
(a)
Interpretation: For a given set of nitrogen containing compounds, the structures have to be drawn using their general or IUPAC names.
Concept Introduction: If  ,
, 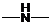 and
and  groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary
groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary
There are two ways followed to name the compound. First one is the method of giving general name in which name of the alkyl group followed by amine name is given. Second one is the method giving IUPAC name in which name of the alkane group followed by amine name is given.
The length of the chain which is having more number of carbon atoms is selected as the parent or main chain. Other chains are considered as substituents to the main chain. Position of the substituents should be included in the name. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in IUPAC system, then the name of the compound comes as methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane, etc. which are the name of
If any configuration is present in the compound, that should be assigned to it while writing the name. If the compound contains heavier groups on the same side, it gets (Z)-configuration. If they are on the opposite directions, (E)-configurations result.
If a carbon has four different groups attached to it, that carbon shows a chirality nature. If that chiral carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a clockwise direction, it gets (R)-isomer. If that carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a counter-clockwise direction, it gets (S)-isomer.
To find: Categorize the number of alkyl groups attached to nitrogen atom
(b)
Interpretation: For a given set of nitrogen containing compounds, the structures have to be drawn using their general or IUPAC names.
Concept Introduction: If  ,
, 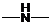 and
and  groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary amines respectively.
groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary amines respectively.
There are two ways followed to name the compound. First one is the method of giving general name in which name of the alkyl group followed by amine name is given. Second one is the method giving IUPAC name in which name of the alkane group followed by amine name is given.
The length of the chain which is having more number of carbon atoms is selected as the parent or main chain. Other chains are considered as substituents to the main chain. Position of the substituents should be included in the name. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in IUPAC system, then the name of the compound comes as methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane, etc. which are the name of alkanes. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in general name method, then the name of the compound comes as methyl, ethyl, propyl, butyl, pentyl, hexyl, etc. which are the name of alkyl groups. If substituent groups are attached to nitrogen atom as in the case of tertiary or secondary amines, the name is given as N-alkyl name of the substituent.
If any configuration is present in the compound, that should be assigned to it while writing the name. If the compound contains heavier groups on the same side, it gets (Z)-configuration. If they are on the opposite directions, (E)-configurations result.
If a carbon has four different groups attached to it, that carbon shows a chirality nature. If that chiral carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a clockwise direction, it gets (R)-isomer. If that carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a counter-clockwise direction, it gets (S)-isomer.
To find: Categorize the number of alkyl groups attached to nitrogen atom
In the given compound (b), three alkyl groups are attached to nitrogen atom. Therefore, it belongs to tertiary amine.
Decide the given name which is in general name method or IUPAC name method
There are three alkyl groups present in the given name. Here, the main chain is cyclopropylamine. Three-membered carbon ring structure is called cyclopropyl group. So, general name system is followed.
Locate the substituents and draw the corresponding structure for the given name
(c)
Interpretation: For a given set of nitrogen containing compounds, the structures have to be drawn using their general or IUPAC names.
Concept Introduction: If  ,
, 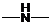 and
and  groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary amines respectively.
groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary amines respectively.
There are two ways followed to name the compound. First one is the method of giving general name in which name of the alkyl group followed by amine name is given. Second one is the method giving IUPAC name in which name of the alkane group followed by amine name is given.
The length of the chain which is having more number of carbon atoms is selected as the parent or main chain. Other chains are considered as substituents to the main chain. Position of the substituents should be included in the name. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in IUPAC system, then the name of the compound comes as methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane, etc. which are the name of alkanes. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in general name method, then the name of the compound comes as methyl, ethyl, propyl, butyl, pentyl, hexyl, etc. which are the name of alkyl groups. If substituent groups are attached to nitrogen atom as in the case of tertiary or secondary amines, the name is given as N-alkyl name of the substituent.
If any configuration is present in the compound, that should be assigned to it while writing the name. If the compound contains heavier groups on the same side, it gets (Z)-configuration. If they are on the opposite directions, (E)-configurations result.
If a carbon has four different groups attached to it, that carbon shows a chirality nature. If that chiral carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a clockwise direction, it gets (R)-isomer. If that carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a counter-clockwise direction, it gets (S)-isomer.
To find: Categorize the number of alkyl groups attached to nitrogen atom
In the given compound (c), only one alkyl group, namely pentane is attached to nitrogen atom. Therefore, it belongs to primary amine.
Decide the given name which is in general name method or IUPAC name method
There is only one alkane group present in the given name. It is pentane attached to primary amine named as pentanamine which is the main chain of the given name. So, IUPAC name system is followed.
Locate the substituents and draw the corresponding structure for the given name
(d)
Interpretation: For a given set of nitrogen containing compounds, the structures have to be drawn using their general or IUPAC names.
Concept Introduction: If  ,
, 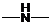 and
and  groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary amines respectively.
groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary amines respectively.
There are two ways followed to name the compound. First one is the method of giving general name in which name of the alkyl group followed by amine name is given. Second one is the method giving IUPAC name in which name of the alkane group followed by amine name is given.
The length of the chain which is having more number of carbon atoms is selected as the parent or main chain. Other chains are considered as substituents to the main chain. Position of the substituents should be included in the name. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in IUPAC system, then the name of the compound comes as methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane, etc. which are the name of alkanes. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in general name method, then the name of the compound comes as methyl, ethyl, propyl, butyl, pentyl, hexyl, etc. which are the name of alkyl groups. If substituent groups are attached to nitrogen atom as in the case of tertiary or secondary amines, the name is given as N-alkyl name of the substituent.
If any configuration is present in the compound, that should be assigned to it while writing the name. If the compound contains heavier groups on the same side, it gets (Z)-configuration. If they are on the opposite directions, (E)-configurations result.
If a carbon has four different groups attached to it, that carbon shows a chirality nature. If that chiral carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a clockwise direction, it gets (R)-isomer. If that carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a counter-clockwise direction, it gets (S)-isomer.
To find: Categorize the number of alkyl groups attached to nitrogen atom
In the given compound (d), only one alkyl group is attached to nitrogen atom. Therefore, it belongs to primary amine.
Decide the given name which is in general name method or IUPAC name method
There is only one alkyl group present in the given name. It is benzyl group. So, simple general name system is followed. If phenyl group is attached to methylene group, it is called benzyl group.
Locate the substituents and draw the corresponding structure for the given name
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Polyethylene furanoate is a polymer made from plant-based sources; it is used for packaging. Identify the monomer(s) used in the production of this polymer using a condensation process.arrow_forwardPhenol is the starting material for the synthesis of 2,3,4,5,6-pentachlorophenol, known al-ternatively as pentachlorophenol, or more simply as penta. At one time, penta was widely used as a wood preservative for decks, siding, and outdoor wood furniture. Draw the structural formula for pentachlorophenol and describe its synthesis from phenol.arrow_forward12 Mass Spectrometry (d) This unknown contains oxygen, but it does not show any significant infrared absorption peaks above 3000 cm . 59 100- BO 40 Relative Abundance M(102) - 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 5 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 mizarrow_forward
- Draw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H HO H HO H HO H H -OH CH2OH Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х : Darrow_forward: Draw the structure of valylasparagine, a dipeptide made from valine and asparagine, as it would appear at physiological pH. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. P Darrow_forwardDraw the Haworth projection of α-L-mannose. You will find helpful information in the ALEKS Data resource. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ཊི Х Darrow_forward
- Draw the structure of serine at pH 6.8. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : d كarrow_forwardTake a look at this molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. CH2OH H H H OH OH OH CH2OH H H H H OH H H OH H OH Is this a reducing sugar? yes α β ロ→ロ no ☑ yes Does this molecule contain a glycosidic bond? If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the symbol describing it. O no 0+0 If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the common names (including anomer and enantiomer labels) of the molecules that would be released if that bond were hydrolyzed. If there's more than one molecule, separate each name with a comma. ☐arrow_forwardAnswer the questions in the table below about this molecule: H₂N-CH₂ -C—NH–CH–C—NH–CH—COO- CH3 CH CH3 What kind of molecule is this? 0= CH2 C If you said the molecule is a peptide, write a description of it using 3-letter codes separated ☐ by dashes. polysaccharide peptide amino acid phospolipid none of the above Хarrow_forward
- Draw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: CH₂OH C=O HO H H -OH H OH CH₂OH Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ☐ Х S '☐arrow_forwardNucleophilic Aromatic Substitution 22.30 Predict all possible products formed from the following nucleophilic substitution reactions. (a) (b) 9 1. NaOH 2. HCI, H₂O CI NH₁(!) +NaNH, -33°C 1. NaOH 2. HCl, H₂Oarrow_forwardSyntheses 22.35 Show how to convert toluene to these compounds. (a) -CH,Br (b) Br- -CH3 22.36 Show how to prepare each compound from 1-phenyl-1-propanone. 1-Phenyl-1-propanone ہتی. Br. (b) Br (racemic) 22.37 Show how to convert ethyl benzene to (a) 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid and (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid. 22.38 Show reagents and conditions to bring about the following conversions. (a) 9 NH2 8 CO₂H NH2 CO₂Et (d) NO2 NH2 S NH₂ NO2 CHS CHarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





