
(a)
Interpretation: The formula of conjugate acid of base dimethylamide should be written.
Concept introduction: In accordance with Bronsted definition, an acid act as proton donor and a base can act as proton acceptor. Thus, in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similarly, curved arrows are used for departing conjugate base. After deprotonation, the species left with negative charge is refers as conjugate base of acid while the other with positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example:
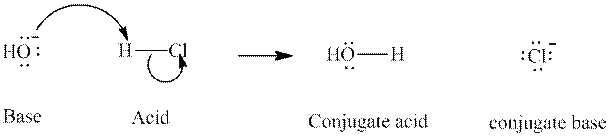
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has weak conjugate base and strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.
(b)
Interpretation: The formula of conjugate acid of sulfide should be written.
Concept introduction: In accordance with Bronsted definition, an acid act as proton donor and a base can act as proton acceptor. Thus, in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similarly, curved arrows are used for departing conjugate base. After deprotonation, the species left with negative charge is refers as conjugate base of acid while the other with positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example:
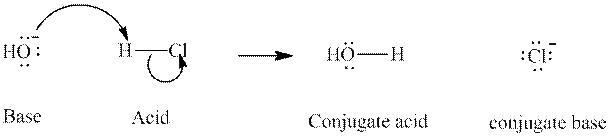
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has weak conjugate base and strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.
(c)
Interpretation: The formula of conjugate acid of ammonia should be written.
Concept introduction: In accordance with Bronsted definition, an acid act as proton donor and a base can act as proton acceptor. Thus, in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similarly, curved arrows are used for departing conjugate base. After deprotonation, the species left with negative charge is refers as conjugate base of acid while the other with positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example:
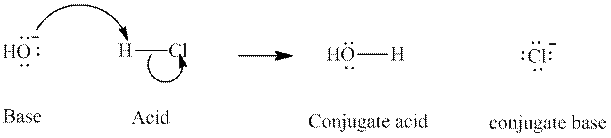
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has weak conjugate base and strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.
(d)
Interpretation: The formula of conjugate acid of acetone should be written.
Concept introduction: In accordance with Bronsted definition, an acid act as proton donor and a base can act as proton acceptor. Thus, in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similarly, curved arrows are used for departing conjugate base. After deprotonation, the species left with negative charge is refers as conjugate base of acid while the other with positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example:
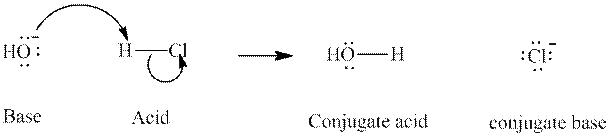
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has weak conjugate base and strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.
(e)
Interpretation: The formula of conjugate acid of
Concept introduction: In accordance with Bronsted definition, an acid act as proton donor and a base can act as proton acceptor. Thus, in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similarly, curved arrows are used for departing conjugate base. After deprotonation, the species left with negative charge is refers as conjugate base of acid while the other with positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example:
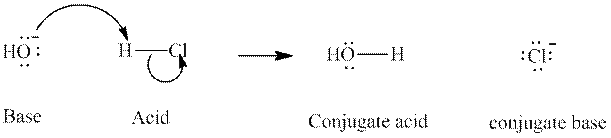
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has weak conjugate base and strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-PACKAGE
- Can you explain step by step behind what the synthetic strategy would be?arrow_forwardPlease explain step by step in detail the reasoning behind this problem/approach/and answer. thank you!arrow_forward2. Predict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. Assume that any necessary catalytic acid is present. .OH HO H₂N OHarrow_forward
- consider the rate of the reaction below to be r. Whats the rate after each reaction? Br + NaCN CN + NaBr a. Double the concentration of alkyl bromide b. Halve the concentration of the electrophile & triple concentration of cyanide c. Halve the concentration of alkyl chloridearrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant that is involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forward
- What is the organic molecule X of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Without using graphs, calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/(mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forward
- Predict the organic products that form in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat are the products of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning

