Problem 23.24QP , additional homework tip 2](https://content.bartleby.com/tbms-images/9781305580343/Chapter-23/images/80343-23-23.24qp_image002.png)
Explanation of Solution
For First structure:
Condensed structural formula can be drawn considering the carbon skeleton in the given ball-stick model. From the ball-stick model we can find that there are four carbon atom present in it and a double bond is present between second and third carbon atom. The single bonds alone are removed to obtain the condensed structural formula as shown below,
![OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook for Ebbing/Gammon's General Chemistry, 11th Edition, [Instant Access], 4 terms (24 months), Chapter 23, Problem 23.24QP , additional homework tip 3](https://content.bartleby.com/tbms-images/9781305580343/Chapter-23/images/80343-23-23.24qp_image003.png)
For Second structure:
Condensed structural formula can be drawn considering the carbon skeleton in the given ball-stick model. The carbon chain is drawn. As this is a cyclic compound, the condensed structural formula can be drawn without removing the single bonds between the carbon atoms.
![OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook for Ebbing/Gammon's General Chemistry, 11th Edition, [Instant Access], 4 terms (24 months), Chapter 23, Problem 23.24QP , additional homework tip 4](https://content.bartleby.com/tbms-images/9781305580343/Chapter-23/images/80343-23-23.24qp_image004.png)
For Third structure:
Condensed structural formula can be drawn considering the carbon skeleton in the given ball-stick model. The carbon chain is drawn. The second carbon atom is attached to two methyl groups and fourth carbon is substituted with one methyl group. The single bonds are removed in the parent structure which results in the condensed structural formula as shown below,
![OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook for Ebbing/Gammon's General Chemistry, 11th Edition, [Instant Access], 4 terms (24 months), Chapter 23, Problem 23.24QP , additional homework tip 5](https://content.bartleby.com/tbms-images/9781305580343/Chapter-23/images/80343-23-23.24qp_image005.png)
The condensed structural formula are written for the given ball-stick model representation of compounds.
(c)
Interpretation:
IUPAC names has to be given for the given set of ball-stick model compounds.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
To Give: The IUPAC name for the given ball-stick model compounds.
Answer to Problem 23.24QP
IUPAC name for the First structure is 2-butene.
IUPAC name for the Second structure is cyclohexane
IUPAC name for the Third structure is 2,2,4-trimethylpentane.
Explanation of Solution
For First structure:
From the given structure the lengthy carbon chain has to be identified. In this case it is a four carbon chain and hence the parent alkane is butane. A double bond is present between the second and third carbon atom. Hence, the compound is named as butane. The position of the double bond should be mentioned in IUPAC name, so that it should get least numbering. Therefore, the name of the given hydrocarbon is written as 2-butene.
For Second structure:
From the given structure we can identify that it is a cyclic compound. As there is no unsaturation present, the given compound is an alkane. Total number of carbon atoms present in it is six. Therefore, the parent hydrocarbon is hexane. As it is a cyclic structure, “-cyclo” has to be added before. Hence, the IUPAC name for the given compound is given as cyclohexane.
For Third structure:
From the given structure, we can see that the lengthy carbon chain consists of five carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent hydrocarbon is pentane. While looking into the structure, we can see that two methyl groups are substituted in second carbon atom and one methyl group is substituted in fourth carbon atom. Hence, we can arrive at the IUPAC name as 2,2,4-trimethylpentane.
IUPAC name for each molecule was given.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook for Ebbing/Gammon's General Chemistry, 11th Edition, [Instant Access], 4 terms (24 months)
- The following 'H NMR spectrum was taken with a 750 MHz spectrometer: 1.0 0.5 0.0 10.0 9.0 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 ' 2.0 1.0 0.0 (ppm) What is the difference Av in the frequency of RF ac Δν ac radiation absorbed by the a and c protons? (Note: it's not equal to the difference in chemical shifts.) Round your answer to 2 significant digits, and be sure it has an appropriate unit symbol. = O O a will shift left, c will shift right. O a will shift right, c will shift left. a and c will both shift left, with more space between them. Suppose a new spectrum is taken with a 500 MHz spectrometer. What will be true about this new spectrum? O a and c will both shift left, with less space between them. O a and c will both shift right, with more space between them. O a and c will both shift right, with less space between them. Which protons have the largest energy gap between spin up and spin down states? O None of the above. ○ a Ob Explanation Check C Ar B 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved.…arrow_forwardWhat mass of Na2CO3 must you add to 125g of water to prepare 0.200 m Na2CO3? Calculate mole fraction of Na2CO3, mass percent, and molarity of the resulting solution. MM (g/mol): Na2CO3 105.99; water 18.02. Final solution density is 1.04 g/mL.arrow_forward(ME EX2) Prblms Can you please explain problems to me in detail, step by step? Thank you so much! If needed color code them for me.arrow_forward
- Experiment #8 Electrical conductivity & Electrolytes. Conductivity of solutions FLINN Scientific Scale RED LED Green LED LED Conductivity 0 OFF OFF 1 Dim OFF 2 medium OFF 3 Bright Dim Low or Nowe Low Medium High 4 Very Bright Medium nd very high AA Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ SE=Strong Electrolyte, FE = Fair Electrolyte CWE = Weak Electrolyte, NE= Noni Electrolyte, #Solutions 1 0.1 M NaCl 2/1x 102 M NaCl, 3/1X103 M Nall Can Prediction M Observed Conductivity Very bright red Bright red Dim red you help me understand how I'm supposed to find the predictions of the following solutions? I know this is an Ionic compound and that the more ions in a solution means it is able to carry a charge, right? AAAA Darrow_forward(SE EX 2) Prblsm 4-7: Can you please explain problems 4-7 and color code if needed for me. (step by step) detail explanationsarrow_forward(SE EX 2) Problems 8-11, can you please explain them to me in detail and color-code anything if necessary?arrow_forward
- (ME EX2) Problems 15-16 Could you please explain problems 15 through 16 to me in detail, step by step? Thank you so much! If necessary, please color-code them for me.arrow_forward1.)show any electrophilic aromatic substitution, identify the electriphile, nucleophile and transition statearrow_forward(SE EX 2) Problems 15-16, can you please explain them to me in detail and color-code anything if necessary?arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning  Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning





