
(a)
Interpretation: Using a Gabriel synthesis, a give set of primary amine compounds have to be synthesized.
Concept Introduction: The general formula for primary amine is –NH2. There are several methods available to prepare primary
Step-1: Formation of potassium phthalimide (deprotonation)
Potassium phthalimide in alkaline KOH acts as the reagent which has negatively charged phthalimide. It is formed by the reaction between phthalimide and potassium hydroxide.
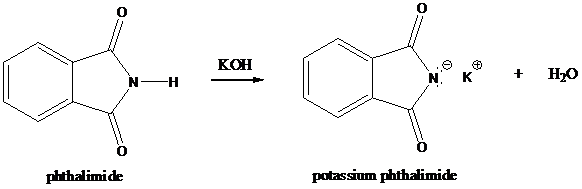
Step-2: Formation of R−N bond by SN2 nucleophilic substitution
The negative charged nitrogen atom in phthalimide can easily attract the positive side of R−X. In primary
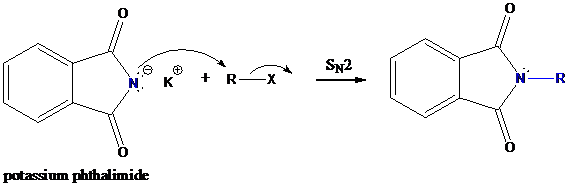
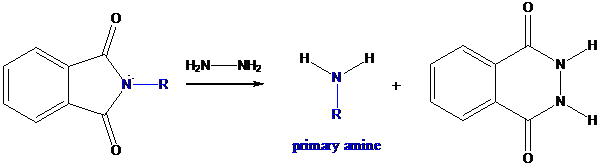
Step-3: Formation of primary amine by hydrolysis
The resultant product further goes for hydrolysis using hydrazine as the reagent. This reaction also follows nucleophilic substitution reaction. Finally, primary amine is formed with a side product of hydrazine derivative.
(b)
Interpretation: Using a Gabriel synthesis, a give set of primary amine compounds have to be synthesized.
Concept Introduction: The general formula for primary amine is –NH2. There are several methods available to prepare primary amines. Among them, Gabriel synthesis plays a very important role for preparing it. In this method, secondary and tertiary amines are not formed as side products. It involves in three steps.
Step-1: Formation of potassium phthalimide (deprotonation)
Potassium phthalimide in alkaline KOH acts as the reagent which has negatively charged phthalimide. It is formed by the reaction between phthalimide and potassium hydroxide.
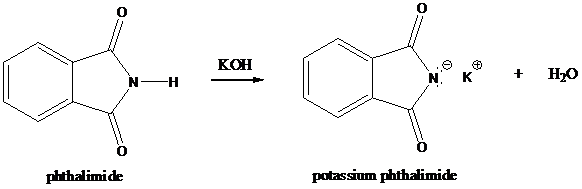
Step-2: Formation of R−N bond by SN2 nucleophilic substitution
The negative charged nitrogen atom in phthalimide can easily attract the positive side of R−X. In primary alkyl halides (R−X), R and X get positive and negative charges, respectively when they ionize. As a result, a bond between nitrogen of phthalimide and carbon of R is formed. This is SN2 nucleophilic substitution reaction. Halogen atom is going away as halide anion.
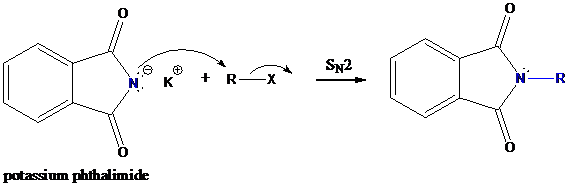
Step-3: Formation of primary amine by hydrolysis
The resultant product further goes for hydrolysis using hydrazine as the reagent. This reaction also follows nucleophilic substitution reaction. Finally, primary amine is formed with a side product of hydrazine derivative.

(c)
Interpretation: Using a Gabriel synthesis, a give set of primary amine compounds have to be synthesized.
Concept Introduction: The general formula for primary amine is –NH2. There are several methods available to prepare primary amines. Among them, Gabriel synthesis plays a very important role for preparing it. In this method, secondary and tertiary amines are not formed as side products. It involves in three steps.
Step-1: Formation of potassium phthalimide (deprotonation)
Potassium phthalimide in alkaline KOH acts as the reagent which has negatively charged phthalimide. It is formed by the reaction between phthalimide and potassium hydroxide.
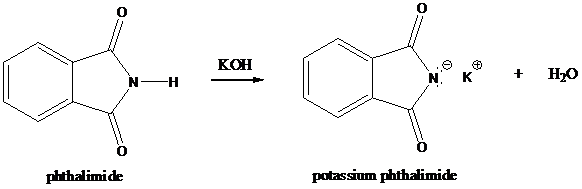
Step-2: Formation of R−N bond by SN2 nucleophilic substitution
The negative charged nitrogen atom in phthalimide can easily attract the positive side of R−X. In primary alkyl halides (R−X), R and X get positive and negative charges, respectively when they ionize. As a result, a bond between nitrogen of phthalimide and carbon of R is formed. This is SN2 nucleophilic substitution reaction. Halogen atom is going away as halide anion.
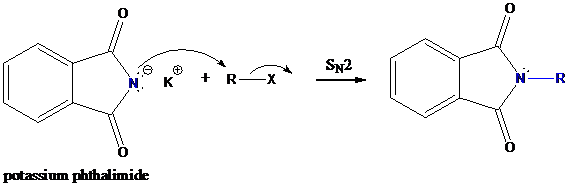
Step-3: Formation of primary amine by hydrolysis
The resultant product further goes for hydrolysis using hydrazine as the reagent. This reaction also follows nucleophilic substitution reaction. Finally, primary amine is formed with a side product of hydrazine derivative.

(d)
Interpretation: Using a Gabriel synthesis, a give set of primary amine compounds have to be synthesized.
Concept Introduction: The general formula for primary amine is –NH2. There are several methods available to prepare primary amines. Among them, Gabriel synthesis plays a very important role for preparing it. In this method, secondary and tertiary amines are not formed as side products. It involves in three steps.
Step-1: Formation of potassium phthalimide (deprotonation)
Potassium phthalimide in alkaline KOH acts as the reagent which has negatively charged phthalimide. It is formed by the reaction between phthalimide and potassium hydroxide.
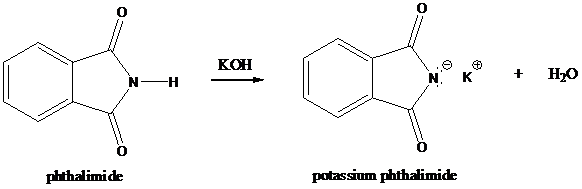
Step-2: Formation of R−N bond by SN2 nucleophilic substitution
The negative charged nitrogen atom in phthalimide can easily attract the positive side of R−X. In primary alkyl halides (R−X), R and X get positive and negative charges, respectively when they ionize. As a result, a bond between nitrogen of phthalimide and carbon of R is formed. This is SN2 nucleophilic substitution reaction. Halogen atom is going away as halide anion.
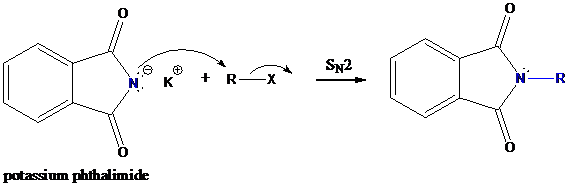
Step-3: Formation of primary amine by hydrolysis
The resultant product further goes for hydrolysis using hydrazine as the reagent. This reaction also follows nucleophilic substitution reaction. Finally, primary amine is formed with a side product of hydrazine derivative.

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 2. Provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the following syntheses. More than one step is required in some cases. a. CH3arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forward
- Instructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardе. Д CH3 D*, D20arrow_forwardC. NaOMe, Br Brarrow_forward
- Please predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forwardin the scope of ontario SCH4U grade 12 course, please show ALL workarrow_forwardIs the chemical reaction CuCl42-(green) + 4H2O <==> Cu(H2O)42+(blue) + 4Cl- exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





